
Concept explainers
To calculate: the magnitude and direction of the net force on each particle
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three positive particles of equal charge
Formula used:
According to coulomb's law the magnitude of force
Here,
The direction of force is along the line joining the two charged particles.
Calculation:
The three charges are same in magnitude, so the magnitude of force between any two particles is equal but differ in direction.
The magnitude of force between any two charged particles is,
Substitute
Therefore, the force between any two charged particles is
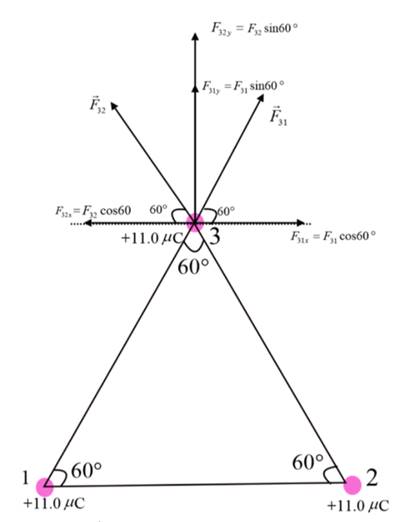
The forces on the
From figure, the force acting on the
Here
From figure, the force acting on the
Here,
The net force acting on the
Substitute
The magnitude of force acting on the
Here,
Therefore, the magnitude of force on
Therefore, the direction of net force on
The force acting on charged particles 1 and 2 and their resolution is shown in the figure given below:
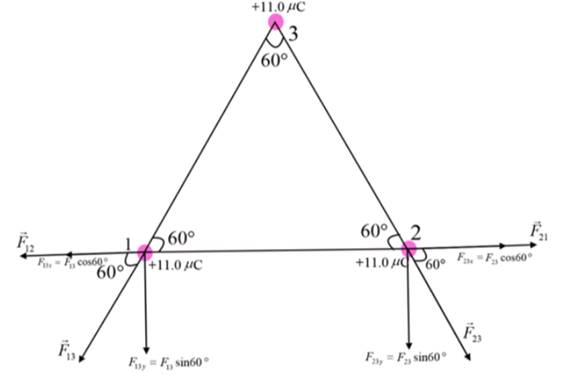
From figure, the force acting on the
Here,
From figure, the force acting on the
Here,
The net force acting on the
Substitute
The magnitude of force acting on the
Here,
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of force on
The angle
The
Therefore, the direction of net force on
From figure, the force acting on the
Here,
From figure, the force acting on the
Here,
The net force acting on the
The magnitude of force acting on the
Here,
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of force on
The angle
Substitute
The
Therefore, the direction of net force on
Chapter 16 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
University Physics (14th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





