
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
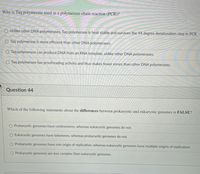
Transcribed Image Text:Why is Taq polymerase used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
O Unlike other DNA polymerases, Taq polymerase is heat stable and survives the 94 degree denaturation step in PCR.
Taq polymerase is more efficient than other DNA polymerases.
O Taq polymerase can produce DNA from an RNA template, unlike other DNA polymerases.
O Taq polymerase has proofreading activity and thus makes fewer errors than other DNA polymerases.
Question 44
Which of the following statements about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes is FALSE?
O Prokaryotic genomes have centromeres, whereas eukaryotic genomes do not.
O Eukaryotic genomes have telomeres, whereas prokaryotic genomes do not.
Prokaryotic genomes have one origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic genomes have multiple origins of replication.
O Prokaryotic genomes are less complex than eukaryotic genomes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Match each term with the correct letterarrow_forwardWhy are Gyrase inhibitors good antibiotics to use therapeutically? DNA Gyrase is required by prokaryotes, but not eukaryotes, to complete chromosomal replication so it's a good target to inhibit. O DNA Gyrase is required by eukaryotes, but not prokaryotes, to complete chromosomal replication so it's a good target to inhibit. It's impossible to develop resistance against Gyrase inhibitors so they are always effective. O DNA Gyrase is required by both prokaryotes and eukaryotes to complete chromosomal replication so it's a good target to inhibit.arrow_forwardWhich of the following steps is NOT part of a typical polymerase chain reaction? Choose an answer below: primer annealing ligation of DNA fragments by DNA ligase primer extension by DNA polymerase heat denaturation of double stranded DNA none of the abovearrow_forward
- In a Sanger sequencing reaction, the template DNA is shown below, with the short sequence on top as the primer: 5' ATG 3' 3' TACACTATCGCA 5' A reaction is carried out with the following components: primer, template, DNA polymerase, dNTPs, and ddGTP. Write out all the possible PCR products (label 5' and 3' end).arrow_forwardCan you please help explain which best describes the role of topoisomerase?arrow_forwardDNA polymerases can only add new dNTPs to a primer strand that is hydrogen-bonded to the template. True or falsearrow_forward
- Translesion synthesis (TLS) polymerase zeta (ζ) is capable of accurately reading through 6,4-photoproducts (cytotoxic damage). If this protein is non-functional: a different TLS polymerase will accurately read through the DNA lesion. a different TLS polymerase will inaccurately read through the DNA lesion resulting in increased mutational frequency. the replicative polymerase will inaccurately read through the DNA damage. DNA polymerase alpha (α) will be recruited to synthesize a primer across the DNA damage. the DNA lesion cannot be bypassed and will result in double stranded DNA breaks.arrow_forwardThe antibiotic Cipro (ciprofloxacin) inhibits DNA gyrase found in bacteria. Why would this stop bacteria from dividing? Group of answer choices 1. DNA polymerase I could not remove RNA primers 2. Helicase would not be able to fully unwind the replication bubble due to stress in the DNA 3. Okazaki fragments would come off of the newly replicated DNA dnaA would not bind to the OriC 4. DNA Polymerase III would be halted on only the lagging strandarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education