
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
A reaction roadmap have to be made for the reactions in the study Guide section of problems 15.19, 16.72 and 17.45.
Concept Introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
Addition of alcohols to
Example: the reaction of methanol with ethanol to form hemiacetals or acetals.
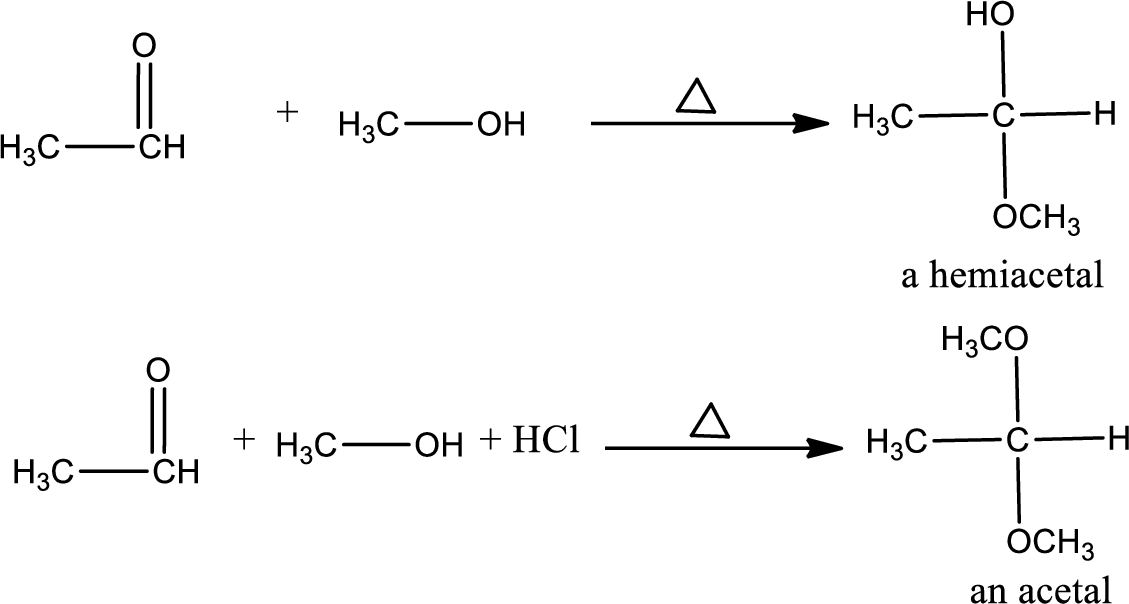
Unsaturated compound: The nucleophile reacts with
The alkylation at the β carbon of ketone or aldehyde is done by the following mechanism;
(1) Alkylating the β carbon via enamine intermediate.
(2) Alkylating the β carbon via a Michael reaction.
Acetals: Acetals are used to protect the ketone and aldehyde (carbonyl group).
In this reaction acetone is protected as acetal by using ethylene glycol. Acetals are less stable compound.
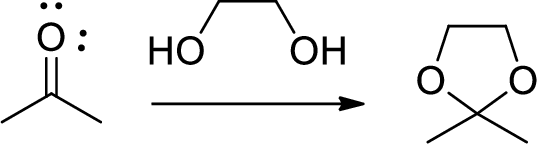
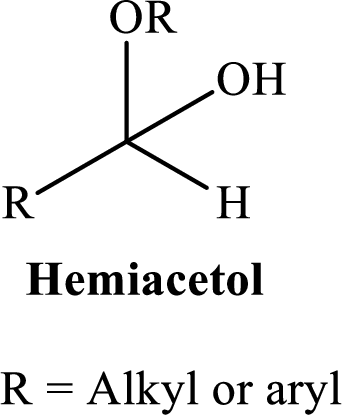
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal: addition of alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone which produce hemi acetal.
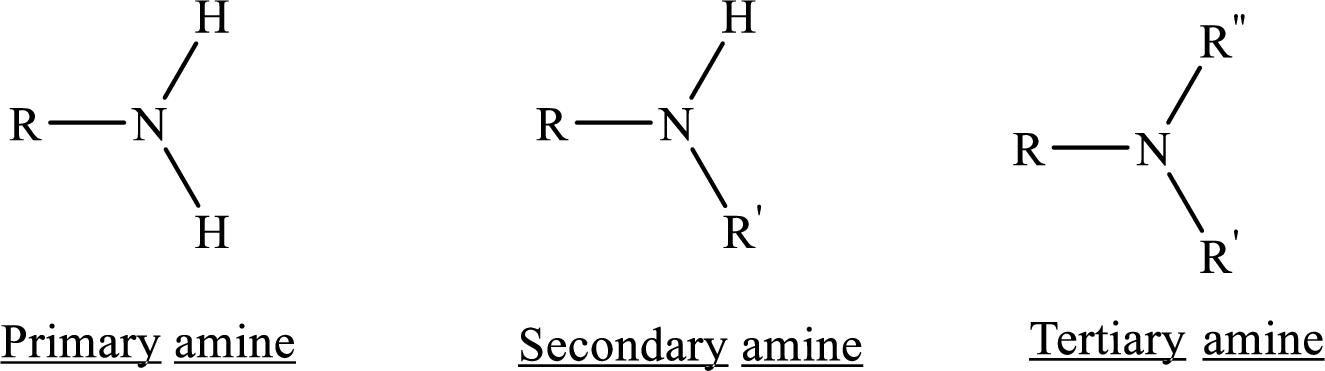
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert propane into propyl propanoate. You must use propane as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents needed and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert butane into butanal. Show all reagents needed and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 1-bromopropane and carbon dioxide into 4-propyl-4-heptanol. You must use 1-bromopropane and carbon dioxide as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forward
- Aspirin is the common name for the compound acetylsalicylic acid, widely used as a fever reducer and as a pain killer. Salicylic acid, whose name comes from Salix, the willow family of plants, was derived from willow bark extracts. In folk medicine, willow bark teas were used as headache remedies and other tonics. Nowadays, salicylic acid is administered in the form of aspirin which is less irritating to the stomach than salicylic acid. To prepare aspirin, salicylic acid is reacted with an excess of acetic anhydride. A small amount of a strong acid is used as a catalyst which speeds up the reaction. In this experiment, phosphoric acid will be used as the catalyst. The excess acetic acid will be quenched with the addition of water. The aspirin product is not very soluble in water so the aspirin product will precipitate when water is added. The synthesis reaction of aspirin is shown below: Actic anhydride 5 ml. Acetic acid Salicylic acid 28 Acetylsalicylie acid Procedure 1) Mix salicylic…arrow_forwardA student is given a mixture of benzoic acid, 3-nitroaniline and naphthalene to separate. The student dissolves the mixture in an organic solvent and adds NaOH to the solution. Two layers form. Which component(s) of the mixture remain in the organic solvent? Group of answer choices Benzoic acid and Naphthalene 3-Nitroaniline and naphthalene 3-Nitroaniline Naphthalenearrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 2-methylpentane into 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Show all reagents needed and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forward
- Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 1-propanol into 2-hexyne. You must use 1-propanol as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents needed and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert 4-methyl-1-pentene and carbon dioxide into 5-methylhexanoic acid. You must use 4-methyl-1-pentene and carbon dioxide as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert 1-bromopentane and sodium cyanide into N-hexylhexanamide. You must use 1-bromopentane and sodium cyanide as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forward
- Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert ethanol into 2-pentanone. You must use ethanol as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forwardWrite the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction roadmaps to see how the combined reactions allow you to navigate between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 611, Chapters 1518, and Chapter 19 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 20 reaction roadmap for these.arrow_forwardUsing your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how to convert propane into butyronitrile. You must use propane and sodium cyanide as the source of all of the carbon atoms in the butyronitrile product. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


