Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.5, Problem 116P
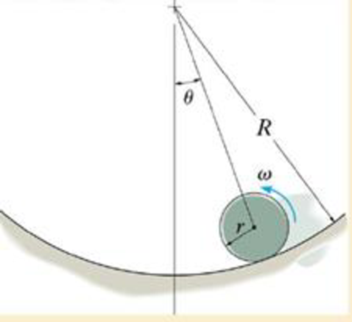
The disk of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on the circular path. Determine the normal force which the path exerts on the disk and the disk’s angular acceleration if at the instant shown the disk has an angular velocity of ω.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The mass of gear A is 25 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 105 mm. The mass of gear B is 13 kg and its centroidal radius
of gyration is 85 mm. Calculate the angular acceleration of gear B when a torque of 16 N-m is applied to the shaft of gear A.
Neglect friction. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise.
TA = 165 mm
TB = 125 mm
2. The uniform bar of mass 5-kg and a length of 0.5 m is balanced in the vertical position when a
horizontal force of P = 20 N is applied to the roller at A. Determine the bar's initial angular
acceleration and the acceleration of its top point B.
B
The 24-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 260 mm, and radius r= 0.4 m. When the wheel is subjected to the
couple moment M = 90 N•m, it slips as it rolls. Determine the linear acceleration of the wheel's center O (in m/s?). The coefficient of
kinetic friction between the wheel and the plane is Uk = 0.45. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are
randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?.
M
Chapter 17 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Iy for the slender...Ch. 17.1 - The solid cylinder has an outer radius R1 height...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the thin ring...Ch. 17.1 - The paraboloid is formed by revolving the shaded...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the radius of gyration kr of the body....Ch. 17.1 - The sphere is formed by revolving the shaded area...Ch. 17.1 - The frustum is formed by rotating the shaded area...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 8PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 9PCh. 17.1 - The pendulum consists of a 4-kg circular plate and...
Ch. 17.1 - The assembly is made of the slender rods that have...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 12PCh. 17.1 - The wheel consists of a thin ring having a mass of...Ch. 17.1 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia about an axis...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 16PCh. 17.1 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 18PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 19PCh. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel about...Ch. 17.1 - The pendulum consists of the 3-kg slender rod and...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 22PCh. 17.1 - Determine the moment of inertia of the overhung...Ch. 17.3 - Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 2PPCh. 17.3 - Prob. 1FPCh. 17.3 - Prob. 2FPCh. 17.3 - Prob. 3FPCh. 17.3 - Prob. 4FPCh. 17.3 - At the instant shown both rods of negligible mass...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 6FPCh. 17.3 - The door has a weight of 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17.3 - The door has a weight or 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17.3 - The jet aircraft has a total mass of 22 Mg and a...Ch. 17.3 - The sports car has a weight of 4500 lb and center...Ch. 17.3 - The assembly has a mass of 8 Mg and is hoisted...Ch. 17.3 - The assembly has a mass of 4 Mg and is hoisted...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform girder AB has a mass of 8 Mg....Ch. 17.3 - A car having a weight of 4000 lb begins to skid...Ch. 17.3 - A force of P = 300 N is applied to the 60-kg cart....Ch. 17.3 - Determine the largest force P that can be applied...Ch. 17.3 - The trailer with its load has a mass of 150-kg and...Ch. 17.3 - The desk has a weight of 75 lb and a center of...Ch. 17.3 - The desk has a weight of 75 lb and a center of...Ch. 17.3 - The 150-kg uniform crate rests on the 10-kg cart....Ch. 17.3 - The 150-kg uniform crate rests on the 10-kg cart....Ch. 17.3 - The bar has a weight per length w and is supported...Ch. 17.3 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17.3 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform crate has a mass of 50 kg and rests on...Ch. 17.3 - Determine the acceleration of the 150-lb cabinet...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 44PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 45PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 47PCh. 17.3 - The snowmobile has a weight of 250 lb, centered at...Ch. 17.3 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 50PCh. 17.3 - The pipe has a mass of 800 kg and is being towed...Ch. 17.3 - The pipe has a mass of 800 kg and is being towed...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 53PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 54PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 55PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 56PCh. 17.4 - The 100-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 8FPCh. 17.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 17.4 - Prob. 10FPCh. 17.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 17.4 - Prob. 12FPCh. 17.4 - The 10-kg wheel has a radius of gyration kA = 200...Ch. 17.4 - The uniform 24-kg plate is released from rest at...Ch. 17.4 - The uniform slender rod has a mass m. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - The tent rod has a mass of 2 kg/m. If it is...Ch. 17.4 - If a horizontal force of P = 100 N is applied to...Ch. 17.4 - The 10-lb bar is pinned at its center O and...Ch. 17.4 - The 10-lb bar is pinned at its center O and...Ch. 17.4 - A cord is wrapped around the outer surface of the...Ch. 17.4 - Disk A has a weight of 5 lb and disk B has a...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 66PCh. 17.4 - If the cord at B suddenly fails, determine the...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 68PCh. 17.4 - The 20-kg roll of paper has a radius of gyration...Ch. 17.4 - The 20-kg roll of paper has a radius of gyration...Ch. 17.4 - The reel of cable has a mass of 400 kg and a...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 72PCh. 17.4 - Cable is unwound from a spool supported on small...Ch. 17.4 - The 5-kg cylinder is initially at rest when it is...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 75PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 76PCh. 17.4 - Disk D turns with a constant clockwise angular...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 78PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 79PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 80PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 81PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 82PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 83PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 84PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 85PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 86PCh. 17.4 - Prob. 87PCh. 17.4 - The 100-kg pendulum has a center of mass at G and...Ch. 17.5 - The Catherine wheel is a firework that consists of...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 60-kg slender bar is initially at rest...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 14FPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 15FPCh. 17.5 - The 20- kg sphere rolls down the inclined plane...Ch. 17.5 - The 200-kg spool has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17.5 - The 12-kg slender rod is pinned to a small roller...Ch. 17.5 - If the disk in Fig. 17-19 rolls without slipping,...Ch. 17.5 - The 20-kg punching bag has a radius of gyration...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17.5 - The tire has a weight of 30 lb and a radius of...Ch. 17.5 - The tire has a weight of 30 lb and a radius of...Ch. 17.5 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17.5 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17.5 - The 12-kg uniform bar is supported by a roller at...Ch. 17.5 - A force of F= 10 N is applied to the 10-kg ring as...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction at C is s =...Ch. 17.5 - The 25-lb slender rod has a length of 6 ft. Using...Ch. 17.5 - The 15-lb circular plate is suspended from a pin...Ch. 17.5 - If P = 30 lb, determine the angular acceleration...Ch. 17.5 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform bar of mass m and length L is balanced...Ch. 17.5 - Solve Prob.17-106 if the roller is removed and the...Ch. 17.5 - The semicircular disk having a mass of 10 leg is...Ch. 17.5 - The 500-kg concrete culvert has a mean radius of...Ch. 17.5 - The 15-lb disk rests on the 5-lb plate. A cord is...Ch. 17.5 - The semicircular disk having a mass of 10 kg is...Ch. 17.5 - The circular concrete culvert rols with an angular...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17.5 - A cord is wrapped around each of the two 10-kg...Ch. 17.5 - The disk of mass m and radius r rolls without...Ch. 17.5 - The uniform beam has a weight W. If it is...Ch. 17.5 - The 500-lb beam is supported at A and B when it is...Ch. 17.5 - The solid ball of radius rand mass m rolls without...Ch. 17.5 - By pressing down with the finger at B, a thin ring...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 1RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 2RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 3RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 4RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 6RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 7RPCh. 17.5 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The spring is uncompressed when the uniform slender bar is in the vertical position shown. Determine the initial angular acceleration a of the bar when it is released from rest in a position where the bar has been rotated clockwise 29° from the position shown. Neglect any sag of the spring, whose mass is negligible. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise and negative if clockwise. The mass m of the bar is 25 kg, the length / is 275 mm and the spring constant k is 640 N/m. A m 4 G B Answer: a = i rad/s? 1/1arrow_forwardThe small end rollers of the 8-lb uniform slender bar (length = 4 ft) are constrained to move in the slots, which lie in the verticalplane. At the instant when θ = 30°, the velocity of roller A is 14 ft/s down the vertical slot. Determine the angular acceleration of the bar, the acceleration of mass center G, and the reactions of points A and B, under the action of the 6-lb force P. Neglect the friction and the mass of the small rollers.arrow_forwardA constant couple moment M is acted on the drum O to pull the spool C up the incline. Both drum O and spool C can be treated as uniform disk. If spool C is rolling without slipping, determine the angular acceleration of the drum and the cord force. R R (0 Marrow_forward
- The mass of gear A is 25 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 105 mm. The mass of gear B is 13 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 85 mm. Calculate the angular acceleration of gear B when a torque of 16 N·m is applied to the shaft of gear A. Neglect friction. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise..arrow_forwardThe uniform rectangular slab is released from rest in the position shown. Determine the value of x for which the angular acceleration is maximum, and determine the corresponding angular acceleration.arrow_forwardThe assembly consisting of a uniform slender bar (mass = 1.5 kg and L = 0.49 m) and a rigidly attached uniform disk (mass = 6.8 kg) is freely pinned to point O on the collar that in turn slides on the fixed horizontal guide. The assembly is at rest when the collar is given a sudden acceleration a = 3.4 m/s² to the left as shown. Determine the initial angular acceleration a of the assembly. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. 6.8 kg Answer: a = i 1.5 kg LA rad/s²arrow_forward
- Solvearrow_forward4 The uniform 16.1-lb slender bar is hinged about a horizontal axis through O and released from rest in the horizontal position. Determine the distance b from the mass center to O which will result in an ini- tial angular acceleration of 16.1 rad/sec?, and find the force R on the bar at O just after release. G 12" 12"arrow_forwardThe wheel has mass m and centroidal radius of gyration (k bar) and rolls without slipping up the incline under action force P. The force is applied to the end of a cord which is wrapped securely around the inner hub of the wheel as shown. Determine the speed Vo of the wheel center O after the wheel center has traveled a distance d up the incline. The wheel is at rest when the force P is first applied.arrow_forward
- 5. A solid sphere of radius 0.3 m and mass 5 kg rolls down the incline without slipping as shown in the figure below. Determine the acceleration and angular acceleration of the sphere. Use 0 = 30°. 0arrow_forwardThe spool has a mass of 105 kg and a radius of gyration of kg = 200 mm about its center of mass G. Assume the spool rolls without slipping. If a vertical force of P = 215 N is applied to the cable, determine the acceleration of G. (Figure 1) Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? Value m/s aG = Determine the angular acceleration of the spool. Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA Value rad /s? 300 mm a = G 150 mmarrow_forwardThe small end rollers of the 6.2-lb uniform slender bar are constrained to move in the slots, which lie in a vertical plane. At the instant when e = 30°, the angular velocity of the bar is 2.6 rad/sec counterclockwise. Determine the angular acceleration of the bar, the reactions at A and B, and the accelerations of points A and B under the action of the 5.1-lb force P. Neglect the friction and mass of the small rollers. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. The acceleration of A is positive if downward, negative if upward. The acceleration of B is positive if down the slot, negative if up the slot. The reaction at A Is positive If to the right, negative If to the left. The reaction at 8 Is positive If up and to the right, negative If down and to the left. L= 5.2 ft 107 P= 5.1 lb Answers: Jad/sec? F = Fg =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Ch 2 - 2.2.2 Forced Undamped Oscillation; Author: Benjamin Drew;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Tb7Rx-bCWE;License: Standard youtube license