
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
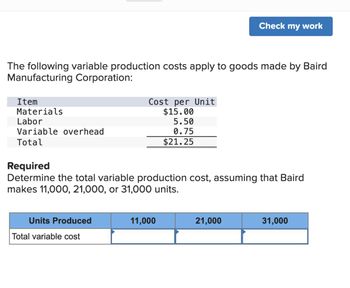
Transcribed Image Text:The following variable production costs apply to goods made by Baird
Manufacturing Corporation:
Item
Materials
Labor
Variable overhead
Total
Units Produced
Cost per Unit
$15.00
Total variable cost
Required
Determine the total variable production cost, assuming that Baird
makes 11,000, 21,000, or 31,000 units.
5.50
0.75
$21.25
11,000
Check my work
21,000
31,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Analyzing Income under Absorption and Variable Costing Variable manufacturing costs are $86 per unit, and fixed manufacturing costs are $64,800. Sales are estimated to be 5,400 units. If an amount is zero, enter "0". Round intermediate calculations to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest dollar. a. How much would absorption costing operating income differ between a plan to produce 5,400 units and a plan to produce 7,200 units? X b. How much would variable costing operating income differ between the two production plans? $ Xarrow_forwardAnalyzing Income under Absorption and Variable Costing Variable manufacturing costs are $85 per unit, and fixed manufacturing costs are $106,400. Sales are estimated to be 5,600 units. If an amount is zero, enter "0". Round intermediate calculations to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest dollar. a. How much would absorption costing operating income differ between a plan to produce 5,600 units and a plan to produce 7,600 units?$fill in the blank 1 b. How much would variable costing operating income differ between the two production plans?$fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Felix & Company reports the following information. Period Units Produced Total Costs 1 0 $4,820 2 4, 120 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 720 1, 120 1,520 1,920 2,320 2,720 3,120 3,520 3,920 4,520 5,120 4,220 4,420 8,920 16,320 Total cost at the highest volume Variable costs at highest volume Highest volume Variable cost per unit Total variable costs at highest volume Total fixed costs 5, 120 14, 228 (1) Use the high-low method to estimate the fixed and variable components of total costs. (2) Estimate total costs if 4,050 units are produced. High-Low method - Calculation of variable cost per unit High-Low method - Calculation of fixed costs Total cost at the lowest volume Variable costs at lowest volume Lowest volume Variable cost per unit Total variable costs at lowest volume Total fixed costs (2) Estimated cost if 4,050 units are produced: Estimated total cost 0arrow_forward
- Vishanuarrow_forwardcarrow_forwardQuestion: Gangwer Corporation produces a single product and has the following cost structure: Number of units produced each year Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct Labor Variable Manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed Costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed Selling and administrative expense The absorption costing unit product cost is: A. $95 B. $119 6,000 $ 43 $ 13 $ 5 $ 1 $2,04,000 $ 1,38,000 C. $61 D. $56arrow_forward
- dog subject-Accountingarrow_forwardSales volume (units) Revenue Variable costs Direct materials Direct labor Contribution margin Fixed costs Profit $30,000 $2.00 $45,000 Use direct labor dollars as the cost driver. Compute allocated fixed costs for Product X: O $20,000 Product X 400 $60,000 $50,000 $25,000 $15,000 $20,000 Product Y 600 $60,000 $15,000 $10,000 $35,000 Total 1,000 $120,000 $40,000 $25,000 $55,000 $50,000 $5,000arrow_forwarded - t 0 ances Benoit Company produces three products-A, B, and C. Data concerning the three products follow (per unit): Product B $ 58.00 Selling price Variable expenses: Direct materials Other variable expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio A $88.00 26.40 26.40 52.80 $ 35.20 40% 12.00 34.40 46.40 $ 11.60 201 Contribution margin per pound of the constraining resource Required 1 C $ 80.00 12.00 44.00 56.00 $ 24.00 The company estimates it can sell 800 units of each product per month. The same raw material is used in each product. The material costs $3 per pound with a maximum of 5,400 pounds available each month. Required: 1. Calculate the contribution margin per pound of the constraining resource for each product. 2. Which orders would you advise the company to accept first, those for A, B, or C? Which orders second? Third? 3. What is the maximum contribution margin the company can earn per month if it makes optimal use of its 5,400 pounds of…arrow_forward
- Benoit Company produces three products—A, B, and C. Data concerning the three products follow (per unit): Product B $ 62.00 Selling price Variable expenses: Direct materials Other variable expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio A $80.00 Required 1 Required 2 24.00 24.00 48.00 $ 32.00 Required 3 40% 18.00 25.40 43.40 $ 18.60 30% с $81.00 The company estimates it can sell 800 units of each product per month. The same raw material is used in each product. The material costs $3 per pound with a maximum of 5,000 pounds available each month. Required: 1. Calculate the contribution margin per pound of the constraining resource for each product. 2. Which orders would you advise the company to accept first, those for A, B, or C? Which orders second? Third? 3. What is the maximum contribution margin the company can earn per month if it makes optimal use of its 5,000 pounds of materials? Contribution margin per pound of the constraining resource 9.00 43.65…arrow_forwardFor each variable cost per unit listed below, determine the total variable cost when units produced and sold are 25, 50, and 100 units. Direct materials $ 40 Direct labor 80 Variable overhead 9 Sales commission 12arrow_forward1. Providence Corporation produces a single product and has the following cost structure: Number of units produced each year Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense lanolevil subivibr The unit product cost under variable costing is: 7,000 mos i h $78 $89 $6 $3 $532,000 $574,000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education