
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylicc carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid which leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.
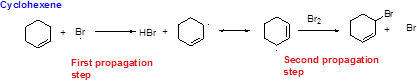
Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reaction with bromine molecule and forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(a)
Answer to Problem 25P
1-pentene undergoes bromination using N-bromosuccinamide and yields brominated compound A and B which is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. Bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
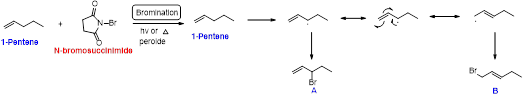
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination of Allylic Carbons:

N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylic carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid. If high concentration of bromine and high concentration of hydrobromic acid which leads to the formation of bromination in the double bond.

Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
NBS bromine radical removes the allylic hydrogen which forms hydrogen bromide and allylic radical in the first propagation step, the allylic radical is stabilized by the double bond in ring. This allylic radical reaction with bromine molecule forms allylic bromide in the second propagation step which are shown above.
(b)
Answer to Problem 25P
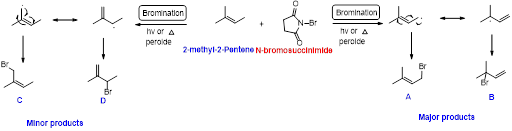
2-methyl-2-pentene undergoes bromination using N-bromo succinamide and yields brominated compound A, B as a major product and C, D as minor product which is shown below.
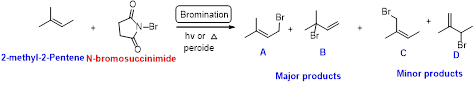
Explanation of Solution
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is used for the allylic bromination through radical reaction. bromination of allylicc carbon requires low concentration of bromine and low concentration of hydrobromic acid
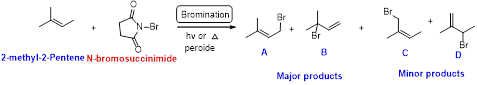
Bromination reaction starts with the homolytic cleavage of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present. (bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(c)
Answer to Problem 25P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
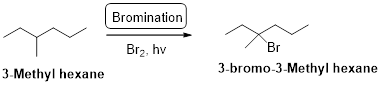
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
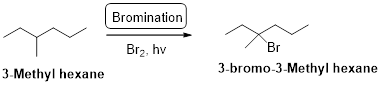
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
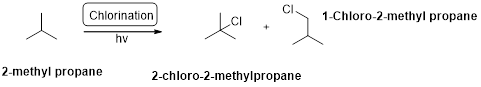
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(d)
Answer to Problem 25P
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane which is shown below
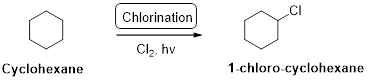
Explanation of Solution
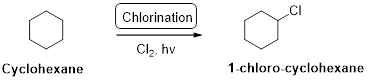
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination, all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane which is shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(e)
Answer to Problem 25P
Cyclopentane has no reaction with chlorine in dichloromethane which is shown below

Explanation of Solution
Cyclopentane has no reaction with chlorine in dichloromethane, because the reaction will not go without light or heat which is shown below

(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
(f)
Answer to Problem 25P
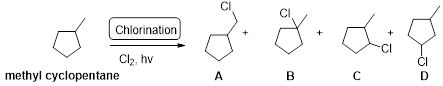
Explanation of Solution
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination, the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane which is shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is (are) the major organic product(s) obtained from the following reaction? Br2 O (2R,3R)-dibromobutane meso-2,3-dibromobutane O (2S,3S)-dibromobutane O Racemic mixturearrow_forwardDraw the cycloalkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O H₂SO4 CH3 ▼ • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. » [ ]# CH3 ? OHarrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. CH3 HCI CH3 CHCCH, ? + Či CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one.arrow_forward
- Draw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O H₂SO4 CH3 CH3CCH3 OH You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. Sn [F ChemDoodleⓇarrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O H₂SO4 CH3 CH3 CHCCH3 OH CH3 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. Sn [F ChemDoodlearrow_forward2. Complete each of the given reactions with the structure of possible product(s). Show proper stereochemistry where needed 2 NO₂ S HN Br₂ FeCl3 AICI, CI AICHarrow_forward
- Draw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + HCI CH3 CH3CCH3 CI • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. #[ ] در ChemDoodlearrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the major product of the reaction shown. -CH₂CH3 Br₂ H₂O • Show product stereochemistry IF the reactant alkene has both carbons of the double bond within a ring. • Do not show stereochemistry in other cases. • If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer.arrow_forwardDraw the organic product of the following reaction. CH3 m-CICgH,CO;H • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer. • If more than one product is possible, only draw the major product. opy astearrow_forward
- Draw the structural formula of the product of the reaction shown below. + H₂O AAVIL H₂SO4 • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer. Sn [F Ⓡ ChemDoodlearrow_forwardThese are synthesis questions. You need to show how the starting material can be converted into the product(s) shown. You may use any reactions we have learned. Show all the reagents you need. Show each molecule synthesized along the way and be sure to pay attention to the regiochemistry and stereochemistry preferences for each reaction. Il a racemic molecule is made along the way, you need to draw both enantiomers and label the mixture as "racemic". All of the carbon atoms of the products must come from the starting material(s)! H ?arrow_forwardwhat are the products? please indicate the relative stereochemistry for the following transformations and indicate the major product.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
