
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The expected product has to be drawn for the given reaction.
Concept Introduction:

Ozonolysis of Alkynes:
Alkynes undergo ozonolysis with ozone. The reaction that takes place when an alkyne is treated with ozone is that an oxidative cleavage. This is followed by treatment with water to give carboxylic acids as products. If the considered alkyne is an internal alkyne then the product will be two carboxylic acids. The general scheme can be shown as given below for reaction involving internal alkyne,
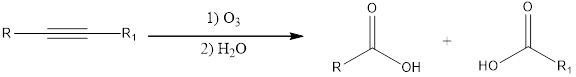
If the alkyne that is considered is a terminal alkyne, then the terminal end is converted into carbon dioxide and the other end gets converted to
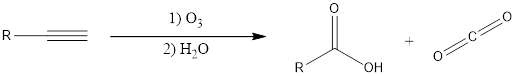
Answer to Problem 12.35P
The expected product is,
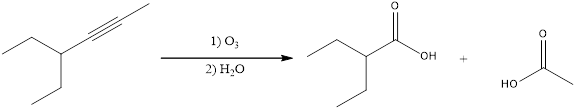
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,

From the given reaction condition, it is clear that the given reaction is ozonolysis reaction. The considered alkyne is an internal alkyne. Hence, two carboxylic acids will be obtained as products from oxidative cleavage of alkyne. This can be shown as given below,

The expected product was drawn for the given reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions need to get full marks it's my quiz okkkk.take your time but solve full accurate okkk chemistry expert solve itarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPart A Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Up Part B Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Uparrow_forwardFrenkel and Schottky are intrinsic or extrinsic defects, point or linear defects.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





