
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To characterize
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A general oxidative deamination reaction is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.45EP
Explanation of Solution
In both transamination and oxidative deamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
(b)
Interpretation: To characterize glutamate as a possible reactant, product, or enzyme involved in transamination, oxidative deamination, or both transamination and oxidative deamination.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A general oxidative deamination reaction is as follows:
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.45EP
Glutamate acts as a reactant in both transamination and oxidative deamination reaction.
Explanation of Solution
In both transamination and oxidative deamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
Glutamate is an amino acid thus acts as a reactant in both transamination and oxidative deamination reaction to give corresponding keto acid
(c)
Interpretation: To characterize glutamate dehydrogenase as a possible reactant, product, or enzyme involved in transamination, oxidative deamination, or both transamination and oxidative deamination.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A general oxidative deamination reaction is as follows:
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.45EP
Glutamate dehydrogenase is the enzyme involved in the oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate to give
Explanation of Solution
Oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate requires dehydrogenase enzyme. It is an oxidoreductase enzyme and works with either
(d)
Interpretation: To characterize
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A general oxidative deamination reaction is as follows:
(d)
Answer to Problem 26.45EP
The ammonium ion is one of the products obtained in oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate.
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an
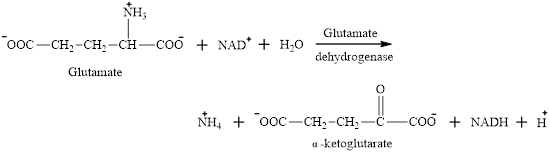
The ammonium ion formed is toxic if build up in the body. Ammonium ion acts as the “nitrogen carrier” for further reactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- A patient who has been drinking large amounts of alcohol for long periods of time shows thefollowing symptoms: apathy, loss of memory, and a rhythmical to-and-fro motion of the eyeballs.Which of the following reactions are most likely to be affected in the patient? A. Conversation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA B. Conversation of a-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor Barrow_forwardIn this transamination reaction (right), which of the following are the products X and Y? Oxaloacetate Glutamate A Alanine, a-ketoglutarate B Aspartate, a-ketoglutarate C Glutamate, alanine D Pyruvate, aspartatearrow_forwardMatch the description with the correct enzyme. Descriptions: a. Uses alpha-keto carboxylic acid as a substrate b. Directly transfers cytosolic reducing equivalents into the electron transport chain c. Its activity depends on magnesium ions Options (enzymes): A. Mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase B. Succinate dehydrogenase C. Cytosolic glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase D. Cytochrome oxidase E. Rubisco F. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexarrow_forward
- Define the following terms: a. thiolytic cleavage b. ketogenesis c. ketone bodies d. α-oxidation e. ACCarrow_forwardConsider the fatty acids: (a) Arachidic acid (C20H40O2); molar mass = 312.5 g/mol) (b) Palmitoleic acid(C16H30O2); molar mass = 256.4 g/mol). i. How many cycles of β -oxidation are needed for complete oxidation?ii. How many molecules of acetyl CoA are formed from its complete catabolism?iii. Calculate the number of molecules (moles) of ATP formed (net) by the completecatabolism of each fatty acid (show your calculation).iv. Calculate number of moles of ATP formed per gram of each fatty acid metabolized.arrow_forwardWhat is the activated reactant in the biosynthesis of each of the following compounds? a. Phosphoribosylamine c. Orotidylate (from orotate) b. Carbamoylaspartate d. Phosphoribosylanthranilatearrow_forward
- Compare and contrast the following items related to lipid metabolism. Cite their main similarities/or differences. 1. Dehydrogenase enzyme vs. dehydratase enzyme(in context of lipid metabolism). 2. Steroid hormones vs. prostaglandins (in terms of their biosynthetic pathways). 3. Fatty acid synthase complex vs. pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.arrow_forwardConsider the docosanoic acid, C21H43CO2H a. Label the a and B carbons b. Draw the acyl CoA derived from this fatty acid c. How many acetyl CoA molecules are formed by complete B-oxidation? d. How many cycles of B-oxidation are needed for complete oxidation? e. How many molecules of ATP are formed from the complete catabolism of this fatty acid?arrow_forwardDescribe the reaction catalyzed by each enzyme: (a) aspartate transaminase; (b) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.arrow_forward
- Suggest a name for an enzyme that catalyzes each of the following reactions. 1. Hydrolysis of lactose 3. Decarboxylation of citrate 4. Reduction of oxalate 2. Oxidation of nitritearrow_forward10a) Outline the mechanism for the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA which is catalyzed by alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. b) Of the five steps involved with this process, which would most likely be metabolically irreversible under physiological conditions?arrow_forwardConsider docosanoic acid C12H43CO2H a. Label the alpha and beta Carbons. Show the beta-oxidation in an EXPANDED structure. b. Draw each acyl CoA derived from this fatty acid. c. How many acetyl Co A molecules are formed by complete beta-oxidation? d. How many cycles of beta-oxidation are needed for complete oxidation? e. How many molecules of ATP are formed from the complete catabolism of this fatty acid? Show the complete computation. f. How many moles of ATP per gram of fatty acid is formed from the complete catabolism of the given fatty acid? g. What is the molar mass of the given fatty acid? Solution: Show here the complete computations, [from a to e]arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





