
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
1. Phosphodiesterase directly functions to
a. enzymatically activate the alpha subunit of the G protein
b. enzymatically cleave a membrane phospholipid to form IP3 and DAG
c. enzymatically inactivate cyclic GMP
d. open Ca++ channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
e. none of the above
2. The molecule on the picture marked (*) is a (mark all apply)
a. G protein-coupled hormone receptor
b. second messenger
c. protein kinase enzyme
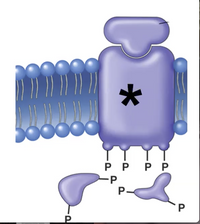
Transcribed Image Text:P P P P
P-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. The most abundant protein found in the extracellular matrix (ECM) is A. elastin B. keratin C. collagen D. myosin 2. One type of ECM component composed of both protein and carbohydrate would be A. lectins B. proteoglycans 17 C. integrins D. claudins 3. Which types of cells don't have an ECM, but rather have something else instead? A. epithelial cells B. connective tissue cells C. white blood cells D. plant cells 4. Which ECM component allows for elastic recoil, almost like a rubber band? mit A. keratin B. recoilin C. elastin D. collagen 5. Which biologists conducted the experiment that showed that the R strain of bacteria could be converted into the S strain through transformation? A. Griffith and colleagues B. Hershey and colleagues C. Avery and colleagues D. Chase and colleagues ulA ns as beitiazacio zi smonsa sit 6. The follow up to the experiments from the previous question showed that DNA was indeed the genetic material. How was this done? A. Digesting the RNA from the extract…arrow_forwardThere is only one correct optionarrow_forward5. Patients suffering from Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) can carry a mutation in one of several genes. Two of these genes are ApoB and PCSK9. 6 a. Diagram the normal cholesterol sensing pathway for a healthy person. This should be focused on the molecules that handle cholesterol and that regulate cholesterol production, NOT on patient symptoms. b. On your diagram indicate where a mutation in Apoß disrupts cholesterol sensing. Then write a paragraph or two explaining how cholesterol sensing is specifically disrupted in patients with an Apoß mutation. c. On your diagram indicate where a mutation in PCSK9 disrupts cholesterol sensing. Then write a paragraph or two explaining how cholesterol sensing is specifically disrupted in patients with PCSK9 mutation. A in cancers. One approach focuses on thearrow_forward
- Which of the following are differences between the assembly processes of intermediate filaments versus that of actin microfilaments? A. New subunits are added internally to the intermediate filament rather than at the ends B. Assembly requires GTP rather than ATP C. Intermediate filaments are assembled from multiple tetramers rather than from monomers. D. A and B E. A and Carrow_forward1. Which of the following is responsible for the transport of vesicles along microfilaments? a. Myosin V b. Dynein c. Myson II d. Cofilin e. Kinesin 2. Which of the following is NOT an example of a microfilament-based structure? a. Microvilli structure b. Phagocytosis c. Scission of new vesicles d. Contractile ring e. Vesicle transportarrow_forward1-what are the largest element of the cytoskeleton and can dynamically grow and shrink by the addition or subtraction of tubulin subunits. 2-Many less dynamic, more permanent cellular structures such as the nuclear lamina have (????) as the major cytoskeletal component Microtubules Intermediate filaments Microfilaments 3-when a ligand binds a (????) the conformation of the receptor changes, opening a selective pore. GPCR Ligand gated ion channel Ligandase pore Voltage gated ion channelarrow_forward
- 3. The /C50 value for a drug called razundib for a Src kinase is 15 nM. The Src kinase is known to bind ATP with a dissociation constant (KD) of 0.05 mM. If the concentration of ATP in the cell is 0.75 mM, what is the value of K, for rasundib with respect to the Src kinase?arrow_forward36. Proteins that will be secreted integrated in the plasma membrane of the cell are translated from ribosomes found a. in the nucleus p. in the cytosol c. on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum d. on the rough endoplasmic reticulum e. in the nucleolus alsa dute/ pd biuil m to sxatuu adT IT.S otyoarrow_forwardOne of the following is TRUE? A. The transport of Na+ across cell membranes depends solely on concentration gradient B. The transport of sucrose across cell membranes depends solely on concentration gradient C. The transport of K+ across cell membranes depends solely on concentration gradient D. The transport of Ca2+ across cell membranes depends solely on concentration gradient E. A & Carrow_forward
- What is the fate of an acid hydrolase that does not get tagged with mannose-6-phosphate in the Golgi? A. returned to the ER B. secreted out of the cell C. transported to the lysosome O D. degraded by the proteasomearrow_forward1) Which of the following contains all of the information required to target a precursor protein from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix? a. N-terminal uptake-targeting sequence b. C-terminal uptake-targeting sequence c. post-translational organelle d. translocon e. None of the above 2) In the absence of targeting information, what is the default location of proteins synthesized on cytosolic ribosomes? a. Golgi apparatus b. ER lumun c. Cytosol d. Cell plasma membrane e. ER membranearrow_forward8. Which of the following is not a feature of voltage-dependent ion channels? A. It has a hydrophobic transmembrane domain B. It is activated by a change in the membrane potential C. It is specific to the ion it lets through D. It is a passive transport E. It can be activated by the binding of a ligandarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON