
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
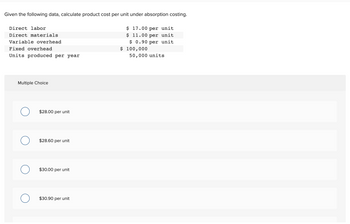
Transcribed Image Text:Given the following data, calculate product cost per unit under absorption costing.
Direct labor
Direct materials
Variable overhead
Fixed overhead
Units produced per year
Multiple Choice
$28.00 per unit
$28.60 per unit
$30.00 per unit
$30.90 per unit
$ 17.00 per unit
$ 11.00 per unit
$ 0.90 per unit
$ 100,000
50,000 units
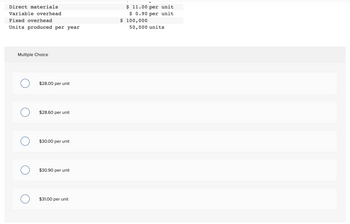
Transcribed Image Text:Direct materials
Variable overhead
Fixed overhead
Units produced per year
Multiple Choice
O
$28.00 per unit
$28.60 per unit
$30.00 per unit
$30.90 per unit
$31.00 per unit
$ 11.00 per unit
$0.90 per unit
$ 100,000
50,000 units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following data was prepared by the Sandhill Company. Total Variable Fixed $ 24/unit Sales price $ 78, 750 Direct materials used Direct labor $91,000 $ 110, 750 $ 13,850 $ 96.900 Manufacturing overhead $ 22,000 $ 12,600 $9,400 Selling and administrative expense 25,500 units Units manufactured 20, 800 units Beginning Finished Goods Inventory 9,000 units Ending Finished Goods Inventory Under variable costing, what is the unit product cost?arrow_forwardFor each variable cost per unit listed below, determine the total variable cost when units produced and sold are 25, 50, and 100 units. Direct materials $ 40 Direct labor 80 Variable overhead 9 Sales commission 12arrow_forwardGiven the following data: Contribution margin per unit: Product A $11Product B $12 Machine hours required for one unit: Product A 2 hoursProduct B 2.5 hours A. Compute the contribution margin per unit of limited resource for each product.arrow_forward
- Question: ABC Company produces a single product and has the following cost structure: Number of units produced each year Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead 3,000 $77 $41 $3 Variable selling and administrative expenses $5 Fixed costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead $36,000 Fixed selling and administrative expenses $249,000 Required: Compute the per unit product cost under absorption costing and variable costing. If ABC company produced 1,000 more units than it sold during the period, which method would produce the highest net income and by how much?arrow_forward8. Given the following data, calculate product cost per unit under variable costing. Direct labor $7 per unit Direct materials $1 per unit Overhead Total variable overhead $20,000 Total fixed overhead $90,000 Expected units to be produced 40,000 units A. $8 per unit B. $8.50 per unit C. $10.25 per unit D. $10.75 per unit E. $12 per unitarrow_forwardA corporation's cost data is: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales commissions Variable administrative expense Fixed selling and administrative expense What is the amount of product costs, if 4,000 units are produced? Multiple Choice O O O O $57,200 $8,800 $44,400 $53,200 Cost per Cost per Unit Period $ 6.00 $ 3.35 $ 1.75 $ 1.00 $ 0.40 $ 8,800 $ 4,000arrow_forward
- Identify the semi-variable costs: 10,000 units 18,000 units Materials $15,000 $27,000Labour $13,000 $19,400Rent $11,500 $11,500Selling overheads $30,000 $46,000 Question 2 options: 1) materials and labour 2) labour and rent 3) rent and selling overheads 4) labour and selling overheadsarrow_forwardFarrow Company reports the following annual results. Contribution Margin Income Statement Sales (200,000 units) Variable costs Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Contribution margin Fixed costs Fixed overhead Fixed general and administrative Income Per Unit $ 15.00 Annual Total $ 3,000,000 2.00 400,000 4.00 800,000 2.50 500,000 6.50 1,300,000 2.00 1.50 400,000 300,000 $ 3.00 $ 600,000 The company receives a special offer for 20,000 units at $13 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its normal sales. Variable costs per unit would be the same for the special offer as they are for the normal units. The special offer would require incremental fixed overhead of $80,000 and incremental fixed general and administrative costs of $86,000. (a) Compute the income or loss for the special offer. (b) Should the company accept or reject the special offer? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Compute the income or loss for the special…arrow_forwardTotal product cost per unit under absorption costing = Units produced = 1000Direct Materials = $ 6Direct Labor = $10Fixed overhead =$ 6000Variable overhead = $ 6Fixed Selling & Admin = $ 2000Variable Selling & Admin $ 2arrow_forward
- Total Amount Units Sales Variable Costs: 31,250 Per Unit $ 445,313 $ 14.25 Direct Materials $ 125,000 4.00 = Direct Labor $ 28,000 0.90 = Variable Manufacturing Overhead $ 66,250 2.12 = Sales Commissions $ 15,625 0.50 = Shipping Variable Billing Total Variable Costs $ 3,125 0.10 $ 313 0.01 $ 238,313 7.63 Contribution Margin $ 207,000 6.62 Fixed Costs: Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Advertising Sales and Admin. Salaries Fixed Billing Total Fixed Costs Net Operating Income (Loss) 40,000 16,800 87,300 10,000 154,100 $ 52,900 F. Using the budgeted contribution margin income statement in part E. above, calculate the following: a. Breakeven in units: b. Operating Leverage Multiplier: Given a sales volume increase of 8%, operating income will increase by: c. Percent: d. Dollars: #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/Aarrow_forward5 Vista Company reports the following information. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Units produced Compute its product cost per unit under absorption costing. Multiple Choice $76.00. $152.00. $171.00. $ 44 per unit 64 per unit $ 44 per unit $ 380,000 per year 20,000 units < Prarrow_forwardSales price per unit. 51.00 Fixed costs (per month): Selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) 900,000 Manufacturing overhead 1,800,000 Variable costs (per unit): Direct labor 8.00 Direct materials 13.00 Manufacturing overhead 9.00 4.00 SG&A Number of units produced per month. 300,000 units Required: Compute the amounts for each of the following assuming that both production levels are within the relevant range. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 300,000 units 400,000 units a. Prime cost per unit. b. Contribution margin per unit. C. Gross margin per unit. d. Conversion cost per unit. e. Variable cost per unit. f. Full absorption cost per unit. g. Variable production cost per unit. h. Full cost per unit. $arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education