
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in NF3 have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals combine to form new hybridized orbitals which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization is also an expansion of the
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.58QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in NF3 is sp3.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of NF3 is,
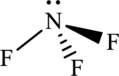
The NF3 have four electron domains and three of them are in bonding which means that the geometry of NF3 is trigonal pyramidal. The trigonal pyramidal geometry around the N means that it has sp3. hybrid orbitals on N atom.
The sp3 hybridization:
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as sp3 hybridization.
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in SCl2 have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.58QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in SCl2 is sp3.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of SCl2 is,
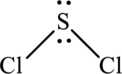
SCl2 have four electron domains and two of them are in bonding which means that the geometry of SCl2 is bent shape. The bent shape geometry around the S means that it has sp3 hybrid orbitals on S atom.
The sp3 hybridization:
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as sp3 hybridization.
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in H3O+ have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.58QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in H3O+ is sp3.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of H3O+ is,
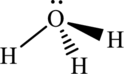
The H3O+ have four electron domains and three of them are in bonding which means that the geometry of H3O+ is trigonal pyramidal. The trigonal pyramidal geometry around the O means that it has sp3 hybrid orbitals on O atom.
The sp3 hybridization:
The process of mixing and rearrangement of one s and three p orbitals of valence shell of same atom to form new four hybrid orbitals having maximum symmetry and definite orientation is known as sp3 hybridization.
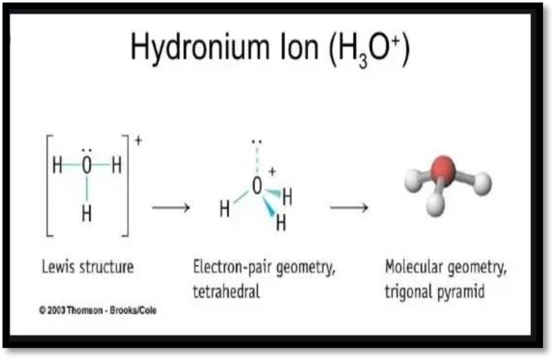
Figure 1
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in IF5 have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 10.58QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in IF5 is sp3d2.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of IF5 is,
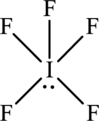
The IF5 have six electron domains and five of them are in bonding which means that the geometry of IF5 is square pyramidal. The Square pyramidal geometry around the iodine means that it has sp3d2. hybrid orbitals on iodine atom.
The sp3d2 hybridization:
The sp3d2 hybridization has 1s, 3p and 2d orbitals they undergo intermixing to form 6 identical sp3d2 hybrid orbitals. These 6 orbitals are directed towards the corners of an octahedron.
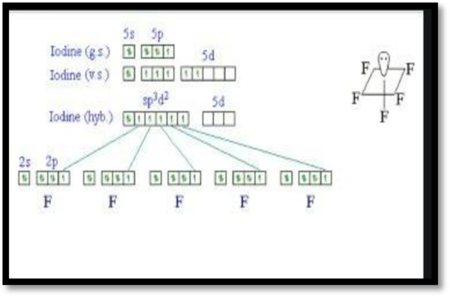
Figure 2
(f)
Interpretation:
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in SCl4 have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(f)
Answer to Problem 10.58QE
The hybrid orbitals on the central atom that form bond in SCl4 is sp3d.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of SCl4 is,
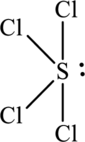
SCl4 have five electron domains and four of them are in bonding which means that the geometry of SCl4 is see-saw. The see-saw geometry around the sulphur means that it has sp3d hybrid orbitals on chlorine atom.
The sp3d hybridization:
The combination of 1s, 3p and 1d orbital result in the formation of sp3d orbital in which three lobes are oriented towards the corners of a triangle and the other lie perpendicular to them to minimize the repulsions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- 3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forwardConcentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forwardDraw the condensed or line-angle structure for an alkene with the formula C5H10. Note: Avoid selecting cis-/trans- isomers in this exercise. Draw two additional condensed or line-angle structures for alkenes with the formula C5H10. Record the name of the isomers in Data Table 1. Repeat steps for 2 cyclic isomers of C5H10arrow_forward
- Explain why the following names of the structures are incorrect. CH2CH3 CH3-C=CH-CH2-CH3 a. 2-ethyl-2-pentene CH3 | CH3-CH-CH2-CH=CH2 b. 2-methyl-4-pentenearrow_forwardDraw the line-angle formula of cis-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene. Then, draw the line-angle formula of trans-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene below. Draw the dash-wedge formula of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. Then, draw the dash-wedge formula of trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane below.arrow_forwardRecord the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. Dicyclopentadiene measured in volume Cyclopentadiene measured in grams 0 Measured Calculated Mol Yield Mass (g) or Volume (mL) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) 0.6 2.955 Part 2 Measurements and Results Record the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. 0.588 0.0044 2.868 0.0434 N/A Table view List view Measured Calculated Mol $ Yield Melting Point (C) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) Mass (g) or Volume (ml.) Cyclopentadiene 0.1 0.08 0.001189 measured in volume Maleic Anhydride 0.196 N/A cis-norbornene-5,6-endo- dicarboxylic anhydride 0.041 0.0002467 N/A N/A N/A 0.002 N/A N/A 128arrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structural formula and line-angle formula for each: 2,3-dimethylheptane 3-bromo-2-pentanol 3-isopropyl-2-hexene 4-chlorobutanoic acidarrow_forwardRecord the IUPAC names for each of the structures shown below. a) b) c) OH d) OH e)arrow_forwardA solution of 14 g of a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte compound in 0.10 kg of benzene boils at 81.7°C. If the BP of pure benzene is 80.2°C and the K, of benzene is 2.53°C/m, calculate the molar mass of the unknown compound. AT₁ = Km (14)arrow_forward
- Please help me answer the following questions. My answers weren't good enough. Need to know whyy the following chemicals were not used in this experiment related to the melting points and kf values. For lab notebook not a graded assignments.arrow_forwardDraw the arrow pushing reaction mechanism. DO NOT ANSWER IF YOU WONT DRAW IT. Do not use chat gpt.arrow_forwardComplete the following esterification reaction by drawing the structural formula of the product formed. HOH HO i catalyst catalyst OH HO (product has rum flavor) (product has orange flavor)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





