
Find the factors of safety with respect to overturning, sliding, and bearing capacity failure.
Answer to Problem 15.2P
The factor of safety with respect to overturning is 4.62_.
The factor of safety with respect to sliding is 2.11_.
The factor of safety with respect to bearing capacity failure is 7.4_.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The cohesion (c′1) of backfill soil is 0.
The unit weight (γ1) of the backfill soil is 18.5 kN/m3.
The friction angle (ϕ′1) of the backfill soil is 35°.
The unit weight
The backfill angle
Calculation:
Check stability with respect to overturning.
Consider point C as the left end of the toe base as named as C.
Divide the retaining wall into section as in Figure 1.
Sketch the section of the retaining wall as shown in Figure 1.
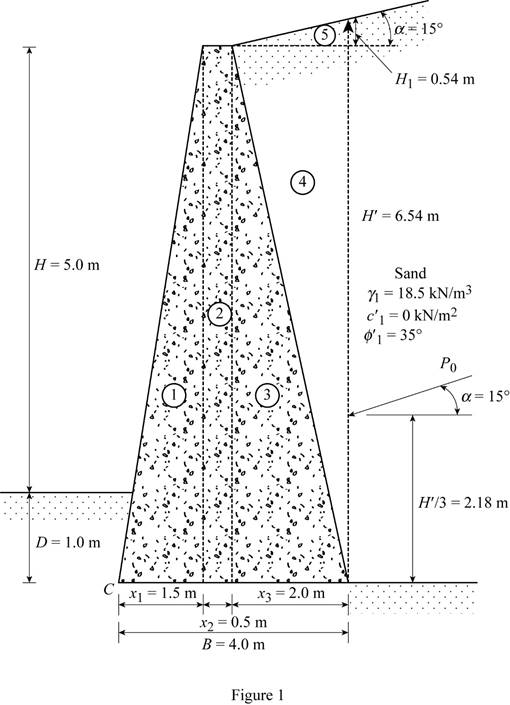
Here,
Refer Table 14.2, “Values of
Take the value of active earth pressure coefficient
Refer Figure 1.
Find the height of the inclined portion of backfill
Substitute 2 m for
Find the total height of the inclined backfill
Here, H is the height of retaining wall and D is the depth to the bottom of the base slab.
Substitute 5.0 m for H, 1.0 m for D, and 0.54 m
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the vertical component of the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the horizontal component of the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the weight of section 1
Here,
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 2
Here,
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 1.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 3
Here,
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 4
Here,
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the weight of section 5
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 2.0 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the moment arm or lever arm
Substitute 0.5 m for
Find the moment about point C
Substitute
Find the total moment about the point C
Substitute
Find the total vertical load
Substitute
Summarize the values of weight, moment arm from C, and moment about C as shown in Table 1.
| Section | Weight (kN/m) | moment arm from C | moment about C |
| 1 | 108 | 1 | 108 |
| 2 | 72 | 1.75 | 126 |
| 3 | 144 | 2.67 | 384.5 |
| 4 | 111 | 3.33 | 369.6 |
| 5 | 10 | 3.33 | 33.33 |
| 4 | 121.6 | ||
Find the overturning moment
Substitute
Find the factor of safety
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to overturning is
Check the stability with respect to sliding.
Find the coefficient of passive earth pressure
Substitute
Find the passive earth pressure
Here,
Substitute 1 m for D,
Find the angle of friction
Substitute
Find the factor of safety against sliding
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to sliding is
Check the stability with bearing capacity failure.
Find the eccentricity (e) using the equation:
Substitute 4 m for B,
Check for eccentricity.
Substitute 0.116 m for e and 4 m for B.
The eccentricity is within the limit. Therefore, there is no tensile stress produced at the end of the steel section.
Find the maximum pressure
Substitute
Find the effective breadth
Substitute 4 m for B and 0.116 m for e.
Refer Table 16.2, “Bearing Capacity Factors” in the textbook.
