
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
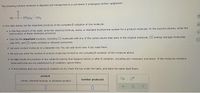
Transcribed Image Text:The following nutrient molecule is digested and transported to a cell where it undergoes further catabolism:
но
c-(CH;)14-CH3
di
In the table below, list the important products of the complete B oxidation of this molecule.
• In the first column of the table, write the chemical formula, name, or standard biochemical symbol for a product molecule. In the second column, write the
total number of these molecules produced.
• Only list the Important products, including (1) molecules with any of the carbon atoms that were in the original molecule, (2) energy storage molecules
(like ATP), and (3) newly oxidized or reduced coenzymes.
List each product molecule on a separate row. You can add more rows if you need them.
• Be sure you write the number of product molecules formed by the complete B oxidation of the molecule above.
• Do not include the products of any catabolic activity that happens before or after B oxidation, including any necessary activation. If the molecule contains
small parts that are not catabolized by B oxidation, ignore them.
• If the molecule does not undergo B oxidation at all, check the box under the table, and leave the table itself blank.
product
number produced
(name, chemical formula, or standard symbol)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q) You are following the metabolism of aspartate that is equally labeled on all 4 carbons. Following a transamination aspartate is converted into oxaloacetate. Assuming the resulting Oxaloacetate is used as the substrate for the TCA cycle answer the following questions: a) Describe ALL the oxaloacetate molecules that would result from the first turn of the TCA cycle. b) Briefly describe how there is still label detected on the carboxylic acids even though they were removed as CO2 during the first turn of the cycle. (2 sentences MAX)arrow_forwarda.) in human, under what condition will pyruvate be converted to lactate? what type of reaction occurs when pyruvate is converted to lactate? b.) in human, what happens to pyruvate when there is sufficient oxygen supply? which enzyme is involved in this chemical reaction?arrow_forwardWhich of the reactions are spontaneous (favorable)? C6H130,P + ATP → › C6H14º₁₂P2 + ADP AG = -14.2 kJ/mol L-malate + NAD+ → oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ AG = 29.7 kJ/mol glutamate + NAD+ + H₂O → NH‡ + α-ketoglutarate + NADH + H+ AG = 3.7 kcal/mol → CH2O4 + H2O AG = 3.1 kJ/mol * CąHẠO, — CH,O4 + H,O DHAP C₂H + H₂ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate AG = 3.8 kJ/mol Rh(I) C2H6 AG-150.97 kJ/molarrow_forward
- 1. (a) The reaction catalyzed by citrate synthase is the first step of the TCA cycle. In glycolysis, two key reactions to produce ATP occur because an unfavorable reaction is coupled to another reaction that is thermodynamically favorable. The reaction catalyzed by citrate synthase is similarly coupled to an unfavorable reaction in the TCA cycle. Write the unfavorable TCA reaction using structural formulas and write the key step that drives the two coupled reactions forward. What is the overall AG" of the coupled reactions? (b). K(yM) 25.7 Inhibitor Bromoacetyl-CoA ATP NADH 6800 8300 The inhibitor constants for three inhibitors of por- cine citrate synthase are summarized in the table on the right. The compounds were all determined to bind in the ac- tive site as competitive inhibitors of acetyl-CoA. Because they bind as competitive inhibitors, all three inhibitors must exhibit structural similarity to some part of acetyl-CoA. Look up in the textbook the structural formulas for…arrow_forward[methyl-14C]Pyruvate was administered to isolated liver cells in the presence of sufficient malonate to block succinate dehydrogenase completely. After a time, isocitrate was isolated and found to contain label in both carbon 2 and carbon 5: How do you explain this result?arrow_forwardE3 of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex performs which main function? A) removing a proton from TPP forming a carbanion b) catalyzing the condensation of the TPP carbanion with pyruvate to form hydroxyethyl-TPP c) oxidation and transfer of the hydroxyethyl group to lipoic acid d) reoxidation of lipoic acid in order to keep the reaction going Once acetyl-CoA is formed, it usually takes one of two paths. The first is further oxidation in the citric acid cycle. The second is: a) conversion to oxaloacetate which generates glucose by gluconeogenesis b) synthesis of galactose c) activates transcription factors which signal the synthesis of peptidase enzymes d) it is used in the synthesis of fatty acids.arrow_forward
- a. Arachidic acid is shown in the diagram below. How many rounds of β-oxidation will be needed to fully catabolize arachidic acid? b. What products will be obtained from the complete β-oxidation of arachidic acid? c. What will be the final ATP output (after TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation) obtained from the complete β-oxidation of arachidic acid?arrow_forward(b) The results in the table below were extracted from clinical reports of pediatric age infants (3 – 5 yr.) who had marked lactic acidosis, elevated blood ammonia, poor motor coordination, and showed mental retardation. From skin fibroblast cell cultures, enzyme assays were carried out, providing the results given below. PDH = pyruvate dehydrogenase; E1, E2, E3 signify the three enzyme activities of the PDH complex measured separately. It should be noted that measurement of the overall activity of the PDH complex employs a different assay system than those used for measurement of the activi- ties of the separate, individual component enzymes. Patient or PDH Complex activity nmol/min/mg protein Native E1 E2 Ез Control +dichloroacetate nmol/h/mg protein Patient 1 0.318 + 0.054 0.322 + 0.053 1.54 0.29 3.69 + 1.21 15.1 + 3.0 Patient 2 0.050 ± 0,031 0.044 + 0.027 0.21 + 0.06 6.5 ± 3.1 9.8 ± 1.3 Patient 3 0.092 + 0.022 0.068 + 0.037 0.21 + 0.06 8.48 13.5 + 2.0 Control 1 0.932 + 0.076 1.368…arrow_forwardYou have discovered an organism incapable of performing the full gluconeogenic pathway. Further analysis tells you these is no issue with glycolysis in this organism, no glucose ever leaves the cell once it enters, and the cell contains unusually large concentrations of the molecules shown below. Which gluconeogenic enzyme is missing/non-functional in this organism? Defend your answer in as much detail as possible and make sure you identify the two compounds accumulating in your answer.arrow_forward
- Below is an image of the Krebs cycle: acetyl-CoA oxaloacetate COASH H20 NADH NAD* H20 malate citrate fumarate isocitrate FADH2 NAD* CO2 FAD АТР NADH + ADP succinate GTP NAD+ a-ketoglutarate H20 GDP NADH + CO2 COASH succinyl CoA COASH Consider the conversion of succinate to fumarate, which is coupled with the production the electron carrier FADH2. If this reaction was NOT coupled with the production of FADH2 (and only catalyzed the conversion of succinate to fumarate), how would this impact ATP production through cell respiration? OATP production would stop because no high energy electron carriers would be produced ATP production would still occur, but there would be a much lower ATP yield because a large number of electron carriers are no longer being made ATP production would stop because without FADH2 we will no longer have electrons moving through the electron transport chain ATP production would still occur, but there would be a slightly lower ATP yield because a small number of…arrow_forwardWrite a balanced equation for the complete metabolic oxidation of each of the following. Include O, ADP, and P; as reactants and ATP, CO, and H;0 as products. (a) Stearic acid (b) Oleic acid (c) Palmitic acid (d) Linoleic acidarrow_forwardDetermine whether the following statements are true or false:- a) The pentose phosphate pathway of glucose conversion is a supplier of NADPH (H +) for reductive syntheses. b) An overdose of insulin causes hypoglycemia in a patient with diabetes mellitus. c) Fructose-6-phosphate is an allosteric regulator of glycolysis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON