
Campbell Biology
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780135188743
Author: Urry
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 13TYU
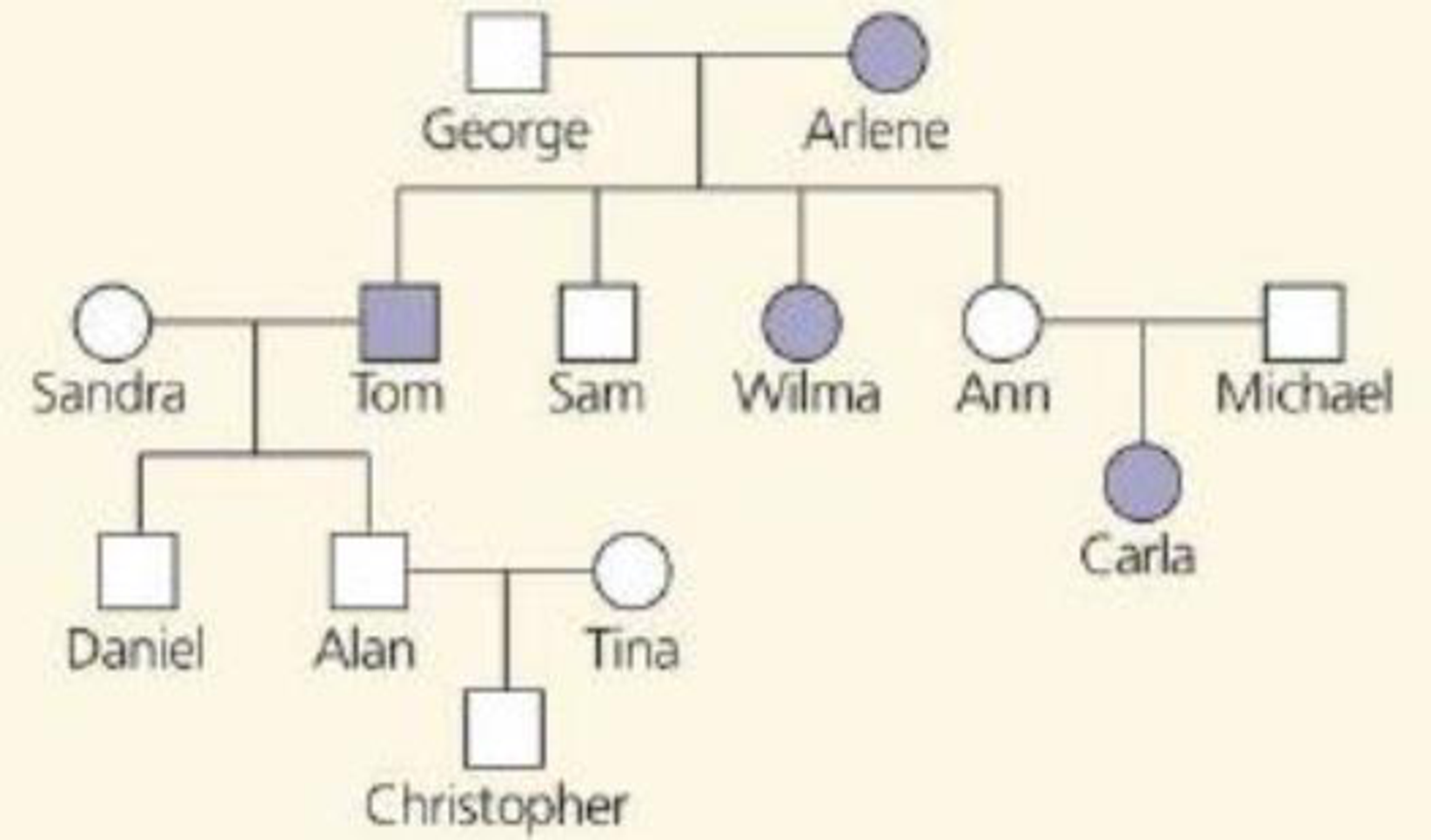
The pedigree belowtraces the inheritance of alkaptonuria, a biochemical disorder. Affected individuals, indicated here by the colored circles and squares, are unable to
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find out about the organisations and the movements aimed at the
conservation of our natural resources. Eg Chipko movement and Greenpeace.
Make a project report on such an organisation.
What are biofertilizers and mention the significance
PCBs and River Otters: Otters in Washington State’s Green-Duwamish River have high levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in their livers. PCBs can bind to the estrogen receptors in animals and disrupt the endocrine system of these otters. The PCBs seem to increase the estrogen to androgen ratio, skewing the ratio toward too much estrogen.
How would increased estrogen affect the river otter population?
Based on your reading of the materials in this unit, what factors can affect fertility in humans?
Explain how each of the factors affecting human fertility that you described can disrupt the human endocrine system to affect reproduction.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Campbell Biology
Ch. 14.1 - DRAW IT Pea plants heterozygous for flower...Ch. 14.1 - WHAT IF? List all gametes that could be made by a...Ch. 14.1 - MAKE CONNECTIONS In some pea plant crosses, the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 14.2 - Two organisms, with genotypcs BbDD and BBDd, are...Ch. 14.2 - WHAT IF? Three characters (flower color, seed...Ch. 14.3 - What two properties, one structural and one...Ch. 14.3 - If a man with type AB blood marries a woman with...Ch. 14.3 - WHAT IF? A rooster with gray feathers and a hen...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 14.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 14.4 - MAKE CONNECTIONS In Table 14.1, note the...Ch. 14 - When Mendel did crosses of true-breeding purple-...Ch. 14 - DRAW IT Redraw the Punnett Square on The right...Ch. 14 - Inheritance patterns are often more complex than...Ch. 14 - Both members of a couple know that they are...Ch. 14 - Prob. 1TYUCh. 14 - A man with type A blood marries a woman with type...Ch. 14 - A man has six fingers on each hand and six toes on...Ch. 14 - Prob. 4TYUCh. 14 - Flower position, stem length, and seed shape are...Ch. 14 - Hemochromatosis is an inherited disease caused by...Ch. 14 - The genotype of F1, individuals in a tetrahybrid...Ch. 14 - What is the probability that each of thc following...Ch. 14 - Prob. 9TYUCh. 14 - Prob. 10TYUCh. 14 - In tigers, a recessive allele of a particular gene...Ch. 14 - In maize (com) plants,a dominant allele I inhibits...Ch. 14 - The pedigree belowtraces the inheritance of...Ch. 14 - Imagine that you are a genetic counselor, and a...Ch. 14 - EVOLUTION CONNECTION Over the past half century,...Ch. 14 - SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY You are handed a mystery pea...Ch. 14 - Prob. 17TYUCh. 14 - SYNTHESIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE Just for fun, imagine...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Practice Problem 1.22 Which of the following alkenes can exist as cis-trans isomers? Write their structures. Bu...
Organic Chemistry
How does the removal of hydrogen atoms from nutrient molecules result in a loss of energy from the nutrient mol...
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Other than oil and alcohol, are there other liquids you could compare to water (that are liquid at room temperature)? How is water unique compared to these other liquids? What follow-up experiment would you like to do, and how would you relate it to your life?arrow_forwardSelection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forward
- Species Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forwardmagine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forward
- What are Amyloid Fibrils? What biological functions are these known to perform?arrow_forwardHow do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How to solve genetics probability problems; Author: Shomu's Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Beyond Mendelian Genetics: Complex Patterns of Inheritance; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EmvmBuK-B8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY