
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 2P
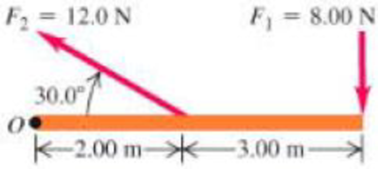
Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in Figure 10.42. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page.
Figure 10.42
Problem 2.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Checkpoint 4
The figure shows four orientations of an electric di-
pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta-
tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque
on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di-
pole, greatest first.
(1)
(2)
E
(4)
What is integrated science.
What is fractional distillation
What is simple distillation
19:39 ·
C
Chegg
1 69%
✓
The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take
F=1700 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
800 lb
||-5-
F
600 lb
بتا
D
E
C
BO
10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft-
Solved Part A The compound
beam is fixed at E and...
Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm
Problem
A-12
% Chia sẻ
kip
800 lb
Truy cập )
D Lưu
of
C
600 lb
|-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft
D
E
5 ft-
Trying
Cheaa
Những kết quả này có
hữu ích không?
There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!)
Chegg
Solved The compound b...
Có Không ☑
|||
Chegg
10
וח
Chapter 10 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 10 - When tightening a bolt, mechanics sometimes extend...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2CQCh. 10 - Two identical uniform 30 cm bricks are placed one...Ch. 10 - (a) If the forces on an object balance, do the...Ch. 10 - (a) Can you change the location of your bodys...Ch. 10 - Serious bicyclists say that if you reduce the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 7CQCh. 10 - In terms of torques, discuss the action of a claw...Ch. 10 - Why is a tapered water glass with a narrow base...Ch. 10 - True or false? In picking an axis about which to...
Ch. 10 - Global warming. As the earths climate continues to...Ch. 10 - If two spinning objects have the same angular...Ch. 10 - You are designing a wheel that must have a fixed...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2MCPCh. 10 - A student is sitting on a frictionless rotating...Ch. 10 - If the torques on an object balance, then it...Ch. 10 - If the forces on an object balance, then it...Ch. 10 - Prob. 6MCPCh. 10 - A person pushes vertically downward with force P...Ch. 10 - String is wrapped around the outer rim of a solid...Ch. 10 - A ball of mass 0.20 kg is whirled in a horizontal...Ch. 10 - A heavy solid disk rotating freely and slowed only...Ch. 10 - A uniform metal meterstick is balanced as shown in...Ch. 10 - Prob. 1PCh. 10 - Calculate the net torque about point O for the two...Ch. 10 - Three forces are applied to a wheel of radius...Ch. 10 - A 4 N and a 10 N force act on an object. The...Ch. 10 - A square metal plate 0.180 m on each side is...Ch. 10 - A cord is wrapped around the rim of a wheel 0.250...Ch. 10 - A certain type of propeller blade can be modeled...Ch. 10 - A 750 g grinding wheel 25.0 cm in diameter is in...Ch. 10 - A grindstone in the shape of a solid disk with...Ch. 10 - A solid, uniform cylinder with mass 8.00 kg and...Ch. 10 - A 2.00 kg stone is tied to a thin, light wire...Ch. 10 - A light rope is wrapped several times around a...Ch. 10 - A thin, light string is wrapped around the rim of...Ch. 10 - 14. A uniform, 8.40-kg, spherical shell 50.0 cm in...Ch. 10 - A hollow spherical shell with mass 2.00 kg rolls...Ch. 10 - A solid disk of radius 8.50 cm and mass 1.25 kg,...Ch. 10 - What is the power output in horsepower of an...Ch. 10 - A solid uniform sphere of mass 5 kg and radius 0.1...Ch. 10 - A playground merry-go-round has a radius of 4.40 m...Ch. 10 - The flywheel of a motor has a mass of 300.0 kg and...Ch. 10 - Calculate the angular momentum and kinetic energy...Ch. 10 - (a) Calculate the magnitude of the angular...Ch. 10 - A small 0.300 kg bird is flying horizontally at...Ch. 10 - A. small 4.0 kg brick is released from rest 2.5 m...Ch. 10 - The London Eye is the tallest Ferris wheel in...Ch. 10 - A certain drawbridge can be modeled as a uniform...Ch. 10 - On an old-fashioned rotating piano stool, a woman...Ch. 10 - The spinning figure skater. The outstretched hands...Ch. 10 - A small block on a frictionless horizontal surface...Ch. 10 - A uniform 2 kg solid disk of radius R 0.4 m is...Ch. 10 - A diver comes off a board with arms straight up...Ch. 10 - A large turntable rotates about a fixed vertical...Ch. 10 - A large wooden turntable in the shape of a flat...Ch. 10 - Which of the objects shown in Figure 10.55 are in...Ch. 10 - (a) In each of the objects in Figure 10.56, what...Ch. 10 - Prob. 36PCh. 10 - Prob. 37PCh. 10 - Prob. 38PCh. 10 - Prob. 39PCh. 10 - Prob. 40PCh. 10 - The horizontal beam in Figure 10.60 weighs 150 N,...Ch. 10 - The boom in Figure 10.61 weighs 2600 N and is...Ch. 10 - A uniform ladder 7.0 m long weighing 450 N rests...Ch. 10 - A 9.0 m uniform beam is hinged to a vertical wall...Ch. 10 - A uniform beam 4.0 m long and weighing 2500 N...Ch. 10 - A diving board 3.00 m long is supported at a point...Ch. 10 - Two people carry a heavy electric motor by placing...Ch. 10 - Pumping iron. A 72.0 kg weightlifter is doing arm...Ch. 10 - The deltoid muscle. The deltoid muscle is the main...Ch. 10 - The rotor (flywheel) of a toy gyroscope has a mass...Ch. 10 - For each of the following rotating objects,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 52GPCh. 10 - A good workout. You are doing exercises on a...Ch. 10 - Prior to being placed in its hole, a 5700 N,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 55GPCh. 10 - One end of a 1.2-m-long beam is hinged to a...Ch. 10 - The farmyard gate. A gate 4.00 m wide and 2.00 m...Ch. 10 - 58. Atwoods machine. Figure 10.72 illustrates an...Ch. 10 - Prob. 59GPCh. 10 - The forces on the foot. A 750 N athlete standing...Ch. 10 - A uniform solid cylinder of mass M is supported on...Ch. 10 - Prob. 62GPCh. 10 - You are trying to raise a bicycle wheel of mass m...Ch. 10 - An experimental bicycle wheel is placed on a test...Ch. 10 - Prob. 65GPCh. 10 - Disks A and B are mounted on shaft SS and may be...Ch. 10 - One end of a thin, uniform rod is connected to a...Ch. 10 - A uniform, 7.5-m-long beam weighing 9000 N is...Ch. 10 - Human moment of inertia. The moment of inertia of...Ch. 10 - While the turntable is being accelerated, the...Ch. 10 - A doubling of the torque produces a greater...Ch. 10 - If the bodys center of mass were not placed on the...Ch. 10 - Torques and tug-of-war. In a study of the...Ch. 10 - If the competitor leans slightly farther back...Ch. 10 - Torques and tug-of-war. In a study of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
28.1 Rigid Bodies; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u_LAfG5uIpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY