
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977305
Author: BEER, Ferdinand P. (ferdinand Pierre), Johnston, E. Russell (elwood Russell), Cornwell, Phillip J., SELF, Brian P.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.1, Problem 17.41P
The
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
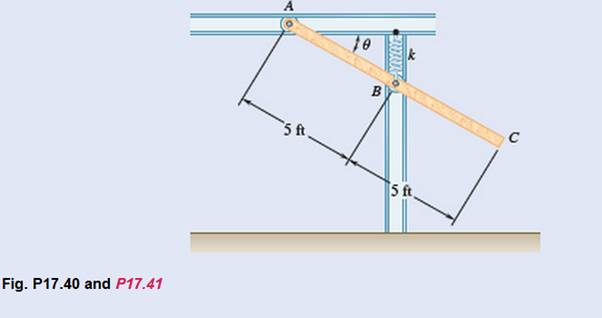
The mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 185-lb uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC of
the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring of constant k is attached to wheel B
in such a way that its tension is zero when e = 30°. Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position e = 45° and reaches the
vertical position with an angular velocity of 0.6 rad/s, determine the spring constant k.
5 ft
C
5 ft
The spring constant is 58.72
Ib/ft.
The mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 180-lb uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC
of the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring of constant k is attached to wheel
Bin such a way that its tension is zero when 0 = 30°. Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position 0 = 45° and reaches
the vertical position with an angular velocity of 0.6 rad/s, determine the spring constant k.
5 ft
5 ft
The spring constant is
Ib/ft.
The mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 200-lb uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC of the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring with a constant of k = 40 lb/ft is attached to wheel B. Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position 0= 30° with the spring unstretched, determine the velocity of wheel A just as the door reaches the vertical position.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 17.1 - A round object of mass m and radius r is released...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ2PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ3PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ4PCh. 17.1 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.1 - A 200-kg flywheel is at rest when a constant 300 N...Ch. 17.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform disks of the same material are...Ch. 17.1 - Two disks of the same material are attached to a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.5P
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.6PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.7PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.8PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.9PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.10PCh. 17.1 - Each of the gears A and B has a mass of 10 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Solve Prob. 17.11, assuming that the 6 N m couple...Ch. 17.1 - The gear train shown consists of four gears of the...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.14PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.15PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17.1 - The 15-kg rear hatch of a vehicle opens as shown...Ch. 17.1 - A slender 9-lb rod can rotate in a vertical plane...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.19PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17.1 - A collar with a mass of 1 kg is rigidly attached...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.22PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17.1 - The 30-kg turbine disk has a centroidal radius of...Ch. 17.1 - A 100-kg solid cylindrical disk, 800 mm in...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.26PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.27PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.28PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.29PCh. 17.1 - A half-cylinder with mass m and radius r is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.31PCh. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - A bar of mass m=5 kg is held as shown between four...Ch. 17.1 - The 1.5-kg uniform slender bar AB is connected to...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.36PCh. 17.1 - A 5-m-long ladder has a mass of 15 kg and is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.38PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.39PCh. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - Each of the two rods shown is of length L=1 m and...Ch. 17.1 - The 4-kg rod AB is attached to a collar of...Ch. 17.1 - If in Prob. 17.43 the angular velocity of the...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC are of mass 3 kg and 8...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC weigh 2.4 kg and 4 kg,...Ch. 17.1 - The 80-mm-radius gear shown has a mass of 5 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.48PCh. 17.1 - Three shafts and four gears are used to form a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.50PCh. 17.1 - The drive belt on a vintage sander transmits 12 hp...Ch. 17.2 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.2 - A 1-m-long uniform slender bar AB has an angular...Ch. 17.2 - The 350-kg flywheel of a small hoisting engine has...Ch. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is placed on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.F3PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.52PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.53PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.54PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.55PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.56PCh. 17.2 - A disk of constant thickness, initially at rest,...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.58PCh. 17.2 - A cylinder of radius r and weight W with an...Ch. 17.2 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a centroidal...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.61PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.62PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.63PCh. 17.2 - A tape moves over the two drums shown. Drum A...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.65PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.66PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.67PCh. 17.2 - Consider a rigid body initially at rest and...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.69PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.70PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.71PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.72PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.73PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.74PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.75PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.76PCh. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.78PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.79PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.80PCh. 17.2 - Two 10-lb disks and a small motor are mounted on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.82PCh. 17.2 - A 1.6-kg tube AB can slide freely on rod DE, which...Ch. 17.2 - In the helicopter shown, a vertical tail propeller...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.85PCh. 17.2 - The 4-kg uniform disk B is attached to the shaft...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.87PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.88PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.89PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.90PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.91PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.92PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.93PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.94PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.95PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB ofmass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F5PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F6PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.96PCh. 17.3 - A bullet weighing 0.08 lb is fired with a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.98PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.99PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.100PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.101PCh. 17.3 - A 45-g bullet is fired with a velocity of 400 m/s...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.103PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.104PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB of mass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.106PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.107PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.108PCh. 17.3 - Determine the height h at which the bullet of...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender bar of length L=200 mm and mass...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod of length L is dropped onto...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB has a mass m, a length L,...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.113PCh. 17.3 - The trapeze/lanyard air drop (t/LAD) launch is a...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rectangular block shown is moving...Ch. 17.3 - The 40-kg gymnast drops from her maximum height of...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.117PCh. 17.3 - A uniformly loaded square crate is released from...Ch. 17.3 - A 1-oz bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 17.3 - For the beam of Prob. 17.119, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - The plank CDEhas a mass of 15 kg and rests on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.122PCh. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.125PCh. 17.3 - A 2-kg solid sphere of radius r=40 mm is dropped...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass mA=2 kg and radius r=40 mm rolls...Ch. 17.3 - A large 3-lb sphere with a radius r=3 in. is...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.131PCh. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass m and radius r rolls without...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.133PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.134PCh. 17 - A uniform disk, initially at rest and of constant...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.136RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.137RPCh. 17 - You are asked to analyze a catcher for a small...Ch. 17 - A uniform slender rod is placed at corner B and is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.140RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.141RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.142RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.143RPCh. 17 - A square block of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.145RPCh. 17 - A 1.8-lb javelin DE impacts a 10-lb slender rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please show all steps.arrow_forwardRequired information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A 4-kg slender rod is welded to the edge of a 3-kg uniform disk as shown. The assembly rotates about A in a vertical plane under the combined effect of gravity and of the vertical force P. Know that at the instant shown, the assembly has an angular velocity of 12 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 36.5 rad/s2, both counterclockwise. 120 mm Determine the force P. B The force P is D 240 mm с 240 mm (You must provide an answer before moving on to the next part.) |N.↓arrow_forwardGear A has a mass of 1 kg and a radius of gyration of 30 mm; gear B has a mass of 4 kg and a radius of gyration of 75 mm; gear C has a mass of 9 kg and a radius of gyration of 100 mm. The system is at rest when a couple M0 of constant magnitude 4 N.m is applied to gear C . Assuming that no slipping occurs between the gears, determine the number of revolutions required for disk A to reach an angular velocity of 300 rpm.arrow_forward
- The mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 200-lb uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC of the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring of constant k= 40 lb/ft is attached to wheel B. Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position O the velocity of wheel A just as the door reaches the vertical position. = 30° with the spring unstretched, determine 5 ft 5 ftarrow_forwardTwo disks of the same material are attached to a shaft as shown. Disk A has a radius r and a thickness 2b, while disk B has a radius nr and a thickness 2b. A couple M with a constant magnitude is applied when the system is at rest and is removed after the system has executed two revolutions. Determine the value of n that results in the largest final speed for a point on the rim of disk B.arrow_forwardThe essential structure of a certain type of aircraft turn indicator is shown. Each spring has a constant of 500 N/m, and the 200-g uniform disk of 40-mm radius spins at the rate of 10 000 rpm. The springs are stretched and exert equal vertical forces on yoke AB when the airplane is traveling in a straight path. Determine the angle through which the yoke will rotate when the pilot executes a horizontal turn of 750-m radius to the right at a speed of 800 km/h. Indicate whether point A will move up or down.arrow_forward
- Required information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A 3.5-kg slender rod AB and a 2-kg slender rod BC are connected by a pin at B and by the cord AC. The assembly can rotate in a vertical plane under the combined effect of gravity and a couple M applied to rod BC. In the position shown, the angular velocity of the assembly is zero and the tension in cord AC is equal to 26.8 N. 300 mm A 400 mm 400 mm M B Determine the angular acceleration of the assembly. (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.) rad/s²0. The angular acceleration of the assembly isarrow_forwardA 5-kg homogeneous disk with a radius of 0.2 m is connected to a spring (k=50 N/m) as shown. At the instant shown (position 1), the spring is undeformed. The disk is released from rest and rolls without slipping to position 2, which is 0.1 m down the 25-degree incline. A clockwise constant 2 N-m couple is applied to the disk as it rolls down the inclined surface. Note: I disk = mR²2 2 N-m 0.2 5-kg 25° k = 50 N/m 10000000 1. Which of the following forces does negative work on the system? Friction between the disk and the inclined surface + x Mark 0.00 out of 20.00 2. Which of the following best approximates the magnitude of the work done by the spring? 0.250 J + ✓ 3. Which of the following best approximates the work done by the 2 N-m couple? -1.000 J + ✓ 4. Which of the following gives the correct expression of the kinetic energy of the system at position 2 in terms of the disk's angular velocity, w₂? 0.15 w2*2 + 4.53 rad/s + x 5. Which of the following best approximates the magnitude…arrow_forwardProblem 2: The mechanism shown is one of two identical mechanisms attached to the two sides of a 90-kg. uniform rectangular door. Edge ABC of the door is guided by wheels of negligible mass that roll in horizontal and vertical tracks. A spring of constant k 600 N/m is attached to wheel B. Knowing that the door is released from rest in the position 6 30° with the spring unstretched, determine the velocity of wheel A just as the door reaches the vertical position,arrow_forward
- When the 18-kg wheel shown is attached to a balancing machine and made to spin at a rate of 12.5 rev/s, it is found that the forces exerted by the wheel on the machine are equivalent to a force-couple system consisting of a force F = (160 N)j applied at and a couple where the unit vectors form a triad that rotates with the wheel. (a ) Determine the distance from the axis of rotation to the mass center of the wheel and the products of inertia Ixy and Ixz (b) If only two corrective masses are to be used to balance the wheel statically and dynamically, what should these masses be and at which of the points A, B, D or E, should they be placed?arrow_forwardA slender homogeneous rod AB of mass m and length L is made to rotate at a constant rate w2 about the horizontal z axis, while frame CD is made to rotate at the constant rate w1 about the y axis. Express as a function of the angle 0 (a)the couple M1 required to maintain the rotation of the frame, (b) the couple M2 required to maintain the rotation of the rod, (C) the dynamic reactions at the supports C and D.arrow_forwardAB and CD are two uniform and identical bars of mass 10 kg each, as shown. The hinges at A and Bare frictionless. The assembly is released from rest and motion occurs in the vertical plane. At the instant that the hinge B passes the point B, the angle between the two bars will be -1 m 30° B. A 0° 3. 0.5 m 0.5 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License