
Concept explainers
Regression, activity-based costing, choosing cost drivers. Sleep Late, a large hotel chain, has been using activity-based costing to determine the cost of a night’s stay at their hotels. One of the activities, “Inspection,” occurs after a customer has checked out of a hotel room. Sleep Late inspects every 10th room and has been using “number of rooms inspected” as the cost driver for inspection costs. A significant component of inspection costs is the cost of the supplies used in each inspection.
Mary Adams, the chief inspector, is wondering whether inspection labor-hours might be a better cost driver for inspection costs. Mary gathers information for weekly inspection costs, rooms inspected, and inspection labor-hours as follows:
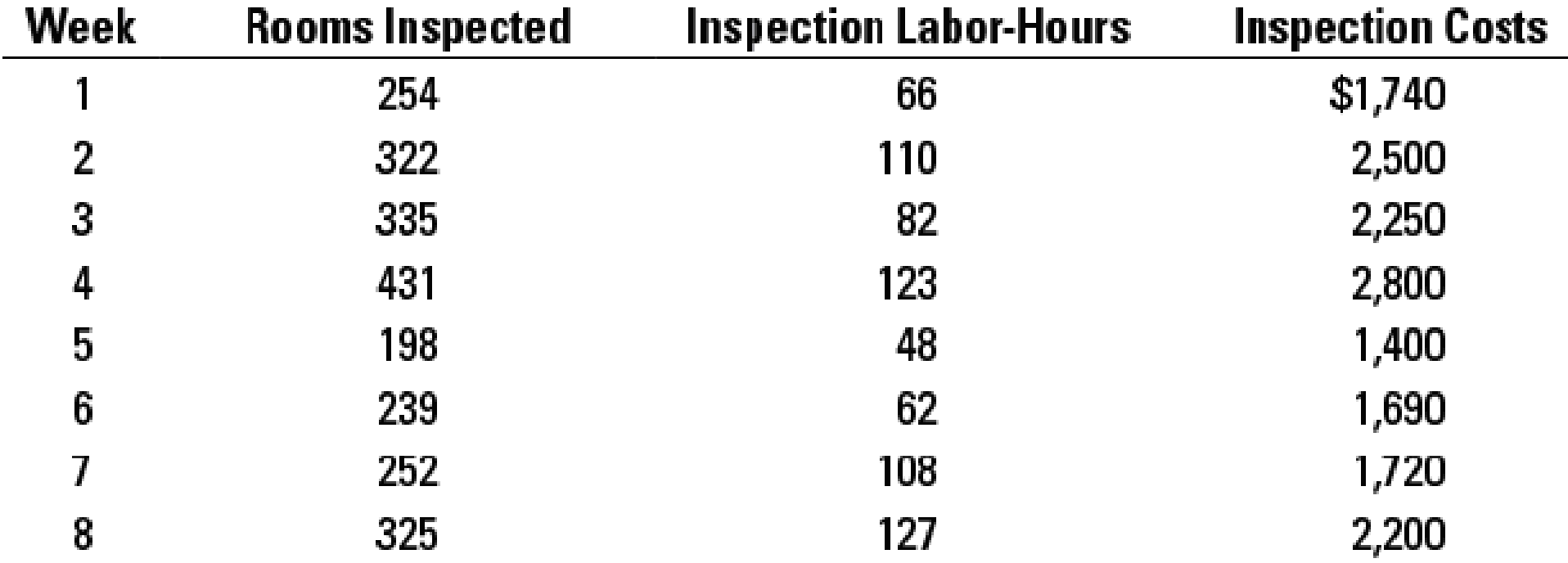
Mary runs regressions on each of the possible cost drivers and estimates these cost functions:
- 1. Explain why rooms inspected and inspection labor-hours are plausible cost drivers of inspection costs.
Required
- 2. Plot the data and regression line for rooms inspected and inspection costs. Plot the data and regression line for inspection labor-hours and inspection costs. Which cost driver of inspection costs would you choose? Explain.
- 3. Mary expects inspectors to inspect 300 rooms and work for 105 hours next week. Using the cost driver you chose in requirement 2, what amount of inspection costs should Mary budget? Explain any implications of Mary choosing the cost driver you did not choose in requirement 2 to budget inspection costs.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 10 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Managerial Chapters (6th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Financial Accounting (11th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (4th Edition)
- Elmo Security Consultants (ESC) offer a standardized review of data security for small business owners. The following data apply to the provision of these reviews: Sales price per unit (1 unit 1 review with recommendations) Fixed costs (per month): Selling and administration Production overhead (e.g., rent of facilities) Variable costs (per review): Labor for oversight and feedback Outsourced security analysis Materials used in reviews Review overhead Selling and administration (e.g., scheduling and billing) Number of reviews per month a Variable review (production) cost per unit b. Variable total cost per unit Required: Calculate the amount for each of the following (one unit = one review) if the number of reviews is 2,500 per month. Also calculate if the number of reviews decreases to 2,000 per month. c. Full cost per unit d. Full absorption cost per unit e. Prime cost per unit f. Conversion cost per unit g Contribution margin per unit h. Gross margin per unit 2,500 Reviews $ 500…arrow_forwardElmo Security Consultants (ESC) offer a standardized review of data security for small business owners. The following data apply to the provision of these reviews: Sales price per unit (1 unit = 1 review with recommendations) Fixed costs (per month): Selling and administration Production overhead (e.g., rent of facilities) Variable costs (per review): Labor for oversight and feedback Outsourced security analysis Materials used in reviews Review overhead Selling and administration (e.g., scheduling and billing) Number of reviews per month Required: a. Variable review (production) cost per unit b. Variable total cost per unit c. Full cost per unit d. Full absorption cost per unit e. Prime cost per unit f. Conversion cost per unit Calculate the amount for each of the following (one unit = one review) if the number of reviews is 2,500 per month. Also calculate if the number of reviews decreases to 2,000 per month. g. Contribution margin per unit h. Gross margin per unit 2,500 Reviews $ 500…arrow_forwardElmo Security Consultants (ESC) offer a standardized review of data security for small business owners. The following data apply to the provision of these reviews: Sales price per unit (1 unit = 1 review with recommendations) Fixed costs (per month): Selling and administration Production overhead (e.g., rent of facilities) Variable costs (per review): Labor for oversight and feedback Outsourced security analysis Materials used in reviews Review overhead Selling and administration (e.g., scheduling and billing) Number of reviews per month Required: d. Full absorption cost per uni! e. Prime cost per unit t Conversion cost per unit 9. Contribution margin per unit h. Gross margin per uni! 2,500 Reviews $ 508 50,000 70,000 Calculate the amount for each of the following (one unit = one review) if the number of reviews is 2.500 per month. Also calculate if the number of reviews decreases to 2,000 per month. 2,000 Reviews 250 43 10 28 38 2,508 reviewsarrow_forward
- Garrell Corporation is conducting a time-driven activity-based costing study in its Customer Support Department. The company has provided the following data to aid in that study: Time-driven activity rate (cost per unit of activity) Activity cost pool: Receiving Calls Resolving Issues Settling Disputes Cost Object Data: Number of calls received Number of issues resolved Number of disputes settled Customer P 31 17 1 $5.46 $8.58 $13.26 Customer Q 21 10 Required: Using time-driven activity-based costing, determine the total Customer Support Department cost assigned to cach customer.arrow_forwardUsing variable costing, service company Henry’s Helpers provides locksmith services. One type of service call is to evaluate private residences for security concerns and make recommendations for Safety plan. Use the data below to determine the company’s total contribution margin, contribution margin per service call, and contribution margin ratio when 220 service calls are made in the month of June.arrow_forwardMethod of Least Squares, Predicting Cost for Different Time Periods from the One Used to Develop a Cost Formula Refer to the information for Farnsworth Company on the previous page. However, assume that Tracy has used the method of least squares on the receiving data and has gotten the following results: Required: 1. Using the results from the method of least squares, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. 2. Using the formula from Requirement 1, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a month in which 1,450 receiving orders are processed? (Note: Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) 3. Prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity for a quarter. Based on this formula, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a quarter in which 4,650 receiving orders are anticipated? Prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity for a year. Based on this formula, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a year in which 18,000 receiving orders are anticipated?arrow_forward
- Assign the customer-related activity costs to each customer type using activity rates. Now calculate the profitability of each customer category. As a manager, how would you use this information? Emery Company sells small machine parts to heavy equipment manufacturers for an average price of 1.05 per part. There are two types of customers: those who place small, frequent orders and those who place larger, less frequent orders. Each time an order is placed and processed, a setup is required. Scheduling is also needed to coordinate the many different orders that come in and place demands on the plants manufacturing resources. Emery also inspects a sample of the products each time a batch is produced to ensure that the customers specifications have been met Inspection takes essentially the same time regardless of the type of part being produced. Emerys Cost Accounting Department has provided the following budgeted data for customer-related activities and costs (the amounts expected for the coming year): Required: 1. Assign the customer-related activity costs to each category of customers in proportion to the sales revenue earned by each customer type. Calculate the profitability of each customer type. Discuss the problems with this measure of customer profitability.arrow_forwardVentana Window and Wall Treatments Company provides draperies, shades, and various window treatments. Ventana works with the customer to design the appropriate window treatment, places the order, and installs the finished product. Direct materials and direct labor costs are easy to trace to the jobs. Ventanas income statement for last year is as follows: Ventana wants to find a markup on cost of goods sold that will allow them to earn about the same amount of profit on each job as was earned last year. Required: 1. What is the markup on cost of goods sold (COGS) that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) 2. A customer orders draperies and shades for a remodeling job. The job will have the following costs: What is the price that Ventana will quote given the markup percentage calculated in Requirement 1? (Round the price to the nearest dollar.) 3. What if Ventana wants to calculate a markup on direct materials cost, since it is the largest cost of doing business? What is the markup on direct materials cost that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) What is the bid price Ventana will use for the job given in Requirement 2 if the markup percentage is calculated on the basis of direct materials cost? (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardDeMarco Company is developing a cost formula for its packing activity. Discussion with the workers in the Packing Department has revealed that packing costs are associated with the number of customer orders, the size of the orders, and the relative fragility of the items (more fragile items must be specially wrapped in bubble wrap and Styrofoam). Data for the past 20 months have been gathered: Required: 1. Using the method of least squares, run a regression using the number of orders as the independent variable. 2. Run a multiple regression using three independent variables: the number of orders, the weight of orders, and the number of fragile items. Which regression equation is better? Why? 3. Predict the total packing cost for 25,000 orders, weighing 40,000 pounds, with 4,000 fragile items.arrow_forward
- Scattergraph, High-Low Method, and Predicting Cost for a Different Time Period from the One Used to Develop a Cost Formula Refer to the information for Farnsworth Company on the previous page. Required: 1. Prepare a scattergraph based on the 10 months of data. Does the relationship appear to be linear? 2. Using the high-low method, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. Using this formula, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a month in which 1,450 receiving orders are processed? 3. Prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity for a quarter. Based on this formula, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a quarter in which 4,650 receiving orders are anticipated? Prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity for a year. Based on this formula, what is the predicted cost of receiving for a year in which 18,000 receiving orders are anticipated? Use the following information for Problems 3-60 and 3-61: Farnsworth Company has gathered data on its overhead activities and associated costs for the past 10 months. Tracy Heppler, a member of the controllers department, has convinced management that overhead costs can be better estimated and controlled if the fixed and variable components of each overhead activity are known. One such activity is receiving raw materials (unloading incoming goods, counting goods, and inspecting goods), which she believes is driven by the number of receiving orders. Ten months of data have been gathered for the receiving activity and are as follows:arrow_forwardClassify each cost as being either variable or fixed with respect to the number of units produced and sold. Also classify each cost as either a period or a product cost. Predicting Cost Preparing Behavior Statements Cost Item 1. Hamburger buns in a Wendy's restaurant. 2. Advertising by a dental office. 3. Apples processed and canned by 4. Shipping canned apples from a Del Monte plant to customers. 5. Insurance on a Bausch & Lomb factory producing contact lensesarrow_forwardDropping a customer, activity-based costing, ethics. Justin Anders is the management accountant for Carey Restaurant Supply (CRS). Sara Brinkley, the CRS sales manager, and Justin are meeting to discuss the profitability of one of the customers, Donnelly’s Pizza. Justin hands Sara the following analysis of Donnelly’s activity during the last quarter, taken from CRS’s activity-based costing system: Sara looks at the report and remarks, “I’m glad to see all my hard work is paying off with Donnelly’s. Sales have gone up 10% over the previous quarter!” Justin replies, “Increased sales are great, but I’m worried about Donnelly’s margin, Sara. We were showing a profit with Donnelly’s at the lower sales level, but now we’re showing a loss. Gross margin percentage this quarter was 40%, down five percentage points from the prior quarter. I’m afraid that corporate will push hard to drop them as a customer if things don’t turn around.” “That’s crazy,” Sara responds. “A lot of that overhead for…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning


