
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
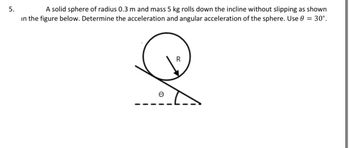
Transcribed Image Text:5.
A solid sphere of radius 0.3 m and mass 5 kg rolls down the incline without slipping as shown
in the figure below. Determine the acceleration and angular acceleration of the sphere. Use 0 = 30°.
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. 1) As shown in the image below, the snowmobile has a weight of 259 lb, centered at G1, while the rider has a weight of 154 Ib, centered at G2. If the acceleration is a = 13.5 ft/s?, dimensions are di = 0.9 ft, d2 = 0.4 ft, d3 = 1.6 ft, d4 = 1.6 ft, and height h of G2 of the rider is 1.8 ft, determine the normal reaction force under the front skid at point B. Assume there is only traction (horizontal) force under the rear tracks, but no friction force under the front skid. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g= 32.2 ft/s2. a G2 G1 h A В dz da -arrow_forwardweighs 270 lbs and angle is 60 degreesarrow_forwardI need handwritten and fast pls fast fastarrow_forward
- 8. 2) Rods AB and BC are linked at Band have weights of 18 lb and 37 lb, respectively. The 8-lb collar C, which is connected to BC and the spring, slides freely along the smooth vertical guide. The lengths of the rods are 4 = 1.4 ft and 2 = 2.9 ft. If the system is released from rest when 0 = 0°, determine the magnitude of the angular velocity (in rad/s) of rod BC when 0 = 90°. The attached spring has spring constant k = 20 Ib/ft, and is unstretched when 0 = 0°. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g= 32.2 ft/s2. k CO Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardRequired information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A force P of magnitude 4.4 N is applied to a tape wrapped around the body indicated. The body rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. Assume the mass of the uniform disk to be 2.4 kg. Determine the acceleration of Point A. B P The acceleration of Point A is 7.967 m/s m/s² →.arrow_forward4. A pair of connected pulleys receive a force F = 75 N and P = 150 N as depicted in the image. The pulley system has a radius of gyration of ko 0.5 m and mass of 50kg. The radius of pulley 1 is r₁ = 600 mm, and the radius of pulley 2 is r2 = 1000 mm. Determine the angular velocity of the pulley system after it undergoes 2 revolutions starting from rest. F P₁ Parrow_forward
- The spool has a mass of 105 kg and a radius of gyration of kg = 200 mm about its center of mass G. Assume the spool rolls without slipping. If a vertical force of P = 215 N is applied to the cable, determine the acceleration of G. (Figure 1) Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? Value m/s aG = Determine the angular acceleration of the spool. Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA Value rad /s? 300 mm a = G 150 mmarrow_forwardSolving dynamics problems in steps: 1. Collect data and assumptions 2. Desired result? 3. Make drawing/sketch of the (sub)problem 4. Equations and calculations 5. Answer and conclusions Furthermore: - - - Write down the steps clearly Check intermediate results (accuracy) Dimension check and units! Magnitude of number in line with expectation?arrow_forwardThe mass of gear A is 25 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 105 mm. The mass of gear B is 13 kg and its centroidal radius of gyration is 85 mm. Calculate the angular acceleration of gear B when a torque of 16 N-m is applied to the shaft of gear A. Neglect friction. The angular acceleration is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. TA = 165 mm TB = 125 mmarrow_forward
- The device shown is a simplified model of an amusement-park ride in which passengers are rotated about the vertical axis of the central post at an angular speed Q while sitting in a pod which is capable of rotating the occupants 360° about the longitudinal axis of the connecting arm attached to the central collar. Determine the percent increase n in angular velocity between configurations (a) and (b), where the passenger pod has rotated 90° about the connecting arm. For the model, m = 1.1 kg, r = 70 mm, I = 315 mm, and L = 640 mm. The post and connecting arms rotate freely about the z-axis at an initial angular speed 2 = 125 rev/min and have a combined mass moment of inertia about the z-axis of 38(10-3) kg m?. %3D (b) Ω (a) -Frame Pod Answer: n = %arrow_forwardSubject: civil engineeringarrow_forwardThe 150-kg wheel shown in Fig. In the initial position shown, the velocity of Gis 2 m/s down the plane, and the spring is stretched 150 mm. If the spring modulus is 1000 N/m, what will be the maximum stretch of the spring? has a radius of gyration of 360 mm with respect to its center of mass G. www 150 kg 30°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY