
To review:
The inactivation of tumor-suppressing genes in colorectal cancer, whose two possible explanations are given below:
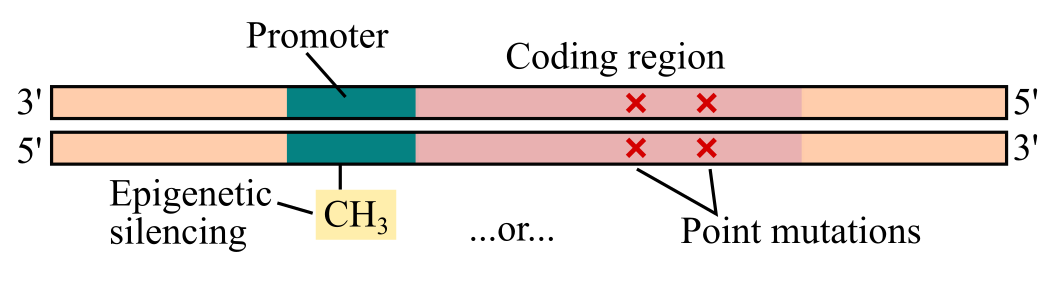
a. Mutations in the coding regions, resulting in inactive proteins.
b. Epigenetic silencing at the promoters of the genes, resulting in reduced transcription.
Given:
Figure shows two possibilities including mutations and epigenetic silencing that are to be explained.
Introduction:
Certain tumor suppressor genes are inactive in colorectal cancer. This further results in a condition characterized by an uncontrolled cell division commonly referred to as cancer. There are two possible reasons behind this cancerous condition including mutations in coding regions and epigenetic silencing at the promoters of genes.
Mutations are defined as the alternations in the sequence of the genetic material of a cell in an organism. On the other hand, the inactivation of a nonmutational gene that propagates from precursor cells to the daughter clone cells.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- A cell inherits a mutation in a gene that results in a transcription factor, called NF-kB, constantly being in its active conformation. When active, NF-kB stimulates the expression of cyclins that promote progression of the cell cycle, regardless of other conditions. As a result of this mutation, how would this cell's phenotype be affected by this mutation? A) This cell would have a cancer phenotype B) This cell would grow larger in size, but would never divide C) This cell would likely undergo apoptosis D) This cell would not duplicate its chromosomes .arrow_forwardCancer often results from a multistage process involving an initiating event (mediated by a viral infection or a carcinogenic chemical), followed by exposure to tumor promoters. Tumor promoters, a group of molecules that stimulate cell proliferation, cannot induce tumor formation by themselves. The phorbol esters, found in croton oil (obtained from the seeds of the croton plant, Croton tiglium), are potent tumor promoters. (Other examples of tumor promoters include asbestos and several components of tobacco smoke.) In one of the tumor-promoting actions of the phorbol esters, these molecules mimic the actions of DAG. In contrast to DAG, the phorbol esters are not easily disposed of. Explain the possible biochemical consequences of phorbol esters in an “initiated” cell. What enzyme is activated by both DAG and phorbol esters?arrow_forwardThe deregulation of several signal transduction pathways is integral to the onset of cancer. These pathways involve both tumor promoters (the "gas pedals") and tumor suppressors (the "brake pedals"). Which would be a more effective treatment for cancer: A small molecule inhibitor that targets a tumor suppressor or one that targets a tumor promoter? Briefly explain your choice. (THIS CAN BE DONE IN LESS THAN TWO SENTENCES, AND MINIMALLY IN ABOUT EIGHT WORDS.) Edit View. Insert Format Tools Table 12pt v Paragraph BI UAV 2VT² V| :arrow_forward
- Cellular levels of tumor suppressor protein p53 is maintained by a ubiquitin ligase protein, called Mdm2. Over expression of Mdm2 destabilizes p53. Another protein p19ARF inhibits the activity of Mdm2, thus stabilizing p53. Loss of p19ARF function converts normal cells into cancer cells With the above information, which of the following statements are true? Mdm2 is a tumor suppressor gene but p19ARF is an oncogene Both Mdm2 & P19ARF are oncogenes Both Mdm2 & P19ARF are tumor suppressor genes O Mdm2 is an oncogene but p19ARF is a tumor suppressor genearrow_forwardD) The level of carbon dioxide increases with the level of available oxygen. 60) The TPS3 gene provides instructions for making a protein called tumor protein p53. Known as the guardlan of the genome, this protein acts as a tumor suppressor, which means that it regulates cell division by keeping cells from growing and dividing t0o fast or in an uncontrolled way. The p53 protein is located in the nucleus of cells throughout the body, where it attaches directly to DNA and plays a critical role in determining whether the DNA will be repaired or the damaged cell will self- destruct (undergo apoptosis). If the DNA can be repaired, p53 activates other genes to fix the damage. If the DNA cannot be repaired, this protein prevents the cell from dividing and signals it to undergo apoptosis. Suppose chromosomes in a skin cell are damaged by ultraviolet radiation. If the damaged genes do not affect p53, which choice correctly predict if the cell will become cancerous and why? No, the cell will not…arrow_forwardDescribe how mutations in genome maintenance factors promote tumorigenesis. Why would inactivation of a mis- match repair gene cause colon cancer?arrow_forward
- p53 is a tumor suppressor gene in human cells. Transcription of this gene leads to the production of the p53 protein in cells which modulates many signal pathways that lead to anti-tumor effects. The strength of anti-tumor effects is directly porportional to the accumulation of the protein within the cells of the person. Suppose a pediatric patient was recently admitted for a rare lung cancer related to p53 deficiencies (although the p53 itself is not mutated). what are some potential reasons for the deficiency in p53 levels and how can you restore them if the reason you assumed for the deficiency is not directly reparable (i.e if you assume that protein degradation is too fast, you cannot directly repair protein degradation but you may want to increase transcription & translation rates to compensate)? Will your hypothesized repair(s) cause negative impacts to the cell? Why?arrow_forwardThe rb gene encodes a protein that inhibits E2F, a transcriptionfactor that activates several genes involved in cell division.Mutations in rb are associated with certain forms of cancer,such as retinoblastoma. Under each of the following conditions,would you expect the cancer to occur?A. One copy of rb is defective; both copies of E2F are functional.B. Both copies of rb are defective; both copies of E2F arefunctional.C. Both copies of rb are defective; one copy of E2F is defective.D. Both copies of rb and E2F are defective.arrow_forwardD) The level of carbon dioxide increases with the level of available oxygen. 60) The TP53 gene provides instructions for making a protein called tumor protein p53. Known as the guardian of the genome, this protein acts as a tumor suppressor, which means that it regulates cell division by keeping cells from growing and dividing too fast or in an uncontrolled way. The p53 protein is located in the nucleus of cells throughout the body, where it attaches directly to DNA and plays a critical role in determining whether the DNA will be repaired or the damaged cell will self- destruct (undergo apoptosis). If the DNA can be repaired, p53 activates other genes to fix the damage. If the DNA cannot be repaired, this protein prevents the cell from dividing and signals it to undergo apoptosis. eg Suppose chromosomes in a skin cell are damaged by ultraviolet radiation. If the damaged genes do not affect p53, which choice correctly predict if the cell will become cancerous and why? No, the cell will…arrow_forward
- Acquired mutation in the p53 gene is the most common genetic alteration found in human cancer (> 50% of all cancers). A germline mutation in p53 is the causative lesion of Li- Fraumeni familial cancer syndrome. In many tumors, one p53 allele on chromosome 17p is deleted and the other is mutated. What type of protein is encoded by the p53 gene? (A) Caspase (B) DNA repair enzyme (C) Membrane cell adhesion molecule (D) Serine phosphatase (E) Telomerase (F) Transcription factor (G) Tyrosine kinasearrow_forwardHow can the role of epigenetics in cancer be reconciled with the idea that cancer is caused by the accumulation of genetic mutations in tumor-suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes?arrow_forwardTumor-suppressor genes are normal human genes that prevent uncontrollable cell growth. Starting with a normal laboratory humancell line, describe how you could use transposon tagging to identifytumor-suppressor genes. (Note: When a TE hops into a tumorsuppressorgene, it may cause uncontrolled cell growth. This is detected as a large clump of cells among a normal monolayer of cells.)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





