
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the intermediate
Concept introduction: Glycolysis is the
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:
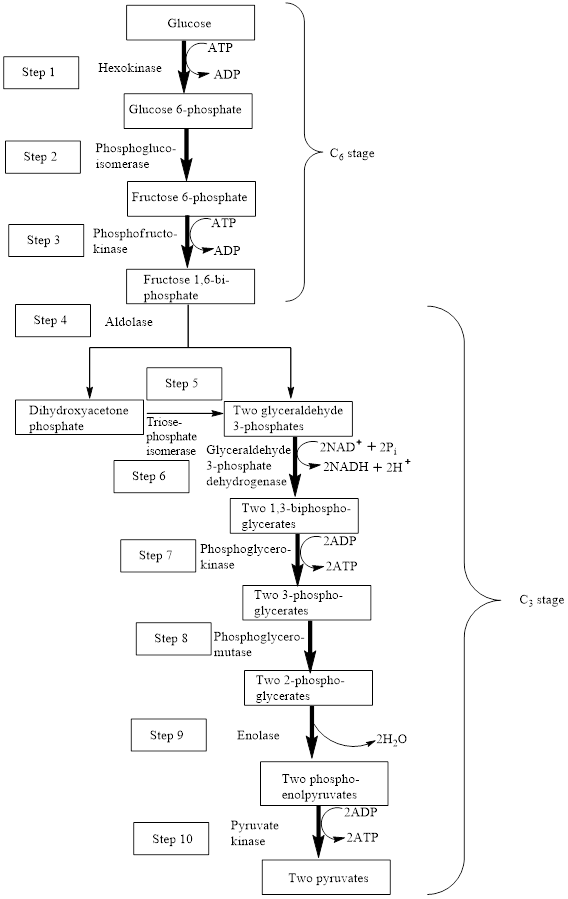
From the above diagram, it is concluded that in the overall process of glycolysis, two stages are present.
a) Steps 1 to 3 represents a six-carbon stage
b) Steps 4 to 10 represent a three-carbon stage
In the
In the
(a)
Answer to Problem 24.9EP
The intermediate
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
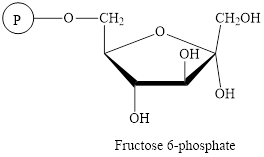
Here,  denotes the
denotes the
The intermediate
The intermediate
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the intermediate phosphoenolpyruvate in the glycolysis pathway is a
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

From the above diagram, it is concluded that in the overall process of glycolysis, two stages are present.
a) Steps 1 to 3 represents a six-carbon stage
b) Steps 4 to 10 represent a three-carbon stage
In the
In the
(b)
Answer to Problem 24.9EP
Phosphoenolpyruvate is a
Explanation of Solution
The structure of phosphoenolpyruvate is as follows:
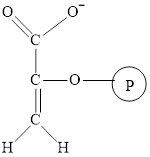
Phosphoenolpyruvate is formed in the
Phosphoenolpyruvate is formed in the
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the intermediate
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

From the above diagram, it is concluded that in the overall process of glycolysis, two stages are present.
a) Steps 1 to 3 represents a six-carbon stage
b) Steps 4 to 10 represent a three-carbon stage
In the
In the
(c)
Answer to Problem 24.9EP
The intermediate
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
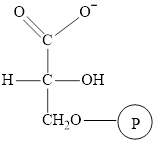
The intermediate
The intermediate
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate
in the glycolysis pathway is a
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

From the above diagram, it is concluded that in the overall process of glycolysis, two stages are present.
a) Steps 1 to 3 represents a six-carbon stage
b) Steps 4 to 10 represent a three-carbon stage
In the
In the
(d)
Answer to Problem 24.9EP
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is a
Explanation of Solution
The structure of dihydroxyacetone phosphate is as follows:
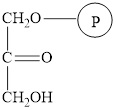
The intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate is formed in the
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is formed in the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- (f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





