
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
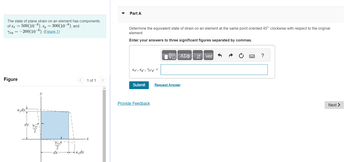
Transcribed Image Text:The state of plane strain on an element has components
of € = 500(10-6), Ey = 300(10-6), and
Yzy = -200(10-6). (Figure 1)
Figure
Gdyt
dy Yay
2
y
2
dx
**
< 1 of 1
-€ dx
X
>
Part A
Determine the equivalent state of strain on an element at the same point oriented 45° clockwise with respect to the original
element.
Enter your answers to three significant figures separated by commas.
Er', Ey', Yr'y' =
Submit
Provide Feedback
VE ΑΣΦ
Request Answer
↓↑
vec
****
?
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can someone please help me to solve the following question using the FACTOR LABEL METHOD OF UNIT CONVERSION. Showing all work and formulas please and thank you!arrow_forwardTwo [0°, 45°, 90°] strain gauge rosettes are placed along the neutral axis of a 4-point bent beam as shown in the figure below. What will the strain reading in each of the 6 gauges be? P L/3 L/3 -45° 45 L/4 L/2 L NA harrow_forwardIf a rubber material is deformed as shown in the following figure, determine the normal strain along diagonal AC. D 2 mm 3 mm 20 mm A B 20 mm Select one: 0.0326 0.0607 0.0853 0.1281 0.1402arrow_forward
- Please show each and every step in detail. Dont miss any steps and highlight the final answer. Thanks!arrow_forwardProblem 2. A block of cast iron was wrapped in the thin aluminum foil as shown on the figure. At room temperature there is no stress on the foil. The whole system is then immersed in liquid nitrogen at -196°C. Find the stress on the aluminum foil. Is the foil going to deform permanently? Is it going to break? Stress [MPa] 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 alu alloy 5083-H34 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 Strain Aluminum foil 5 µm thick, this is a continuous strip with the ends welded together Cast iron 20 mm thick a aluminum = 2.4 105 K-¹, Stress MPa 400 300 200 100 a iron 1.2 105 K-1 ↑ 11 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 Strain Fig. 2. Stress-strain diagrams for aluminum. Left: Low strain region. Right: Full strain range. Hint: you can get the Young's modulus, proportions limit (elastic limit), and break point from the graphs.arrow_forward1arrow_forward
- You need the shear modulus for a particular material in order to calculate shear strain for a known applied shear shear stress. You can't find shear modulus for the material, but you can find elastic modulus (200 GPa) and Poisson's ratio (0.3). Which of the following could you use as the shear modulus for your calculations? 200 GPa O 60 GPa O 77 GPa O 154 GPaarrow_forward! How to compute the strain displacement matrix for each element?arrow_forwardQuestion 1 The wedge shaped bar shown in Figure Q1 is to be analysed using a single one dimensional quadratic element as shown. The bar has a rectangular cross section with a constant width and a linearly varying depth. 500 k = 10E 2 100 3 Figure Q1. +1] a) Calculate the strain shape function matrix, [B], for the element. b) Using the strain shape function matrix derived in (a), show that the stiffness matrix for the element is given by the equation: I 255+ ALL DIMENSIONS IN mm (3-5) d h 100- with units of N/mm Where: E = Young's modulus of the material 10 c) Show how the strain shape function matrix may be used to determine the stress from the nodal displacement for this type of element. Do not attempt to calculate the stress. LEGION Question 2 Figure Q2 shows a two-dimensional quadratic element that has been distorted such that one Q Searcharrow_forward
- Q1arrow_forward1.40 Given a major principal strain of 600µ and strain invariants I, = 400µ and I, = - 4800µ, find the remaining principal strains. Find, in magnitude and direction, the octahedral normal and shear strains. Answer: (1u = 1 x 10 ) 200p.- 400u. 133µ, 822uarrow_forwardPlease answer in proper unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY