
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
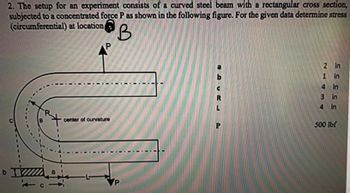
Transcribed Image Text:2. The setup for an experiment consists of a curved steel beam with a rectangular cross section,
subjected to a concentrated force P as shown in the following figure. For the given data determine stress
(circumferential) at location
DIZZZZZZ
b
-
P
center of curvature
2 in
1
in
4
3
4
in
in
in
500 lbf
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve two problems on statically indeterminate structures(strain energy method), two on thin wall pressure vessels(1-sphere and 2-cylinder), and one on thick wall cylinder, given below. A steel cylinder is 160 mm ID and 320 mm OD. If it is subject to an internal pressure of 150 MPa, determine the radial and tangential stress. Determine the maximum shear stress in the cylinder. Assume it has closed ends.arrow_forwardFigure Q5 shows a thick cylinder of 50 mm internal radius and 130 mm outer radius is subjected to an internal pressure of 60 MN/m2 and an external pressure of 30 MN/m2. Determine the hoop and radial stresses at the inside and outside of the cylinder together with the longitudinal stress if the cylinder is assumed to have closed ends using analytical and graphical approachesarrow_forward(1) In the figure below, the cross section areas of rods AB and BC are A1, A2, and the Young's moduli are E1 and E2, respectively. For loads P1 and P2 applied as shown in the figure, (a) determine the normal stresses in rods AB and BC; (b) determine the deformation at C. D L1/2 A B C P1 P2 Li L2 A1, E1 A2, E2arrow_forward
- Calculate non-zero stress components (normal and shear) at points A, B and C. Point C is located at the center of the cross section attached to the wall. Calculate non-zero strain components at point B. Neglect shear stress due to shear force. Given: loading F = 400 N, P-2000 N, and T = 75 N·m, Young's modulus E = 70 GPa, Poisson's ratio v = 0.25 15-mm D. -100 mmarrow_forwardThe cross-sectional area of the prismatic bar is 0.02 m². If the normal and shear stresses on the plane P are d = 1.25 MPa and Te = -1.5 MPa, what are the angle and the axial force P. Figure 1arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A steel bar with length of 4.5 m is subjected to forces as shown in the figure: 1. Determine the stress in the square section 2. Determine the elongation of each sections Take the modules of elasticity for the bar is 200 GPa Circular section Square section Circular section Diameter =15 mm Area =20 mm*20mm Diameter =10 mm 50 kN 35 kN 30 kN 45 kN 1 m 2 m 1.5 marrow_forward
- Try One scene 7 of 7 The bar has a 90 mm by 20 mm rectangular cross section. If P = 80 kN, determine the force components perpendicular (N) and parallel (V) to a – a, the inclined surface area, and the normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on surface a – a. 90 mm 62° a N kN kN Aa-a mm2 P = 80 kN MPa MPа Try one 1st 2nd 3rd Enter attemptarrow_forwardThe solid shaft is fixed in the wall at A (Figure Q2). A force F is applied at B, determine a) the stress components at points D and E, b) the principal stress at each of these points. (Draw free body diagram to show all loading forces and moments) Take F = 12 N and 0 = 45°. 1,25 mm 6 mm. 8 mm. 3 mm B F Figure Q2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY