
The black silver sulfide discoloration of silverware canbe removed by heating the silver article in a sodiumcarbonate solution in an aluminum pan. The reaction is
a. Using data in Appendix 4, calculate
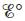 for the above reaction at 25°C. [For
for the above reaction at 25°C. [For
b. Calculate the value of the standard reduction potentialfor the following half-reaction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Calculate K at 25°C for each of the reactions referred to in Question 32. Assume smallest whole-number coefficients.arrow_forwardCalculate G and K at 25C for the reactions in Exercises 37 and 41.arrow_forwardCalculate G at 355 K for each of the reactions in Question 17. State whether the reactions are spontaneous.arrow_forward
- Adenosine triphosphate, ATP, is used as a free-energy source by biological cells. (See the essay on page 624.) ATP hydrolyzes in the presence of enzymes to give ADP: ATP(aq)+H2O(l)ADP(aq)+H2PO4(aq);G=30.5kJ/molat25C Consider a hypothetical biochemical reaction of molecule A to give molecule B: A(aq)B(aq);G=+15.0kJ/molat25C Calculate the ratio [B]/[A] at 25C at equilibrium. Now consider this reaction coupled to the reaction for the hydrolysis of ATP: A(aq)+ATP(aq)+H2O(l)B(aq)+ADP(aq)+H2PO4(aq) If a cell maintains a high ratio of ATP to ADP and H2PO4 by continuously making ATP, the conversion of A to B can be made highly spontaneous. A characteristic value of this ratio is [ATP][ADP][H2PO4]=500 Calculate the ratio [B][A] in this case and compare it with the uncoupled reaction. Compared with the uncoupled reaction, how much larger is this ratio when coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP?arrow_forwardCalculate K for the reaction SnO2(s) + 2 CO(g) Sn(s) + 2 CO2(g) given the following information: SnO2(s)+2H2(g)Sn(s)+2H2O(g)K=8.12H2(g)+CO2(g)H2O(g)+CO(g)K=0.771arrow_forwardElemental boron, in the form of thin fibers, can be made by reducing a boron halide with H2. BCl3(g) + 3/2 H2(g) B(s) + 3HCl(g) Calculate H, S, and G at 25 C for this reaction. Is the reaction predicted to be product favored at equilibrium at 25 C? If so, is it enthalpy driven or entropy driven?arrow_forward
- For the reaction 2Cu(s)+S(s)Cu2S(s) H and G are negative and S is positive. a At equilibrium, will reactants or products predominate? Why? b Why must the reaction system be heated in order to produce copper(I) sulfide?arrow_forwardHydrogen gas and iodine gas react to form hydrogen iodide. If 0.500 mol H2 and 1.00 mol I2 are placed in a closed 10.0-L vessel, what is the mole fraction of HI in the mixture when equilibrium is reached at 205C? Use data from Appendix C and any reasonable approximations to obtain K.arrow_forwardA crucial reaction for the production of synthetic fuels is the production of H2 by the reaction of coal with steam. The chemical reaction is C(s) + H2O(g) CO(g) + H2(g) (a) Calculate rG for this reaction at 25 C, assuming C(s) is graphite. (b) Calculate Kp for the reaction at 25 C. (c) Is the reaction predicted to be product-favored at equilibrium at 25 C? If not, at what temperature will it become so?arrow_forward
- Pencil lead is almost pure graphite. Graphite is the stable elemental form of carbon at 25C and 1 atm. Diamond is an allotrope of graphite. Given diamond: H f =1.9 kJ/mol; S =2.4 J/mol k at what temperature are the two forms in equilibrium at 1 atm? C(graphite)C(diamond)arrow_forwardUse the values for G f in Appendix 1 to calculate Ksp for barium sulfate at 25C. Compare with the value given in Chapter 15.arrow_forwardConsider the equilibrium system HF(aq)H+(aq)+F(aq) Given HfHF(aq)=320.1kJ/mol , HfF(aq)=332.6kJ/mol ; SF(aq)=13.8kJ/molK ; KaHF=6.9104 at 25°C calculate S° for HF(aq).arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





