
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Standard DM price per pound (Lbs): $20
Standard DM needed per unit: 2 Lbs
Standard DL rate: $15 per hour
Standard DL hours per unit: 2 hours of Direct Labor per unit
*The actual DM used for 11000 units of production is 24200 lbs which means:
24200 lbs / 11000 actual units produced = 2.2 lbs actual quantity of DM used per unit
Actual DL hours: 20000 hours
Variable
*Note: I am helping you here!
- AQ (AP-SP) = DM Price Variance
- (AQ x AP) - (AQ x SP) = -42000 Favorable (less spending for DM)
- $442,000 - (24200 x $20) = DM Price Variance
- 442,000 - 484,000 = DM Price Variance
- $42,000 Favorable DM Price Variance
please answer the following questions:
1. After preparing DM
2. Material price variance :
3. Total Material spending variance:
4. Labor efficiency variance:
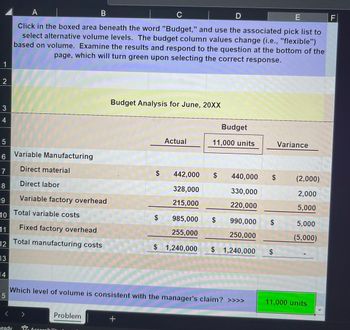
Transcribed Image Text:1
2
3
4
14
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 Fixed factory overhead
12 Total manufacturing costs
13
15
A
C
D
E
Click in the boxed area beneath the word "Budget," and use the associated pick list to
select alternative volume levels. The budget column values change (i.e., "flexible")
based on volume. Examine the results and respond to the question at the bottom of the
page, which will turn green upon selecting the correct response.
Ready
Variable Manufacturing
Direct material
Direct labor
Variable factory overhead
Total variable costs
B
Problem
Accessibilit
Budget Analysis for June, 20XX
+
Actual
$ 442,000
328,000
215,000
SA
11,000 units
SA
Budget
$
Which level of volume is consistent with the manager's claim? >>>>
440,000
330,000
220,000
985,000 $
990,000
255,000
250,000
$ 1,240,000 $ 1,240,000
$
SA
$
Variance
(2,000)
2,000
5,000
5,000
(5,000)
11,000 units
F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ken's Fish & Tackle manufactures two reel models, Standard and Premium. Weekly demand is estimated to be 110 units of the Standard Model and 72 units of the Premium Model. The following per unit data apply: Standard Premium Contribution margin per unit $24 $30 Number of machine - hours required 6 5 The contribution per machine - hour is:arrow_forwardGiven the following data: Contribution margin per unit: Product A $11Product B $12 Machine hours required for one unit: Product A 2 hoursProduct B 2.5 hours A. Compute the contribution margin per unit of limited resource for each product.arrow_forwardCycle Time and Velocity Bemidii Company has the following data for one of its production departments: Theoretical velocity: 620 units per hour Productive minutes available per year: 31,000,000 Annual conversion costs: $186,000,000 Actual velocity: 310 units per hour Required: 1. Calculate the actual conversion cost per unit using actual cycle time and the standard cost per minute. Round your actual cycle time answer to three decimal places and your cost per unit answer to the nearest cent. Actual cycle time Standard cost per minute Conversion cost per unit 2. Calculate the ideal conversion cost per unit using theoretical cycle time and the standard cost per minute. If required, round your intermediate calculations and final answers to two decimal places. Theoretical cycle time minutes per unit per unit Conversion cost per unit What incentive exists for managers when cycle time costing is used? minutes per unit $ per minute per unit 3. What if the actual velocity is 434 units per hour?…arrow_forward
- Crystal Pools estimates overhead will utilize 200,000 machine hours and cost $800,000. It takes 3 machine hours per unit, direct material cost of $13 per unit, and direct labor of $22 per unit. What is the cost of each unit produced? Cost per unit $fill in the blank 1arrow_forwardMenk Corporation has provided the following information: Cost per Unit Cost per Period Direct materials $ 6.80 Direct labor $ 3.80 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 2.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 20,200 Sales commissions $ 0.50 Variable administrative expense $ 0.40 Fixed selling and administrative expense $ 10,100 Required: a. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the variable cost per unit sold? Note: Round "Per unit" answer to 2 decimal places. b. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the total amount of variable costs related to the units sold? c. If 5,220 units are produced, what is the total amount of manufacturing overhead cost incurred? a. Variable cost per unit sold b. Total variable costs c. Total manufacturing overhead costarrow_forwardSTANDARD COSTINGA company produces a product which has a standard variable production cost of $8 per unit made up as follows:$ per unitDirect material $4.60 (2kg X $2.30 per kg)Direct labour $2.10 (0.7 hours X $3.00 per our)Variable overhead $1.30Fixed manufacturing costs are treated as period costs. The following information is availablefor the period just ended.Variable manufacturing cost of sales (at standard cost) $263,520Opening stock of finished goods (at standard cost) $120,800Closing stock of finished goods (at standard cost) $146,080Direct material rice variance $2,571 unfavourableRaw materials used in manufacture (at actual cost) $170,310Direct labour rate variance $4,760 unfavourableDirect labour efficiency variance $3,240 favourableRequired:(a) Determine for the period just ended(i) the number of units produced(ii) the raw material usage variance(iii) the total actual direct labour cost, and(iv) the actual cost per kg of raw material used.arrow_forward
- If direct materials are $8 per unit, direct labor is $4 per unit, variable manufacturing overhead is $6 per unit, and fixed costs are $12,000 for 6,000 units produced, then the total cost per unit under throughput costing isarrow_forwardCostingTo manufacture 500,000 TBS, the direct material cost per item is AED 120 and material scrap is estimated to be 3.5% of the material costs. The direct labour costs total AED 250,000 and the labour scrap rate is 3% of direct labour cost. The variable overheads are 75 - 80% of direct labour costs and the fixed overloads are 30 - 40% of the variable costs. Packaging, tooling and freight costs are 7.5% of manufacture costs. The company requires a profit of 45% to be successful. Calculate the selling price for one unit of TBS.arrow_forwardThree production processes - A, B, and C - have the following cost structure: the selling price is 5.26 per unit Process Fixed Cost per Year Variable Cost per Unit A 119164 2.54 B 80631 4.52 C 70617 5.27 1. What is the cost of process A for a volume of 7104 units? (round to the nearest cent).arrow_forward
- A standard cost card for one unit of a product may look like the following: Direct materials (4 pounds @ $1.25 per pound) $5.00 Direct labor (0.1 DLH @ $18 per hour) 1.80 Variable overhead (0.1 DLH @ $2.00 per hour) 0.20 Fixed overhead (0.1 DLH @ $4.60 per hour) 0.46 Total cost per unit $7.46 The standard cost to produce one unit is $7.46. The standard cost to produce 600 units are $ Of course, this is a simplification as the standard cost does not take fixed and variable costs into account. However, if the firm is producing at or near capacity, then the cost per unit of $7.46 could be multiplied by total units to get total standard cost. The standard cost card gives both unit and cost standards. The direct materials total of $5.00 is based on the use of four pounds of material at $1.25 per pound. Similarly, it should take six minutes (0.1 direct labor hour) to produce one unit. This makes it easy to determine total quantities and cost would be for multiple units. If 400 units were…arrow_forwardKubin Company's relevant range of production is 15,000 to 19,000 units. When it produces and sells 17,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Amount per Unit $ 7.60 $ 4.60 $ 2.10 $ 5.60 $ 4.10 $ 3.10 $ 1.60 $ 1.10 Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling expense Fixed administrative expense Sales commissions Variable administrative expense Required: 1. If 15,000 units are produced and sold, what is the variable cost per unit produced and sold? 2. If 19,000 units are produced and sold, what is the variable cost per unit produced and sold? 3. If 15,000 units are produced and sold, what is the total amount of variable cost related to the units produced and sold? 4. If 19,000 units are produced and sold, what is the total amount of variable cost related to the units produced and sold? 5. If 15,000 units are produced, what is the average fixed manufacturing cost per unit produced? 6. If 19,000 units are produced,…arrow_forwardStandard Product CostsDeerfield Company manufactures product M in its factory. Production of M requires 2 pounds of material P, costing $8 per pound and 0.5 hour of direct labor costing, $14 per hour. The variable overhead rate is $12 per direct labor hour, and the fixed overhead rate is $16 per direct labor hour. What is the standard product cost for product M? Direct material Answer Direct labor Answer Variable overhead Answer Fixed overhead Answer Standard product cost per unit Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education