
Concept explainers
Match the vapor pressure diagrams with the solute-solvent combinations and explain your answers.
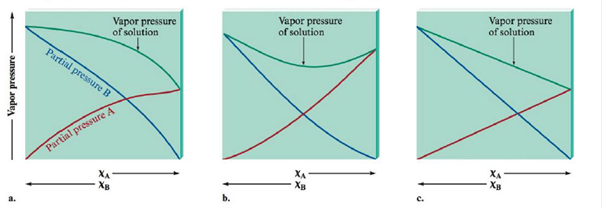
a.  and
and 
b.  and
and 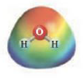
c. 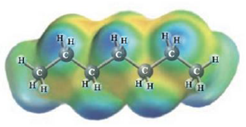 and
and 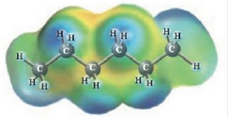
d. 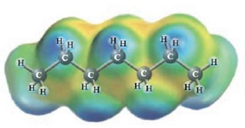 and
and 
(a)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Psolution=P°solventXsolvent......(1) P is vapor pressure of the solution P°solvent pressure of the solvent Xsolvent mole fraction of solvent
Answer to Problem 69E
A Negative deviations from Raoult’s law is the right option for Acetone-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the second diagram match with Acetone and Water
The second diagram illustrates negative variation from Raoult's law. This occurs whilst the solute-solvent connections are stronger than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
CH3COCH3 and H2O
These two molecules are named Acetone ( CH3COCH3) and Water. As discussed in non-ideal solutions, Acetone-Water solutions exhibit negative deviations from Raoult’s law. Acetone and Water have the capability to hydrogen bond with each other, which gives the solution stronger intermolecular forces as compared to the pure states of together solute and solvent. In the pure state, Acetone cannot H-bond through itself. Consequently the second diagram illustrating negative deviations from Raoult’s law is the right option for Acetone-Water solutions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Psolution=P°solventXsolvent......(1) P is vapor pressure of the solution P°solvent pressure of the solvent Xsolvent mole fraction of solvent
Answer to Problem 69E
A Positive deviation from Raoult’s law is the right option for Ethanol-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the first diagram match with CH3CH2OH and Water
CH3CH2OH and Water
The first diagram shows positive deviation from Raoult's law. This occurs when the solute-solvent connections are weaker than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
These two molecules are named Ethanol ( CH3CH2OH) and Water. Ethanol-water solutions demonstrate positive deviations from Raoult’s law. Equally substances can hydrogen bond in the pure state, and they can carry on this in solution. Yet, the solute-solvent interactions are rather weaker for Ethanol-Water solutions due to the important non-polar part of Ethanol ( CH3-CH2 is the non-polar part of Ethanol). This non-polar part of Ethanol weakens the intermolecular forces in solution. As a result the first diagram illustrating positive deviations from Raoult’s law is the right option for Ethanol-Water solutions.
(c)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Psolution=P°solventXsolvent......(1) P is vapor pressure of the solution P°solvent pressure of the solvent Xsolvent mole fraction of solvent
Answer to Problem 69E
No deviation from Raoult’s law is the correct choice for Heptane-Hexane. solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the polarity of Heptane and Hexane
Heptane and Hexane
The third diagram illustrates an perfect solution with no difference from Raoult's law. This occurs what time the solute-solvent interactions are concerning equal to the pure solvent and pure solute interactions.
These two molecules are named Heptane ( C7H16) and Hexane ( C6H14). Heptane and hexane are very similar non-polar substances. Equally are collected totally of non-polar C-C bonds and relatively non-polar C-H bonds, with together have a similar size and form. Solutions of Heptane and Hexane should be ideal. So the third diagram illustrating no deviation from Raoult’s law is the correct choice for Heptane-Hexane solutions.
(d)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Psolution=P°solventXsolvent......(1) P is vapor pressure of the solution P°solvent pressure of the solvent Xsolvent mole fraction of solvent
Answer to Problem 69E
Heptane and Water results in positive deviations from Raoult’s law (the first diagram).
Explanation of Solution
To find: The Heptane Vs Water.
C7H16 and Water
These two molecules are named Heptane ( C7H16) and Water. The connections flanked by the non-polar Heptane molecules and the polar water molecules will surely be weaker in solution as compared to the pure solvent and pure solute interactions. These results in positive deviations from Raoult’s law (the first diagram).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Lab Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste¿s Chemistry, 10th Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Physical Universe
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardWhen anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forward
- For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forwardConsider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forward
- For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forwardGiven the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





