
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
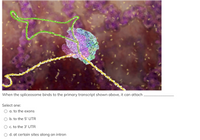
Transcribed Image Text:When the spliceosome binds to the primary transcript shown above, it can attach
Select one:
O a. to the exons
O b. to the 5' UTR
O c. to the 3' UTR
O d. at certain sites along an intron
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A principle function of 5' and 3' end modifications of eukaryotic mRNA is: a. to ensure that all nucleotides are phosphorylated b. to protect RNA from nucleolytic degradation c. to guide the removal of introns d. to serve as binding sites for translation release factorsarrow_forwardThe initiation factors a. help assembling both ribosomal subunits with mRNA and initiator tRNA b. help with the peptide bond formation c. help starting the translation elongation d. are responsible for the initiation of ribosome translocationarrow_forwarda. What is grey donut shaped object supposed to represent? b. Label with the word "promoter" where one might find the promoter region in this image. c. In the magnified insert, label the template strand that is being transcribed with the word "template". d. In the magnified insert label the 5' and 3' ends of the transcript. e. What entity functions to break the complementary base pairing of a gene at its transcription start site? CS Scanned with CamScannerarrow_forward
- In eukaryotes, why is the initial RNA transcript usually longer than the mature mRNA molecule? Group of answer choices Because a guanosine cap has to be removed Because exons have to be removed Because a poly-A tail has to be removed Because introns have to be removed Because the RNA primer has to be removedarrow_forwardFind the events from prokaryotic translation from the list below and list them below in order, by letter, from earliest to latest during translation A. Incoming tRNA occupies the A-site B. Small ribosome binds to Shine Dalgarno sequence C. 5’ methyl cap binds small ribosome D. Large ribosome subunit binds the small ribosome subunit E. P-site tRNA peptide is attached to the amino acid of the A-site tRNA. F. f-Met tRNA binds to P site G. Small ribosomal subunit binds mRNA H. Peptide released from complex.arrow_forwardDescribe three (3) ways in which the primary transcript is modified as it is converted to mRNA.arrow_forward
- Define (whether post-transcriptional, post-translational, transcription) and describe the regulation of the Ferretin mRNA in the diagram below.arrow_forward1. (a) By binding one L-tryptophan molecule/monomer, the trp repressor binds to DNA to sup- press synthesis of L-tryptophan in E. coli. Below is the amino acid sequence of the helix - reverse turn - helix region of the trp repressor that binds to DNA compared to the sequence of the corresponding DNA binding motif of the Prl protein. A diagram of the trp repressor dimer is also shown. Trp Prl Trp Prl 80 -Gly-Glu-Met-Ser-Gln-Arg-Glu-Leu-Lys-Asn-Glu-Leu-Gly-Ala-Gly-Ile- -Ser-Glu-Glu-Ala-Lys-Glu-Glu-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Cys-Gly-Ile-Thr-Val- trp helix 5 70 trp helix 4 Prl helix 80 Prl helix Ala-Thr-Ile-Thr-Arg-Gly-Ser-Asn-Ser-Leu-Lys-Ala-Ala- Ser-Gln-Val-Ser-Asn-Trp-Phe-Gly-Asn-Lys-Arg-Ile-Arg- reverse turn 90 Comparing the two protein sequences above, identify all amino acid pairs that differ in electrostatic charge due to proton dissociable groups (assume pH 7). Indicate the charge of both residues for each such pair. (b) Circle the pair of residues for which the electrostatic charge due to…arrow_forwardTranscription in prokaryotic cells O A. is initiated at a promoter and uses only one strand of DNA (the template strand) to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. B. occurs in the nucleus, whereas translation occurs in the cytoplasm. C. is terminated at a stop codon. D. does not need a promoter. O E. is initiated at a start codon with the help of initiation factors and the small subunit of the ribosome. 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education