
Concept explainers
Problem 10.16 projected financial statements for Walmart for Years +1 through +5. The following data for Walmart include the actual amounts for 2012 and the projected amounts for Years +1 through +5 for comprehensive income and common shareholders’ equity, assuming it will use implied dividends as the financial flexible account to balance the balance sheet (amounts in millions).
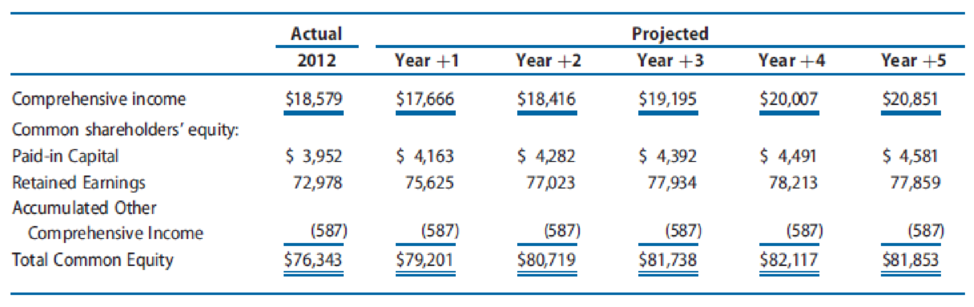
Assume that the market equity beta for Walmart at the end of 2012 was 1.00. Assume that the risk-free interest rate was 3.0% and the market risk premium was 6.0%. Also assume that Walmart had 3,314 million shares outstanding at the end of 2012, and share price was $69.09.
REQUIRED
- a. Use the
CAPM to compute the requiredrate of return on common equity capital for Walmart. - b. Compute the weighted-average cost of capital for Walmart as of the start of Year +1. At the end of 2012, Walmart had $48,222 million in outstanding interest-bearing debt on the balance sheet and no preferred stock. Assume that the balance sheet value of Walmart’s debt is approximately equal to the market value of the debt. Assume that at the start of Year +1, it will incur interest expense of 4.2% on debt capital and that its average tax rate will be 32.0%. Walmart also had $5,395 million in equity capital from noncontrolling interests. Assume that this equity capital carries a 15.0% required rate of return. (For our forecasts, we assume noncontrolling interests are similar to
preferred shares and receive dividends equal to the required rate of return each year.) - c. Use the clean surplus accounting approach to derive the projected dividends for common shareholders for Years +1 through +5 based on the projected comprehensive income and shareholders’ equity amounts. (Throughout this problem, you can ignore dividends to noncontrolling interests.)
- d. Use the clean surplus accounting approach to project the continuing dividend to common shareholders in Year +6. Assume that the steady-state long-run growth rate will be 3% in Years +6 and beyond.
- e. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate, compute the sum of the present value of dividends to common shareholders for Walmart for Years +1 through +5.
- f. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate and the long-run growth rate from Requirement d, compute the continuing value of Walmart as of the beginning of Year +6 based on its continuing dividends in Years +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value, bring continuing value back to present value at the start of Year +1.
- g. Compute the value of a share of Walmart common stock, as follows:
- (1) Compute the sum of the present value of dividends including the present value of continuing value.
- (2) Adjust the sum of the present value using the midyear discounting adjustment factor.
- (3) Compute the per-share value estimate.
- h. Using the same set of
forecast assumptions as before, recompute the value of Walmart shares under two alternative scenarios. To quantify the sensitivity of your share value estimate for Walmart to these variations in growth and discount rates, compare (in percentage terms) your value estimates under these two scenarios with your value estimate from Requirement g.- Scenario 1: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 2%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of
return on equity is 1 percentage point higher than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a. - Scenario 2: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 4%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of return on equity is 1 percentage point lower than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a.
- Scenario 1: Assume that Walmart’s long-run growth will be 2%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of
- i. What reasonable range of share values would you expect for Walmart common stock? Where is the current price for Walmart shares relative to this range? What do you recommend?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
- Please answer Question 8 & 9 8.On March 24, 2020, the Dow Jones Industrial Average opened at $18,591.93 and closed at $20,704.91. What was the daily return that day, and what was the effective annual rate return (in percent) of the stock market that day?Daily Return: __________% EAR:_________ % 9. Financial analysts forecast GDY Inc.’s growth for the future to be 8%. GDY's recent annual dividend was $6.00. What is the value of GDY stock when the required return is 11%?Stock Value: $___________________arrow_forwardProblem . Valuation of equity X Company paid dividends of 2.12 in 2022. The dividends are expected to grow at 5%per year in the long term and the company has a cost of equity of 9.40%. What is the value per equity share?arrow_forwardPLEASE SOLVE THIS QUESTION, ASAP: Q: Suppose a company estimates following one year returns from investing in the common stock of Leopard Corporation: Possibility of Occurrence .1 .25 .1 .15 .1 .2 .1 Possible returns 15% 30% 15% -10% -5% 20% 10% Required: Calculate Expected return & Risk {Standard Deviation)arrow_forward
- A project hasan equity beta of 1.10 (based on similar listed company after making all necessary adjustments); the market risk premium is expected to be 59% and the yield on government bonds has been and remains at 7.5%. Determine the company's cost of equity based on the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)arrow_forwardIntegrative Risk and valuation Giant Enterprises' stock has a required return of 13.9%. The company, which plans to pay a dividend of $2.01 per share in the coming year, anticipates that its future dividends will increase at an annual rate consistent with that experienced over 2013-2019 period, when the following dividends were paid: a. If the risk-free rate is 3%, what is the risk premium on Giant's stock? b. Using the constant-growth model, estimate the value of Giant's stock. (Hint: Round the computed dividend growth rate to the nearest whole percent.) c. Explain what effect, if any, a decrease in the risk premium would have on the value of Giant's stock. a. If the risk-free rate is 3%, the risk premium on Giant's stock is %. (Round to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardCorporate Finance An equity analyst estimates the S&P500 dividends for the next twelve months will be $74. The analyst came up with this estimate by looking at CME dividend futures. Assume a year’s worth of dividends is paid exactly twelve months from now, and that over the next several years the annual growth rate in the dividend yield would be 8%. Assuming that the appropriate risk-free interest rate to use for CAPM is 5.25%, and that the current price of theS&P500 is $5,211, what is the market-implied Equity Risk Premium based on the analyst’s predictions?arrow_forward
- Common stock value-Constant growth Personal Finance Problem Over the past 6 years, Elk County Telephone has paid the dividends shown in the following table,. The firm's dividend per share in 2020 is expected to be $10.12. a. If you can earn 13% on similar-risk investments, what is the most you would be willing to pay per share in 2019, just after the $9.73 dividend? b. If you can earn only 10% on similar-risk investments, what is the most you would be willing to pay per share? c. Compare your findings in parts a and b, what is the impact of changing risk on share value? a. If you can earn 13% on similar-risk investments, the most you would be willing to pay per share is $ Data table Year 2019 2018 (Click on the icon here in order to copy the contents of the data table below. into a spreadsheet.) 2017 2016 2015 2014 IXIE Dividend per share $9.73 $9.36 $9.00 $8.65 $8.32 $8.00 (Round to the nearest cent.) Xarrow_forwardSelf-Test Problem Given are the following possible dollar returns (dividends plus capital gains) over the coming year from a $10,000 investment in General Motors common stock: State of Economy Probability 0.20 0.60 Return $-1,000 1,500 2,500 Recession Normal year Boom 0.20 Convert the dollar returns to percentage returns and then determine the a. Expected return b. Standard deviation of returnsarrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion A company is expected to maintain its dividend payout ratio of 70% in the long term. The earnings per share of the company are expected to be $1.575 next year. Earnings are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5% per year. The current risk-free rate is 1%, the implied equity risk premium is 7.0%, and the estimated beta of the firm is 2.10. If the firm is currently trading in the market at a P/E of 13.5, which of the following statements is correct A) firm correctly priced B) firm overvalued C) firm undervaluedarrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning





