
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals combine to form new hybridized orbitals which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization is also an expansion of the
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.57QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
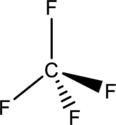
The
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as
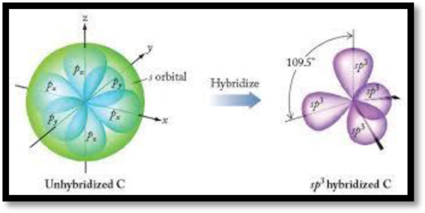
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.57QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
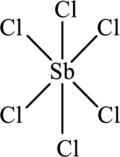
The
The
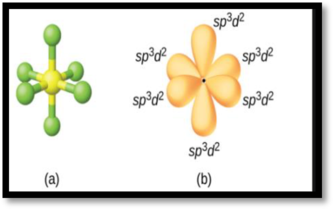
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.57QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
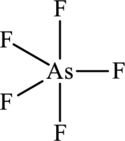
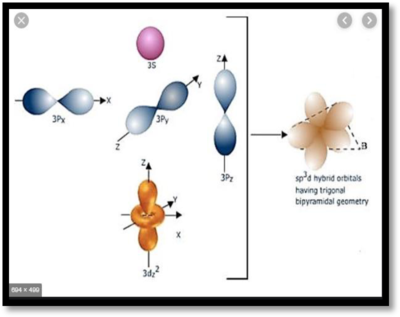
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 10.57QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
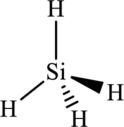
The
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as
(e)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem 10.57QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
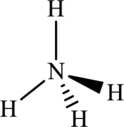
The
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Describe the hybridization around the central atom and the bonding in SCl2 and OCS.arrow_forwardAcrylonitrile, C3H3N is the building mer Orlon. Its Lewis structure is What is the hybridization of nitrogen and of the three numbered carbon atoms?arrow_forwardIdentify the hybrid orbitals used by boron in BCl3 and in BCl4, the ion formed from the reaction of BCl3 and Cl. Explain your choices.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





