
Concept explainers
Purchasing department cost drivers, activity-based costing, simple regression analysis. Perfect Fit operates a chain of 10 retail department stores. Each department store makes its own purchasing decisions. Carl Hart, assistant to the president of Perfect Fit, is interested in better understanding the drivers of purchasing department costs. For many years, Perfect Fit has allocated purchasing department costs to products on the basis of the dollar value of merchandise purchased. A $100 item is allocated 10 times as many
Hart recently attended a seminar titled “Cost Drivers in the Retail Industry.” In a presentation at the seminar, Kaliko Fabrics, a leading competitor that has implemented activity-based costing, reported number of purchase orders and number of suppliers to be the two most important cost drivers of purchasing department costs. The dollar value of merchandise purchased in each purchase order was not found to be a significant cost driver. Hart interviewed several members of the purchasing department at the Perfect Fit store in Miami. They believed that Kaliko Fabrics’ conclusions also applied to their purchasing department.
Hart collects the following data for the most recent year for Perfect Fit’s 10 retail department stores:
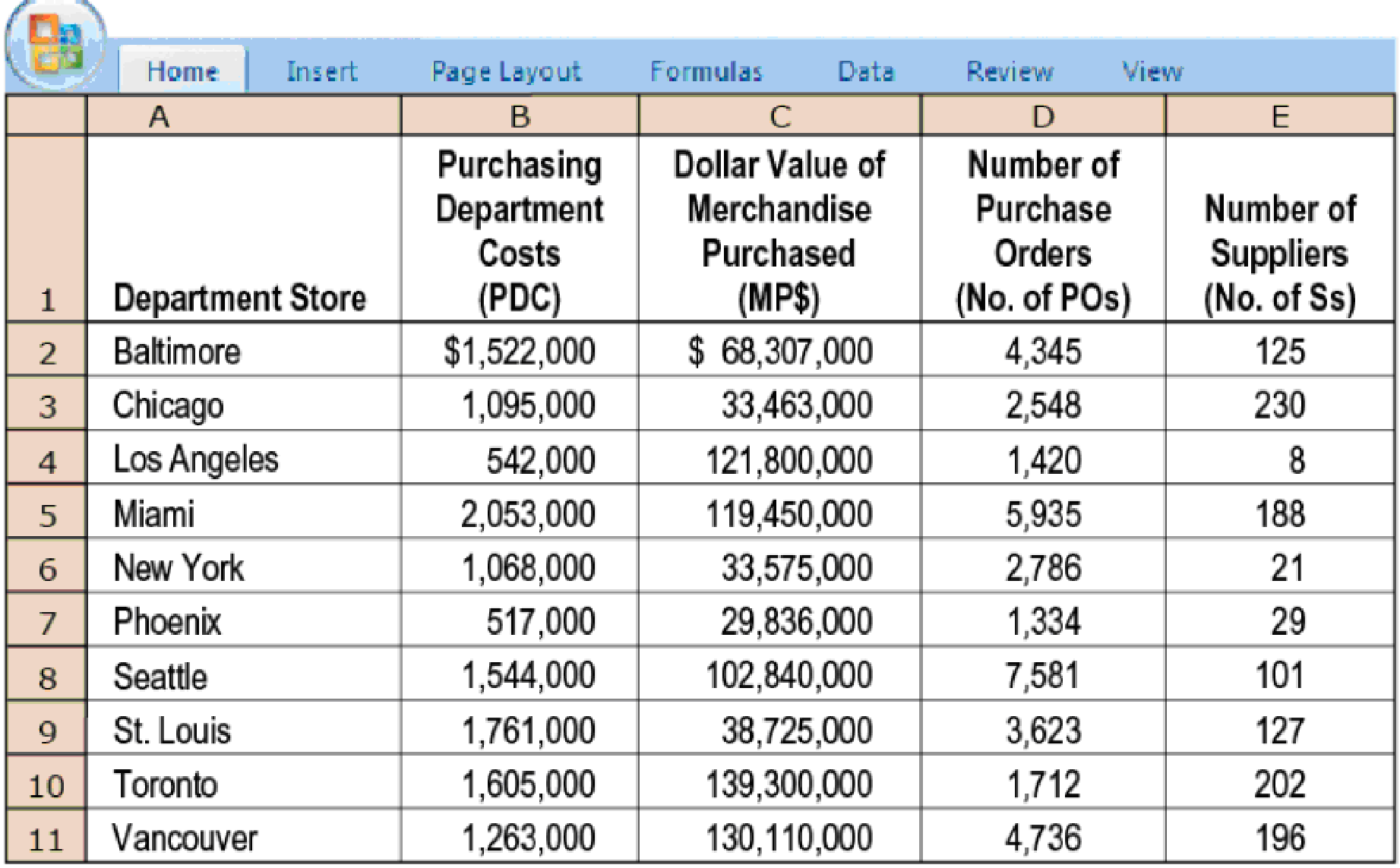
Hart decides to use simple regression analysis to examine whether one or more of three variables (the last three columns in the table) are cost drivers of purchasing department costs. Summary results for these regressions are as follows:
Regression 1: PDC = a + (b × MP$)

Regression 2: PDC = a + (b × No. of POs)
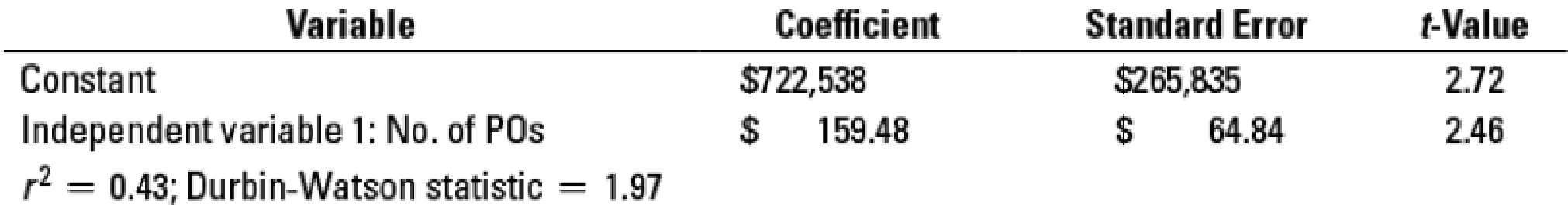
Regression 3: PDC = a + (b × No. of Ss)
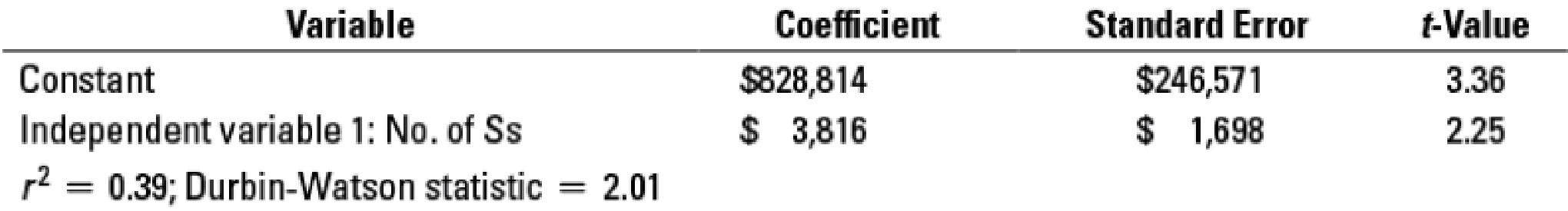
- 1. Compare and evaluate the three simple regression models estimated by Hart. Graph each one. Also, use the format employed in Figure 10-18 (page 406) to evaluate the information.
- 2. Do the regression results support the Kaliko Fabrics’ presentation about the purchasing department’s cost drivers? Which of these cost drivers would you recommend in designing an ABC system?
- 3. How might Hart gain additional evidence on drivers of purchasing department costs at each of Perfect Fit’s stores?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- The Chocolate Baker specializes in chocolate baked goods. The firm has long assessed the profitability of a product line by comparing revenues to the cost of goods sold. However, Barry White, the firms new accountant, wants to use an activity-based costing system that takes into consideration the cost of the delivery person. Following are activity and cost information relating to two of Chocolate Bakers major products: Using activity-based costing, which of the following statements is correct? a. The muffins are 2,000 more profitable. b. The cheesecakes are 75 more profitable. c. The muffins are 1,925 more profitable. d. The muffins have a higher profitability as a percentage of sales and, therefore, are more advantageous.arrow_forwardThe controller of Emery, Inc. has computed quality costs as a percentage of sales for the past 5 years (20X1 was the first year the company implemented a quality improvement program). This information is as follows: Required: 1. Prepare a trend graph for total quality costs. Comment on what the graph has to say about the success of the quality improvement program. 2. Prepare a graph that shows the trend for each quality cost category. What does the graph have to say about the success of the quality improvement program? Does this graph supply more insight than the total cost trend graph does? 3. Prepare a graph that compares the trend in relative control costs versus relative failure costs. Comment on the significance of this trend.arrow_forwardBig Mikes, a large hardware store, has gathered data on its overhead activities and associated costs for the past 10 months. Nizam Sanjay, a member of the controllers department, believes that overhead activities and costs should be classified into groups that have the same driver. He has decided that unloading incoming goods, counting goods, and inspecting goods can be grouped together as a more general receiving activity, since these three activities are all driven by the number of receiving orders. The 10 months of data shown below have been gathered for the receiving activity. Required: 1. Prepare a scattergraph, plotting the receiving costs against the number of purchase orders. Use the vertical axis for costs and the horizontal axis for orders. 2. Select two points that make the best fit, and compute a cost formula for receiving costs. 3. Using the high-low method, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. 4. Using the method of least squares, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. What is the coefficient of determination?arrow_forward
- Ventana Window and Wall Treatments Company provides draperies, shades, and various window treatments. Ventana works with the customer to design the appropriate window treatment, places the order, and installs the finished product. Direct materials and direct labor costs are easy to trace to the jobs. Ventanas income statement for last year is as follows: Ventana wants to find a markup on cost of goods sold that will allow them to earn about the same amount of profit on each job as was earned last year. Required: 1. What is the markup on cost of goods sold (COGS) that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) 2. A customer orders draperies and shades for a remodeling job. The job will have the following costs: What is the price that Ventana will quote given the markup percentage calculated in Requirement 1? (Round the price to the nearest dollar.) 3. What if Ventana wants to calculate a markup on direct materials cost, since it is the largest cost of doing business? What is the markup on direct materials cost that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) What is the bid price Ventana will use for the job given in Requirement 2 if the markup percentage is calculated on the basis of direct materials cost? (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardThe Chocolate Baker specializes in chocolate baked goods. The firm has long assessed the profitability of a product line by comparing revenues to the cost of goods sold. However, Barry Love, the firm’s new accountant, wants to use an activity-based costing system that takes into consideration the cost of the delivery person. Listed below are activity and cost information relating to two of Chocolate Baker’s major products. Muffins Cheesecake Revenue $53,000 $46,000 Cost of goods sold 26,000 21,000 Delivery activity: Number of deliveries 150 85 Average length of delivery 10 minutes 15 minutes Cost per hour for delivery $20.00 $20.00 Using activity-based costing, which one of the following statements is correct? A. The cheesecakes are $75 more profitable. B. The muffins have a higher profitability as a percentage of sales and therefore are more advantageous. C. The muffins are $2,000 more…arrow_forwardRupert’s Appliance Warehouse (RAW) delivers appliances to retailers throughout the city. The firm adds 6 percent to the cost of the appliances to cover the delivery cost. The delivery fee is meant to cover the cost of delivery. The finance team at RAW has analyzed the delivery service using activity-based costing methods and identified four activities. Data on these activities follow: Activity Cost Driver Activity Cost Cost Driver Volume Processing order Number of orders $ 84,000 6,000 orders Loading truck Number of items 290,000 145,000 items Delivering order Number of orders 102,000 6,000 orders Billing Number of invoices 85,000 5,000 invoices Total overhead $ 561,000 Two of Rupert's customers are McLean Designs and Neveux Appliances. Data for orders and deliveries to these two customers follow: McLean Designs Neveux Appliances Order value (total) $ 86,000 $ 96,000 Number of orders 66 236 Total number of items 900 1,600 Number of invoices 14 180…arrow_forward
- You are working as a manager accountant for a retail company which markets and sells two products product 1 and product 2. The following information is available for last year. The actual fixed product overheads for the same period were 95000 and fixed administration overheads were 25000. a) Please develop both marginal costing and absorption costing income statements. b) elaborate the findings, key advantages and limitations. Please donot provide solution in image format provide solution in step by step format and fast solutionarrow_forwardRupert’s Appliance Warehouse (RAW) delivers appliances to retailers throughout the city. The firm adds 6 percent to the cost of the appliances to cover the delivery cost. The delivery fee is meant to cover the cost of delivery. The finance team at RAW has analyzed the delivery service using activity-based costing methods and identified four activities. Data on these activities follow: Activity Cost Driver Activity Cost Cost Driver Volume Processing order Number of orders $ 70,000 5,000 orders Loading truck Number of items 105,000 75,000 items Delivering order Number of orders 85,000 5,000 orders Billing Number of invoices 68,000 4,000 invoices Total overhead $ 328,000 Two of Rupert's customers are McLean Designs and Neveux Appliances. Data for orders and deliveries to these two customers follow: McLean Designs Neveux Appliances Order value (total) $ 72,000 $ 82,000 Number of orders 52 96 Total number of items 510 1,200 Number of invoices 12 90…arrow_forwardR.p Within a company there is a (micro)economy that is monitored by the accounting procedures. In terms of the accounts, the various departments "produce" costs, some of which are internal and some of which are direct costs. This problem shows how an open Leontief model can be used to determine departmental costs. The sales department of an auto dealership charges 10% of its total monthly costs to the service department, and the service department charges 20% of its total monthly costs to the sales department. During a given month, the direct costs are $68,600 for sales and $49,000 for service. Find the total costs of each department. (Round your answers to the nearest whole number.) sales department $service department $arrow_forward
- Within a company is a (micro)economy that is monitored by the accounting procedures. In terms of the accounts, the various departments "produce" costs, some of which are internal and some of which are direct costs. This problem shows how an open Leontief model can be used to determine departmental costs. The sales department of an auto dealership charges 10% of its total monthly costs to the service department, and the service department charges 20% of its total monthly costs to the sales department. During a given month, the direct costs are $88,200 for sales and $29,400 for service. Find the total costs (in dollars) of each department. (Round your answers to the nearest whole number.) sales department $ service department $arrow_forwardSoft Cushion Company is highly decentralized. Each division is empowered to make its own sales decisions. The Assembly Division can purchase stuffing, a key component, from the Production Division or from external suppliers. The Production Division has been the major supplier of stuffing in recent years. The Assembly Division has announced that two external suppliers will be used to purchase the stuffing at $26per pound for the next year. The Production Division recently increased its unit price to $54.The manager of the Production Division presented the following information — variable cost $38 and fixed cost $14 — to top management in order to attempt to force the Assembly Division to purchase the stuffing internally. The Assembly Division purchases 21,000 pounds of stuffing per month. What would be the monthly operating advantage (disadvantage) of purchasing the goods internally, assuming the external supplier increased its price to $88 per pound and the Production Division…arrow_forwardManagement would like an analysis of the profitability of a particular customer, Cell City, which has ordered the following products over the last 12 months: Number of cases Number of orders. Direct labour-hours per case Selling price per case. Direct materials cost per case Sales Costs: Direct materials Direct labour Supporting manufacturing Order processing Customer service The company's direct labour rate is $30 per hour. Required: Using the company's ABC system, compute the customer margin of Cell City. Customer margin Standard Model 290 5 0.25 $49 $ 26 70 Deluxe Model 105 2 $ 0.40 $ 69 $29 70 (70)arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