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Take the value of bearing capacity factor,
Find the load (q) due the soil in front of heel using the equation:
Substitute 1.0 m for D and
Find the inclination angle of vertical load
Substitute
Find the inclination factor
Substitute
Find the depth factor
Here,
Substitute
The depth factor
Find the inclination factor
Substitute
Find the ultimate bearing capacity of the shallow foundation
Substitute
Find the factor of safety against bearing capacity failure
Substitute
Therefore, the factor of safety with respect to bearing capacity failure is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- Q1/ The specific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively calculate the equivalent moisture content as equivalent depth for 1.2m root zone : 1. at permanent wilting point 2. at field capacity 3. for ready available waterarrow_forwardKindy explain the pie chart percentage and give some related study and references about Value of travel time connected to the pie chartarrow_forwardConsider the specifications for an asphaltic concrete mixture and the results of a sieve analysis below. Coarse aggregates: Fine aggregates: Filler: 60% 35% 5% Percent of Weight of Aggregate or Filler Passing Sieve Designation Retained on Sieve Designation Coarse Aggregate Fine Aggregate Mineral Filler 3/4 in. (19 mm) 1/2 in. 6 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) 3/8 in. 15 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) No. 4 50 - No. 4 (4.75 mm) No. 10 20 1 No. 10 (2 mm) No. 40 (0.425 mm) No. 40 9 35 - No. 80 31 40 No. 80 (0.180 mm) No. 200 (0.075 mm) Total No. 200 - 33 - - 25 35 100 100 100 Determine the proportion of different aggregates to obtain the required gradation. Percent of Total Weight of Mixture Passing Sieve Designation Retained on Sieve Designation Coarse Aggregate Fine Aggregate 3/4 in. (19 mm) 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) 1/2 in. 3/8 in. No. 4 No. 4 (4.75 mm) No. 10 No. 10 (2 mm) No. 40 No. 40 (0.425 mm) No. 80 No. 80 (0.180 mm) No. 200 No. 200 (0.075 mm) Total Need Help? Read It Mineral Filler Total 100arrow_forward
- Results obtained from laboratory tests on a sample of RC-250 asphalt cement are given. Determine whether the properties of this material meet the Asphalt Institute specifications for this type of material; if not, note the differences. (For each specification, enter the minimum acceptab value in the same units as used in the test results.) • Kinematic viscosity at 140°F (60°C) = 230 centistokes • Flash point (Tagliabue open cup) = 89°F • Distillation test where distillate percent by volume of total distillate to 680°F (360ºC) • To 437°F (225°C) = 27% • To 500°F (260°C) = 69% • To 600°F (316°C) = 72% • Residue from distillation to 680°F (360°C) by volume percentage of sample by difference • Tests on Residue from Distillation: • Ductility at 77°F (25°C) = 92 cm • Absolute viscosity at 140°F (60°C) = 620 poises ⚫ Solubility = 90% Property Kinematic Viscosity = 74% Specification Test Results Were Specifications Met? centistokes 230 centistokes ---Select--- ✓ Flash Point °F 89°F…arrow_forwardProblem 2 Two machines produce rivets for a factory job. The number of sub-standard rivets per hour by the two machines are random variables, denoted by X1 and X2. The bivariate PMF of X1 and X2, Px,x,(x1,x2), is given in the table below. X2=0 X2=1 X2=2 X2=3 X₁-0 0.07 0.05 0.02 0.01 X₁ =1 0.05 0.16 0.12 0.02 X₁ =2 0.02 0.12 0.17 0.05 X₁ =3 0.01 0.01 0.05 0.07arrow_forwardPlease provide a handwritten solution to the questionarrow_forward
- AS Q1/ The specific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively calculate the equivalent moisture content as equivalent depth for 1.2m root zone : 1. at permanent wilting point 2. at field capacity 3. for ready available waterarrow_forwardQuestion 6 The following figure shows peak-hour volumes for an intersection. Using Webster's method, determine a suitable signal timing for the intersection using the four-phase system shown below. Use an amber interval of 3 seconds and the saturation flow given in the table. O 100 O Phase Lime Group Saturation Flow A e 1615-> 370 3700 B 1615 1615 3700 1615 3700arrow_forwardPHF-0.91 Pedestrian volume is negligible. Question 7 A parking area with 60 bays has an initial count of 35 vehicles. The in-out survey data for 10-minute intervals is as per the table below. Complete the table, calculate the accumulation, occupancy (%), and parking load (veh.hrs) for each interval. Time (min) In Out Accumulation Occupancy Parking load (%) 0 3 10 2 4 20 1 1 30 1 3 40 1 6 50 1 4 60arrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning



