
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The mass of nitrogen in grams should be determined when total mass of compound is 475 g. 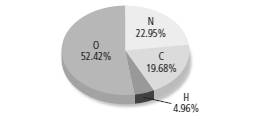
- 33.93 g
- 52.78 g
- 67.86 g
- 109.0 g
- 110.5 g
Concept introduction:
Number of moles is equal to the ratio of given mass to the molar mass.
The mathematical expression is given by:
Number of moles =
Molar mass of the molecule is equal to the sum of the masses of atoms present in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 17STP
Mass of nitrogen in 475 g of compound is
Explanation of Solution
According to the given figure,
Percentage of carbon = 19.68 %
Percentage of oxygen = 52.42 %
Percentage of hydrogen = 4.96 %
Percentage of nitrogen = 22.95 %
Let, total mass of the compound = 100 grams.
Thus, mass of carbon (
Mass of oxygen (
Mass of hydrogen (
Mass of nitrogen (
Now,
Molar mass of carbon = 12.011 g/mole
Number of moles of carbon =
=
Molar mass of oxygen = 15.999 g/mole
Number of moles of oxygen =
=
Molar mass of hydrogen = 1.008 g/mole
Number of moles of hydrogen =
=
Molar mass of nitrogen = 14.007 g/mole
Number of moles of nitrogen =
=
Divide each number of moles by smallest number 1.64.
Number of moles of carbon =
= 1 mole
Number of moles of oxygen =
= 2 moles
Number of moles of hydrogen =
= 3 moles
Number of moles of nitrogen =
= 1 mole
Thus, the formula of compound is
Total mass of compound is 475 g.
Molar mass of
Number of moles of
In
Number of moles of nitrogen = 1 mole
Molar mass of nitrogen = 14.007 g/mole
Thus, mass of nitrogen in 475 g of compound =
=
Mass of nitrogen =
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- Briefly indicate, with examples, the use of inorganic heterocycles in the synthesis of the corresponding polymers.arrow_forward1) Show how to use solid phase techniques to synthesize Ala-Val-Phe. You may use any amino acids (including protected amino acids) and any inorganic reagents that you wish in carrying out your synthesis. You don't need to show any mechanisms for this synthesis. You can maximize your chances of partial credit by showing key intermediates. (12 points)arrow_forward5) AZT is a drug that is used to treat HIV/AIDS. When cells take up AZT, they convert it to AZT- triphosphate. AZT-triphosphate prevents the virus from synthesizing new DNA from its RNA code. a. Write a 1-2 sentence explanation describing how AZT-triphosphate prevents DNA synthesis. (4 points) HO NH 'N' O © © N=N=N AZT b. Circle the location on AZT where the triphosphate group is appended (2 points)arrow_forward
- 1) What is epimerization? A) It involves changing the configuration of a carbon B) It involves oxidation of an aldose. C) It involves lengthening the chain of an aldose. D) It involves reduction of an aldose. E) none of the above 2) Which of the following monomer: polymer pairings is mismatched? a. Amino acids: proteins b. Amino acids: peptides c. Monosaccharides: polysaccharides d. Nucleotides: DNA e. They are all correctly matched 3) How do the a and ẞ anomer of a sugar differ? a. By the configuration of the acetal carbon in the ring form b. c. By whether a ketone or aldehyde is present in the straight chained form By the presence/absence of a 2' OH d. By whether the OH on the last chiral center is pointed right or left in the Fischer projection of the straight chained form 4) A salt bridge can occur as part of the apply) a. Primary structure b. Secondary structure of a protein (select all that c. Tertiary structure d. Quaternary structuré 5) True or false: A protein that has been…arrow_forward11C.7 Before solving the problem please also give a brief explanation of the concept or associated equation(s) and variables.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism in the paperarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





