
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is a convenient way to convey information such as which atoms are bonded to each other by which type of bond. Only valence electrons take part to draw Lewis structure.
Valence electrons that participate in bond formation are called bonding electron pairs whereas electrons that do not take part in bonding and that remain as non-bonding electrons are termed as lone pair of electrons.
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count of each atom in the molecule. Skeleton structure for the given molecule is drawn with atoms bonded with a single bond, the central atom is always less electronegative atom. Electrons that participate in forming the bond are bonding electrons. Remaining electrons are distributed first to outer atoms such that each atom completes its octet other than hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 1.44P
Lewis structure for
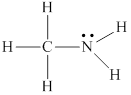
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule
Thus the skeleton structure for
Remaining two valence electrons are contributed as lone pair of electrons to the outer atom which is nitrogen.
Hence the complete Lewis structure for

Lewis structure for
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count of each atom in the molecule. Skeleton structure for the given molecule is drawn with atoms bonded with a single bond, the central atom is always less electronegative atom. Electrons that participate in forming the bond are bonding electrons. Remaining electrons are distributed first to outer atoms such that each atom complete its octet other than hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 1.44P
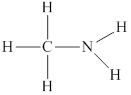
Lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
In
Remaining
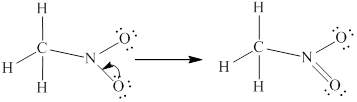
Lewis structure for
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count of each atom in the molecule. Valence electrons participate in bond formation are called bonding electron pairs whereas electrons that do not take part in bonding and that remain as non-bonding electrons are termed as lone pair of electrons. Skeleton structure for the given molecule is drawn with atoms bonded with a single bond, the central atom is always less electronegative atom.
Lone pair of electrons contributed to outer atoms to complete octet except hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 1.44P
The Lewis structure for
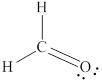
Explanation of Solution
Carbon is the central atom in
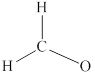
Remaining six electrons are contributed as lone pairs to the outer atom oxygen but one electron is involved in bonding with complete octet of oxygen atom.
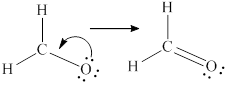
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count.
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count of each atom in the molecule. Skeleton structure for the given molecule is drawn with atoms bonded with a single bond, the central atom is always less electronegative atom. Electrons that participate in forming the bond are bonding electrons. Remaining electrons are distributed first to outer atoms such that each atom completes its octet other than hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 1.44P
Lewis structure for
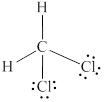
Explanation of Solution
In
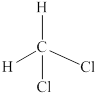
Eight electrons from total
Therefore the Lewis structure for

Lewis structure is drawn from total valence electron count.
(e)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is drawn from the total valence electron count of each atom in the molecule. Valence electrons that participate in bond formation are called bonding electron pairs whereas electrons that do not take part in bonding and that remain as non-bonding electrons are termed as lone pair of electrons. Skeleton structure for the given molecule is drawn with atoms bonded with a single bond, the central atom is always less electronegative atom.
Lone pair of electrons contributed to outer atoms to complete octet except hydrogen.
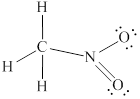
Answer to Problem 1.44P
Lewis structure for
![]()
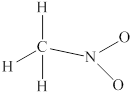
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule
![]()
Remaining
Hence the Lewis structure for
![]()
Lewis structure is drawn from total valence electron count.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Experiment 27 hates & Mechanisms of Reations Method I visual Clock Reaction A. Concentration effects on reaction Rates Iodine Run [I] mol/L [S₂082] | Time mo/L (SCC) 0.04 54.7 Log 1/ Time Temp Log [ ] 13,20] (time) / [I] 199 20.06 23.0 30.04 0.04 0.04 80.0 22.8 45 40.02 0.04 79.0 21.6 50.08 0.03 51.0 22.4 60-080-02 95.0 23.4 7 0.08 0-01 1970 23.4 8 0.08 0.04 16.1 22.6arrow_forward(15 pts) Consider the molecule B2H6. Generate a molecular orbital diagram but this time using a different approach that draws on your knowledge and ability to put concepts together. First use VSEPR or some other method to make sure you know the ground state structure of the molecule. Next, generate an MO diagram for BH2. Sketch the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs of the BH2 fragment. These are called frontier orbitals. Now use these frontier orbitals as your basis set for producing LGO's for B2H6. Since the BH2 frontier orbitals become the LGOS, you will have to think about what is in the middle of the molecule and treat its basis as well. Do you arrive at the same qualitative MO diagram as is discussed in the book? Sketch the new highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs for the molecule (B2H6).arrow_forwardQ8: Propose an efficient synthesis of cyclopentene from cyclopentane.arrow_forward
- Q7: Use compound A-D, design two different ways to synthesize E. Which way is preferred? Please explain. CH3I ONa NaOCH 3 A B C D E OCH3arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward(10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardQ3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forward
- Q5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardQ4: Circle the substrate that gives a single alkene product in a E2 elimination. CI CI Br Brarrow_forwardPlease calculate the chemical shift of each protonsarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
