
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
When there is a plane stress condition as shown in the figure, display this stress in the form of the maximum in-plane shear stress and the corresponding average vertical stress.
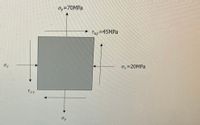
Transcribed Image Text:ッ=70MPa
Txy 45MPA
Ox
0,=20MPA
Txy
Oy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the main stress plane and main stress at the plane stress conditions as shown in the following figure.arrow_forward(3) The cantilever bar as shown on next page is made of a brittle material. At D, Fx-300 lb. F-250 lb, and F-100 lb. Determine the precise location of critical stress element at the cross section at A. Determine the magnitude for each of the stress components considering the stress concentration at A. Find the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at this location. 2 in 1-in dia. -in R. 12 inarrow_forwardFind p1 and p2arrow_forward
- The stresses shown act at a point in a stressed body. Normal and shear stress magnitudes acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are S, = 20 MPa, S, = 24 MPa, and Sy = 29 MPa. Assume ß = tan = 21.8°, a = 5, and b = 2. Using the equilibrium equation approach, determine the normal and shear stresses o (positive if tensile, negative if compressive) and z (magnitude only) at this point on the inclined plane shown. Answers: i MPa, T = i MPа.arrow_forward3. An element in plane stress on the fuselage of an airplane (figure part a) is subjected to compressive stresses of magnitude 35 MPa in the horizontal direction and tensile stresses of magnitude 10.5 MPa in the vertical direction (see figure part b). Also, shear stresses of magnitude 12.5 MPa act in the directions shown. Determine the stresses acting on an element oriented at a clockwise angle of 40° from the horizontal. Show these stresses on a sketch of an element oriented at this angle. (a) 10.5 MPa Ţ (b) 35 MPa 12.5 MPaarrow_forwarda. Determine the principal stresses at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress. b. Determine maximum in-plane shear stress at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress.arrow_forward
- Please show full work than youarrow_forward2. The figure below shows a shaft with pulley and gear. Find the location along the x axis where the normal and shear stresses are the greatest. Create an element drawing of the stress state at this location. Find the principal stresses. Hints:1. the shaft diameter is not given, but you can find the stresses as a function of diameter. 2. Because the shaft is rotating, the maximum normal stress can be determined by using the resultant moment. 1. 622 YA ΤΑ 6 in. - 4 in. Gear/ 600 lb 2000 lb 79 Fp=? 12 in. 200 lb 1 +3 in.-102 D 8 in. Pulley B Xarrow_forward4- Calculate the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress for an element in plane stress and subjected to the stresses as shown in the below figure. 40 MPa 10 MPa 70 MPaarrow_forward
- Calculate non-zero stress components (normal and shear) at points A, B and C. Point C is located at the center of the cross section attached to the wall. Calculate non-zero strain components at point B. Neglect shear stress due to shear force. Given: loading F = 400 N, P-2000 N, and T = 75 N·m, Young's modulus E = 70 GPa, Poisson's ratio v = 0.25 15-mm D. -100 mmarrow_forwardSuppose that σ = 330 psi and Try = 150 psi in (Figure 1). Figure Part D Specify the orientation of the principal stress. Take the positive direction of rotation counterclockwise. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. Op₁= Part E OF 0₂ = ΑΣΦΙΚΗ vec Specify the orientation of the maximum in-plane shear stress. Take the positive direction of rotation counterclockwise. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. 0/ —| ΑΣΦ 11 | vec ? ? oarrow_forwardQ 1-3 Determine the maximum tensile, compressive, and shear stresses at point A on the bicycle pedal crank shownin the figure. The pedal and crank are in a horizontal plane and point A is located on the top of the crank. The load P = 160 lb acts in the vertical direction and the distances (in the horizontal plane) between the line of action of the load and point A are b, = 5.0 in. and b, = 2.5 in. Assume that the crank has a solid circular cross section with diameter d = 0.6 in. P = 160 lb Crank d = 0.6 in. b = 5.0 in. b2 = 2.5 in.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY