
Concept explainers
Propose a structural formula for each compound consistent with its 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra.
- (a) C5H10O2
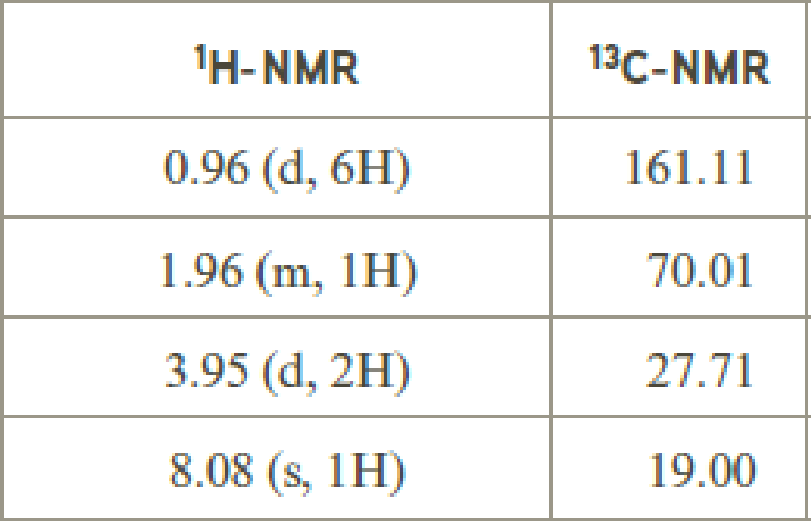
- (b) C7H14O2
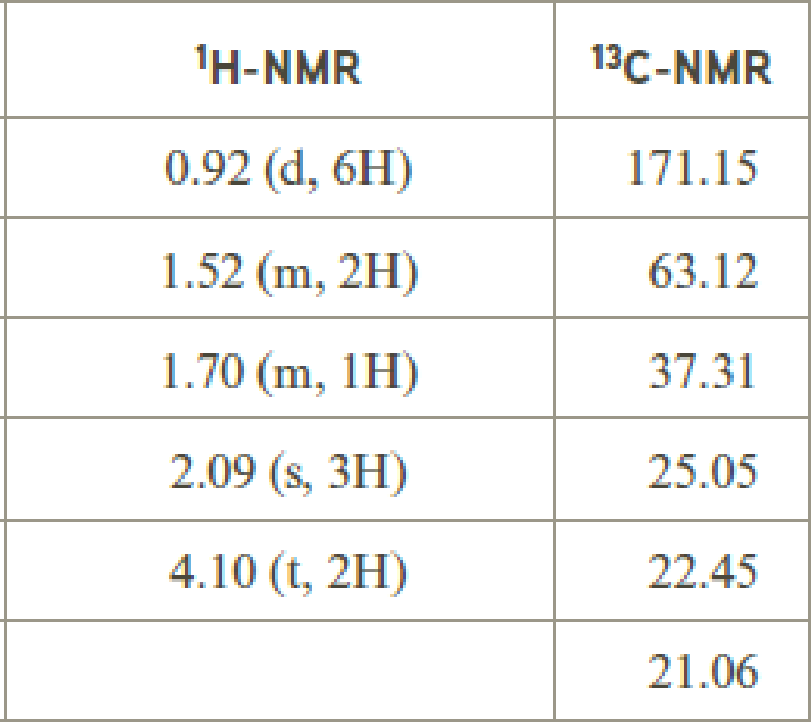
- (c) C6 H12O2
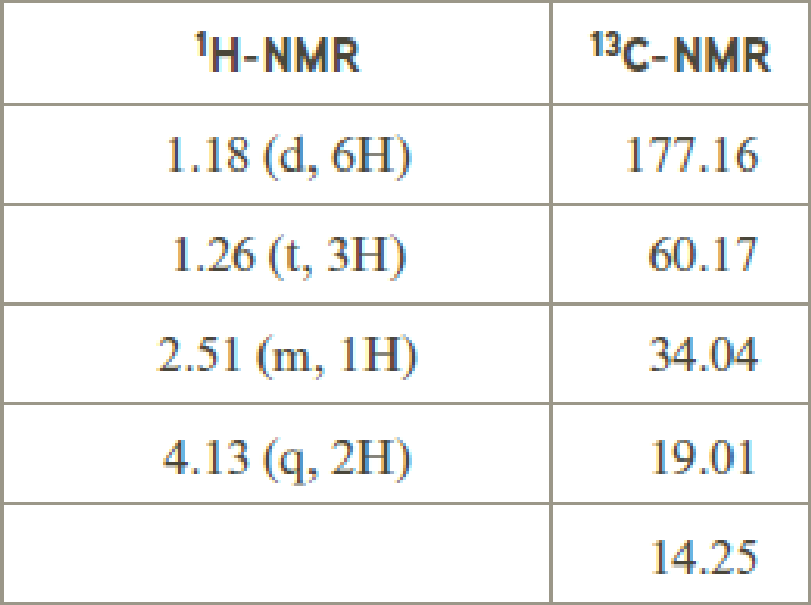
- (d) C7H12O4
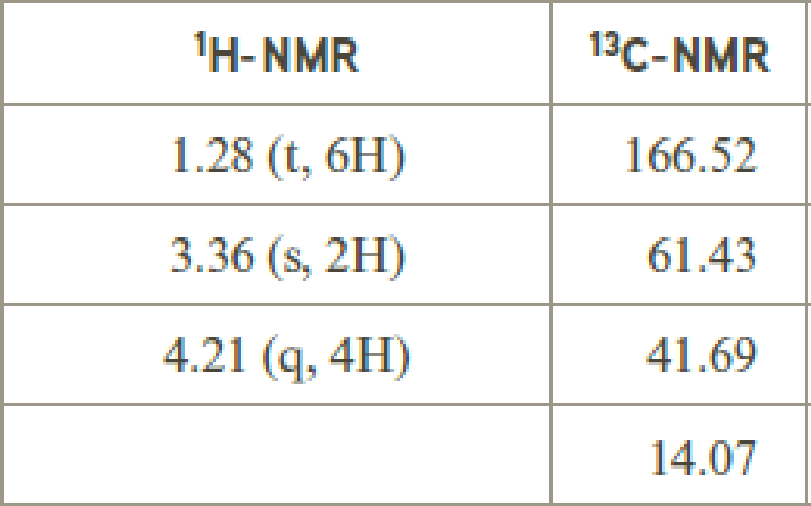
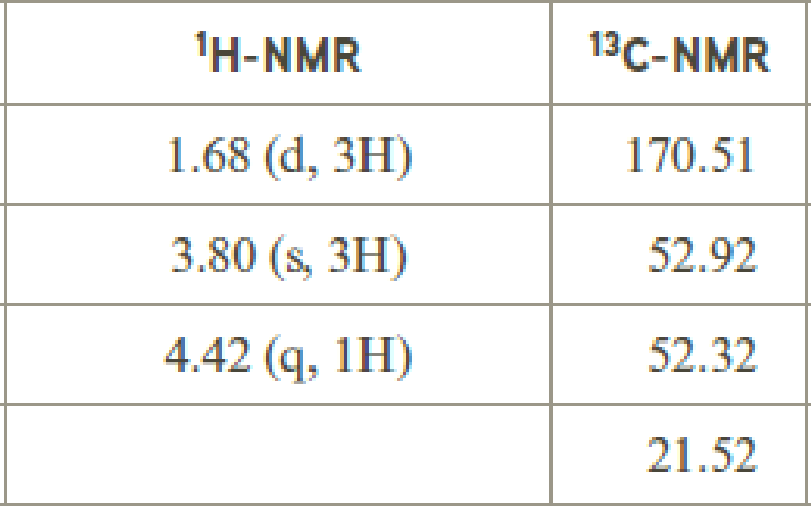
- (e) C4H7ClO2
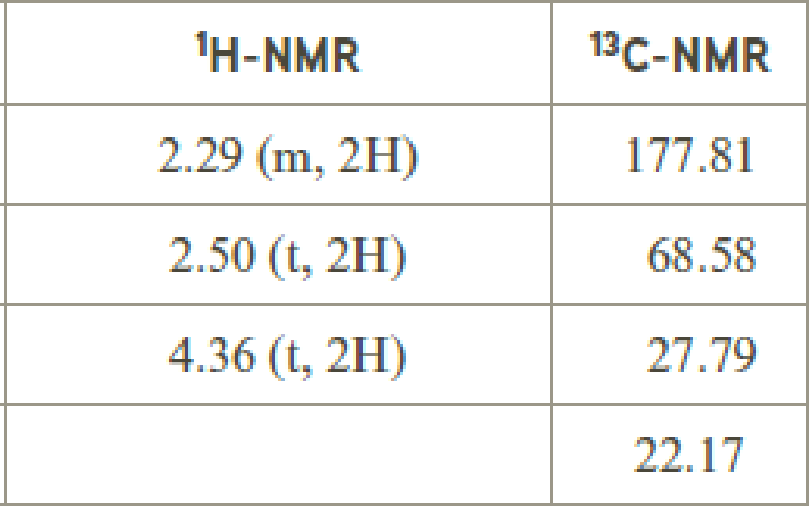
- (f) C4H6O2
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
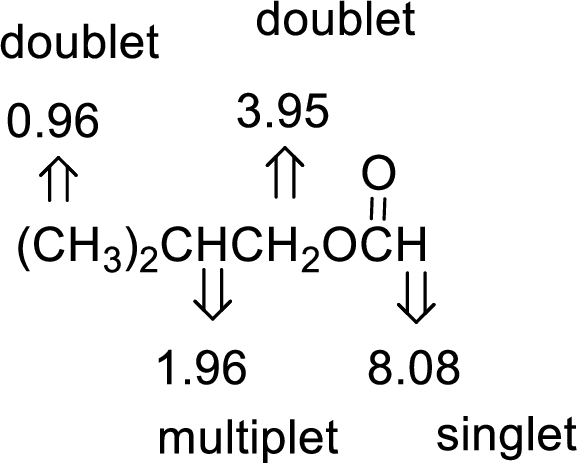
The value of 8.08 suggests an aldehyde proton. 0.96 will indicate the presence of methyl groups and 1.96 indicates the methylene proton
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
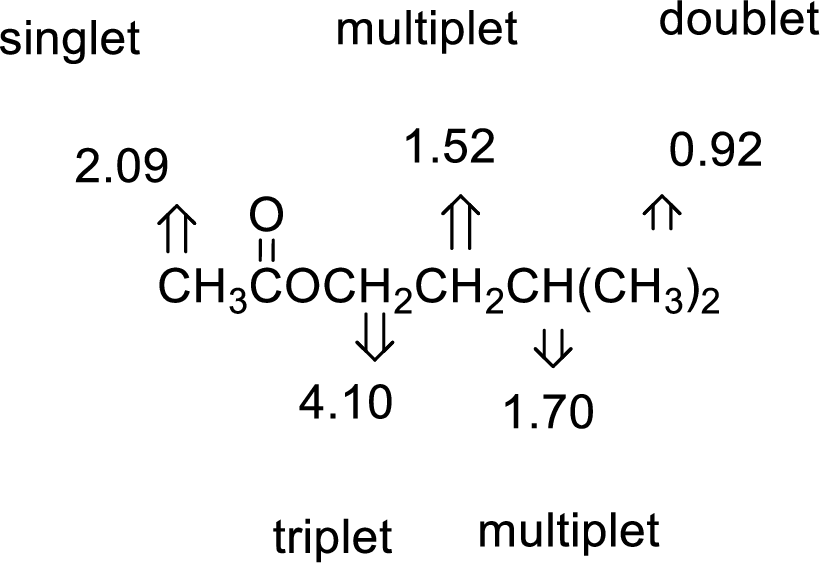
The value of 2.09 indicates a methyl group
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
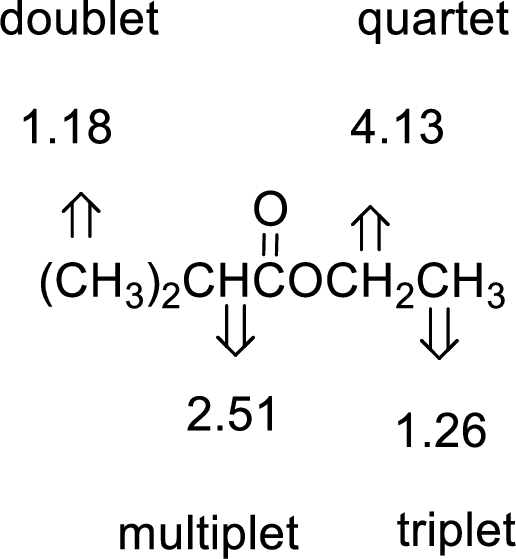
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
1.18 and 1.26 will indicate the presence of methyl groups and 4.13 indicates the methylene proton
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
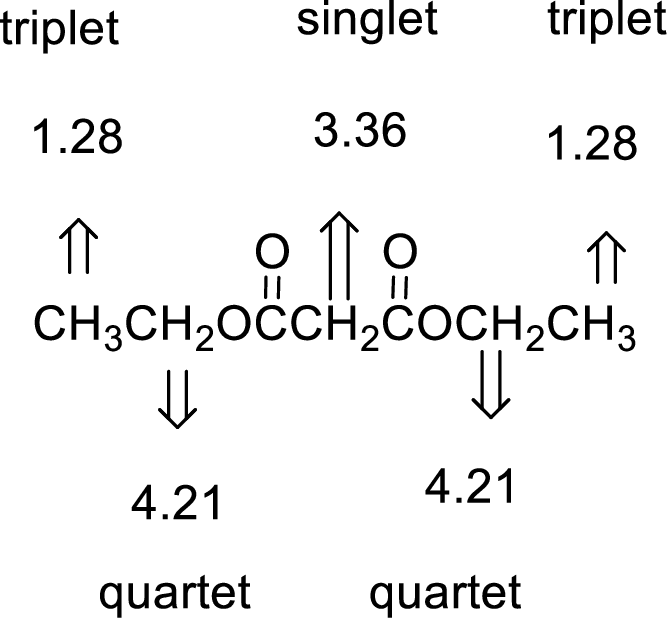
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
The value of 3.36 suggests a methylene directly attach to a carbonyl group. 1.28 will indicate the presence of methyl groups and 4.21 indicates the methylene proton
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
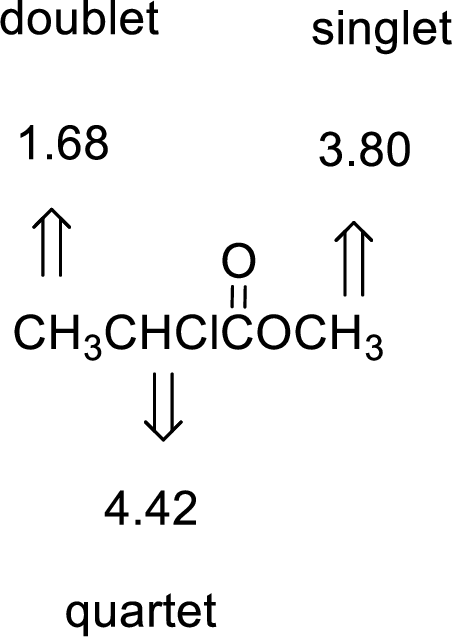
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
The value of 4.42 suggests a proton group directly attach to a chlorine group. 3.80 will indicate the presence of methyl group which is
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for compound having molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen atoms.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the
Chemical shift values for protons in different electronic environment
| FUNCTIONAL GROUP | EFFECT ON THE ALPHA PROTONS | EFFECT ON THE BETA PROTONS |
| Oxygen of an alcohol or ether | ||
| Oxygen of ester | ||
| Carbonyl groups |
It is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the nuclei of the carbon atoms.
The signals in the
Explanation of Solution
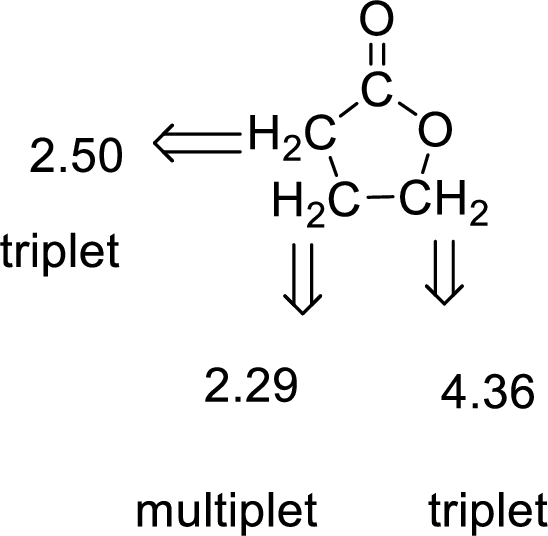
Given compound has the molecular formula
Spectral data is given below:
By analyzing the spectral data, the structure can be predicted.
The value of 4.36 suggests a methylene directly attach to a oxygen group. 2.50 will indicate the presence of methylene proton
The structure proposed according to the data is given below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Compound I (C11H14O2) is insoluble in water, aqueous acid, and aqueous NaHCO3, but dissolves readily in 10% Na2CO3 and 10% NaOH. When these alkaline solutions are acidified with 10% HCl, compound I is recovered unchanged. Given this information and its 1H-NMR spectrum, deduce the structure of compound I.arrow_forward(b) One isomer of dimethoxybenzoic acid has 1H NMR spectrum dµ (ppm) 3.85 (6H, s), 6.63 (1H, t, J 2 Hz), and 7.17 (2H, d, J 2Hz), One isomer of coumalic acid has 'H NMR spectrum dн (ppm) 6.41 (1H, d, J 10 Hz), 7.82 (1H, dd, J 2 Hz, 10 Hz) and 8.51 (1H, d, J 2Hz). In each case, which isomer is represented here? The bonds sticking into the centre of the ring can be to any carbon atom. Note: COOH proton is not indicated in the spectra MeO HO₂C CO2H MeO dimethoxybenzoic acid coumalic acidarrow_forwardWhen compound A (C5H12O) is treated with HBr, it forms compound B (C5H11Br). The 1H NMR spectrum of compound A has a 1H singlet, a 3Hdoublet, a 6H doublet, and two 1H multiplets. The 1H NMR spectrum of compound B has a 6H singlet, a 3H triplet, and a 2H quartet. Identifycompounds A and B.arrow_forward
- Given here are 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectral data for nine compounds. Each compound shows strong absorption between 1720 and 1700 cm-1 and strong, broad absorption over the region 2500–3300 cm-1. Propose a structural formula for each compound.arrow_forwardA and B are isomeric dicarbonyl compounds of the molecular formula C5H&O2. The 'H NMR spectrum of A contains a singlet at 2.05 ppm and another singlet at 5.40 ppm. The 'H NMR spectrum of B contains three signals: a singlet at 2.3 ppm, a triplet at 1.10 ppm and a quartet at 2.70 ppm. Suggest structures for A and B and draw them in their respective boxes below. 1st attemptarrow_forwardGiven here are 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectral data for nine compounds. Each compound shows strong absorption between 1720 and 1700 cm-1 and strong, broad absorption over the region 2500–3300 cm-1. Propose a structural formula for each compound.arrow_forward
- Compound A has molecular formula C5H10O. It shows three signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum - a doublet of integral 6 at 1.1 ppm, a singlet of integral 3 at 2.14 ppm, and a quintet of integral 1 at 2.58 ppm. Suggest a structure for A and explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardPropose a structural formula for each compound consistent with its 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra.arrow_forwardThe 1H-NMR spectrum of Compound C shows five signals – δ 2.38 (1H, dt), 2.72 (1H, dt), 5.34 (1H, t), 5.49 (2H, ddd), 6.27 (2H, dd) ppm. Its 13C-NMR spectrum has four signals – δ 26, 58, 127, 129 ppm. In the compound’s mass spectrum, the M+1 peak appears at m/z = 115. An M+2 peak, whose intensity is roughly one-third that of the M+1 peak, also appears. Suggest a structure for this compound.arrow_forward
- Propose a structure for each of the following two isomers with formula C6H14 given their 1H-NMR spectra. Isomer A: δ = 0.84 (d, 12 H), 1.39 (septet, 2H) ppm Isomer B: δ = 0.84 (t, 3 H), 0.86 (t, 9H), 1.22 (q, 2H) ppmarrow_forwardA compound with molecular formula C7H1402 upon hydrolysis produces an alcohol and an acid. It has the following (b) NMR data : 'H-NMR (at 298 K, 600 MHz, CDC13) : 80-92 (d, 6H), 1:52 (т, 2н), 1-69 (m, 1Н), 2-04 (s, ЗH) and 4-09 (t, 2H). 13 C-NMR : 8 21-0, 22:5, 25:1, 37.4, 63·1 and 171-2 ppm DEPT provided two inverted signals. Predict the structure of the alcohol that is obtained through hydrolysis of the mentioned parent compound. Assign appropriate IR values, 'H and 13C-NMR resonances along with a mass spectral pattern for the alcohol.arrow_forwardFollowing are 1H-NMR spectra for compounds B (C6H12O2) and C (C6H10O). Upon warming in dilute acid, compound B is converted to compound C. Deduce the structural formulas for compounds B and C.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
