
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Standard DM price per pound (Lbs): $20
Standard DM needed per unit: 2 Lbs
Standard DL rate: $15 per hour
Standard DL hours per unit: 2 hours of Direct Labor per unit
*The actual DM used for 11000 units of production is 24200 lbs which means:
24200 lbs / 11000 actual units produced = 2.2 lbs actual quantity of DM used per unit
Actual DL hours: 20000 hours
Variable
*Note: I am helping you here!
- AQ (AP-SP) = DM Price Variance
- (AQ x AP) - (AQ x SP) = -42000 Favorable (less spending for DM)
- $442,000 - (24200 x $20) = DM Price Variance
- 442,000 - 484,000 = DM Price Variance
- $42,000 Favorable DM Price Variance
please answer the following questions:
7. Variable overhead efficiency variance:
8. Variable overhead rate variance:
9. Total variable overhead:
10. Total fixed overhead spending variance:
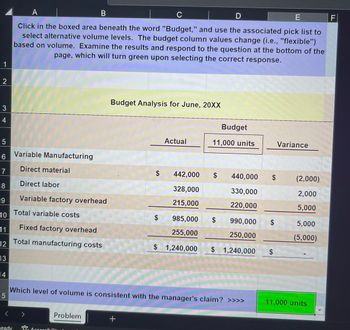
Transcribed Image Text:1
2
3
4
14
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 Fixed factory overhead
12 Total manufacturing costs
13
15
A
C
D
E
Click in the boxed area beneath the word "Budget," and use the associated pick list to
select alternative volume levels. The budget column values change (i.e., "flexible")
based on volume. Examine the results and respond to the question at the bottom of the
page, which will turn green upon selecting the correct response.
Ready
Variable Manufacturing
Direct material
Direct labor
Variable factory overhead
Total variable costs
B
Problem
Accessibilit
Budget Analysis for June, 20XX
+
Actual
$ 442,000
328,000
215,000
SA
11,000 units
SA
Budget
$
Which level of volume is consistent with the manager's claim? >>>>
440,000
330,000
220,000
985,000 $
990,000
255,000
250,000
$ 1,240,000 $ 1,240,000
$
SA
$
Variance
(2,000)
2,000
5,000
5,000
(5,000)
11,000 units
F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8. Given the following data, calculate product cost per unit under variable costing. Direct labor $7 per unit Direct materials $1 per unit Overhead Total variable overhead $20,000 Total fixed overhead $90,000 Expected units to be produced 40,000 units A. $8 per unit B. $8.50 per unit C. $10.25 per unit D. $10.75 per unit E. $12 per unitarrow_forwardFarrow Company reports the following annual results. Contribution Margin Income Statement Sales (200,000 units) Variable costs Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Contribution margin Fixed costs Fixed overhead Fixed general and administrative Income Per Unit $ 15.00 Annual Total $ 3,000,000 2.00 400,000 4.00 800,000 2.50 500,000 6.50 1,300,000 2.00 1.50 400,000 300,000 $ 3.00 $ 600,000 The company receives a special offer for 20,000 units at $13 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its normal sales. Variable costs per unit would be the same for the special offer as they are for the normal units. The special offer would require incremental fixed overhead of $80,000 and incremental fixed general and administrative costs of $86,000. (a) Compute the income or loss for the special offer. (b) Should the company accept or reject the special offer? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Compute the income or loss for the special…arrow_forwardSkolnick Corporation has provided the following information: Cost per Unit Direct materials $ 5.20 Direct labor $ 4.70 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 1.80 Cost per Period Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 126,000 Sales commissions $ 1.40 Variable administrative expense $ 0.60 Cost per Period Fixed selling and administrative expense $39,600 Selling price $20.6 per unit. The value of break-even point sales is:arrow_forward
- Total product cost per unit under absorption costing = Units produced = 1000Direct Materials = $ 6Direct Labor = $10Fixed overhead =$ 6000Variable overhead = $ 6Fixed Selling & Admin = $ 2000Variable Selling & Admin $ 2arrow_forwardThe standard costs and actual costs for factory overhead for the manufacture of 3,000 units of actual production are as follows: Standard Costs Fixed overhead (based on 10,000 hours) Variable overhead 3 hours per unit @ $0.78 per hour 3 hours per unit @ $2.00 per hour a. $0 b. $624 favorable O c. $780 unfavorable O d. $624 unfavorable Actual Costs Total variable cost, $18,000 Total fixed cost, $7,900 The amount of the fixed factory overhead volume variance isarrow_forwardTotal Amount Units Sales Variable Costs: 31,250 Per Unit $ 445,313 $ 14.25 Direct Materials $ 125,000 4.00 = Direct Labor $ 28,000 0.90 = Variable Manufacturing Overhead $ 66,250 2.12 = Sales Commissions $ 15,625 0.50 = Shipping Variable Billing Total Variable Costs $ 3,125 0.10 $ 313 0.01 $ 238,313 7.63 Contribution Margin $ 207,000 6.62 Fixed Costs: Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Advertising Sales and Admin. Salaries Fixed Billing Total Fixed Costs Net Operating Income (Loss) 40,000 16,800 87,300 10,000 154,100 $ 52,900 F. Using the budgeted contribution margin income statement in part E. above, calculate the following: a. Breakeven in units: b. Operating Leverage Multiplier: Given a sales volume increase of 8%, operating income will increase by: c. Percent: d. Dollars: #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/Aarrow_forward
- Sales price per unit. 51.00 Fixed costs (per month): Selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) 900,000 Manufacturing overhead 1,800,000 Variable costs (per unit): Direct labor 8.00 Direct materials 13.00 Manufacturing overhead 9.00 4.00 SG&A Number of units produced per month. 300,000 units Required: Compute the amounts for each of the following assuming that both production levels are within the relevant range. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 300,000 units 400,000 units a. Prime cost per unit. b. Contribution margin per unit. C. Gross margin per unit. d. Conversion cost per unit. e. Variable cost per unit. f. Full absorption cost per unit. g. Variable production cost per unit. h. Full cost per unit. $arrow_forwardCostingTo manufacture 500,000 TBS, the direct material cost per item is AED 120 and material scrap is estimated to be 3.5% of the material costs. The direct labour costs total AED 250,000 and the labour scrap rate is 3% of direct labour cost. The variable overheads are 75 - 80% of direct labour costs and the fixed overloads are 30 - 40% of the variable costs. Packaging, tooling and freight costs are 7.5% of manufacture costs. The company requires a profit of 45% to be successful. Calculate the selling price for one unit of TBS.arrow_forwardActivity Rates and Product Costs using Activity-Based Costing Lonsdale Inc. manufactures entry and dining room lighting fixtures. Five activities are used in manufacturing the fixtures. These activities and their associated budgeted activity costs and activity bases are as follows: Budgeted Activity Activity Cost Activity Base Casting $215,160 Machine hours Assembly 189,550 Direct labor hours Inspecting 30,520 Number of inspections Setup 39,730 Number of setups Materials handling 36,960 Number of loads Corporate records were obtained to estimate the amount of activity to be used by the two products. The estimated activity-base usage quantities and units produced follow: Activity Base Entry Dining Total Machine hours 5,180 4,600 9,780 Direct labor hours 4,460 6,690 11,150 Number of inspections 1,660 520 2,180 Number of setups 230 60 290 Number of loads 700 180 880 Units produced 10,400 5,200 15,600 a. Determine the activity rate for each activity. If required, round the rate to the…arrow_forward
- Three production processes - A, B, and C - have the following cost structure: the selling price is 5.26 per unit Process Fixed Cost per Year Variable Cost per Unit A 119164 2.54 B 80631 4.52 C 70617 5.27 1. What is the cost of process A for a volume of 7104 units? (round to the nearest cent).arrow_forwardGiven the following data, calculate product cost per unit under absorption costing. Direct labor Direct materials Variable overhead Fixed overhead Units produced per year Multiple Choice $28.00 per unit $28.60 per unit $30.00 per unit $30.90 per unit $ 17.00 per unit $ 11.00 per unit $ 0.90 per unit $ 100,000 50,000 unitsarrow_forwardFarrow Company reports the following annual results. Contribution Margin Income Statement Sales (420, 00 units) Variable costs Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Per Unit $ 15.00 Annual Total $ 6, 300, 000 2.00 4.00 2.50 840, 000 1,680, 000 1,050, 000 2,730, 000 Contribution margin Fixed costs Fixed overhead 6.50 2.00 840, 000 630, 000 Fixed general and administrative 1.50 Incone $ 3.00 $ 1, 260, 000 The company receives a special offer for 42,000 units at $12 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its normal sales. Variable costs per unit would be the same for the special offer as they are for the normal units. The special offer would require incremental fixed overhead of $168,000 and incremental fixed general and administrative costs of $181,000. (a) Compute the income or loss for the special offer. (b) Should the company accept or reject the special offer? ces Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Compute the income or…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education