
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Part B - Normal Strain, Cross-Sectional Area, Load, and Poisson’s Ratio**
Four axially loaded members are shown below. All members have the same value for \( E \) (Young’s modulus).
**Task:** Rank the members from largest to smallest absolute value of the average normal strain perpendicular to the applied load at cross section a-a shown in the figure.
*Note: Refer to the accompanying diagram for a visual representation of the axially loaded members to complete the ranking task.*
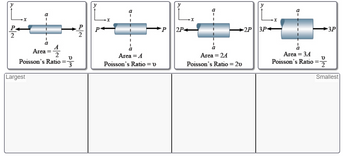
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates four horizontal cylinders subjected to axial forces. The cylinders vary in area and are labeled with their respective Poisson's ratios.
1. **First Cylinder**:
- **Forces**: \( \frac{P}{2} \) applied on both sides.
- **Area**: \( \frac{A}{2} \)
- **Poisson's Ratio**: \( \frac{\nu}{3} \)
2. **Second Cylinder**:
- **Forces**: \( P \) applied on both sides.
- **Area**: \( A \)
- **Poisson's Ratio**: \( \nu \)
3. **Third Cylinder**:
- **Forces**: \( 2P \) applied on both sides.
- **Area**: \( 2A \)
- **Poisson's Ratio**: \( 2\nu \)
4. **Fourth Cylinder**:
- **Forces**: \( 3P \) applied on both sides.
- **Area**: \( 3A \)
- **Poisson's Ratio**: \( \frac{\nu}{2} \)
Below the cylinders, there is a row labeled from "Largest" to "Smallest", pointing towards a possible task or activity, possibly organizing or comparing these properties in order of magnitude.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Simple Stress and Strain Question 2 At short, reinforced cement concrete column 600 mm x 600 mm has eight steel rods of 25mm diameter reinforcement. Find the stresses in steel and concrete, and the elastic shortening of the column if E= 200,000 N/mm² for steel and 10,000 N/mm² for concrete. Load on column= 3000 kN and length = 3 m. 30 Aarrow_forward(1) In the figure below, the cross section areas of rods AB and BC are A1, A2, and the Young's moduli are E1 and E2, respectively. For loads P1 and P2 applied as shown in the figure, (a) determine the normal stresses in rods AB and BC; (b) determine the deformation at C. D L1/2 A B C P1 P2 Li L2 A1, E1 A2, E2arrow_forwardA circular tube is subjected to torque T at itsends. The resulting maximum shear strain in the tubeis 0.005. Calculate the minimum shear strain in thetube and the shear strain at the median line of thetube section.arrow_forward
- The stresses shown act at a point in a stressed body. Normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are S, = 20 MPa, S, = 24 MPa, and Sy = 29 MPa. Assume ß = tan = 21.8°, a = 5, and b = 2. Using the equilibrium equation approach, determine the normal and shear stresses o (positive if tensile, negative if compressive) and z (magnitude only) at this point on the inclined plane shown. Answers: i MPa, T = i MPа.arrow_forward2. An Aluminum-alloy block is loaded as shown in the figure. The application of this load produces a tensile strain of 500 x 10 at gage A. Calculate the magnitude of the applied load P. Let E = 100GPa 400mm 120 Gage A P 20mmarrow_forwardFind the interal normal stress in all relevant segments of the bar in the picture.arrow_forward
- For the bar in the way the loading status is seen determine the strain energy on the rod so that the shear stress on the rod is maximum 120 MPa.( Part of BC is hollow)arrow_forwardThe two bars shown in the figure are used to support a load P. When unloaded, joint B has coordinates (0, 0). After load P is applied, joint B moves to the coordinate position (0.20 in., -0.55 in.). Assume a = 9 ft, b = 6 ft, and h = 7 ft. Determine the normal strain in each bar. B P b harrow_forwardDetermine the normal strain AB and BCarrow_forward
- Consider the pre-deformation cross-section of a bar, a side view of which is shown in the figure below. h ΫΠ' ΑΣΦ D The diameter of the bar is d = 230 mm. A bending moment is applied that causes the neutral axis to become concave up. What is the normal strain h = 40 mm from the bottom of the bar if the radius of curvature is measured to be p = 6.7 m? Express your answer to three significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) Ax ↓↑ vec t O ? mm/mmarrow_forwardTry One scene 7 of 7 The bar has a 90 mm by 20 mm rectangular cross section. If P = 80 kN, determine the force components perpendicular (N) and parallel (V) to a – a, the inclined surface area, and the normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on surface a – a. 90 mm 62° a N kN kN Aa-a mm2 P = 80 kN MPa MPа Try one 1st 2nd 3rd Enter attemptarrow_forwardThe stresses shown act at a point in a stressed body. The stress magnitudes are Sx = 50 MPa and Sy = 250 MPa, acting in the directions indicated in the figure. Using the equilibrium equation approach, determine the normal and shear stresses at this point on the inclined plane shown. Assume β = 46°.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY