
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Practice question 1F)
In the above signalling diagram, hormone H binds to both an intracellular and a cell surface receptor.
Initially you assume that homone H must therefore be a small hydrophobic molecule. However,
further analysis revealed that it is a large hydrophilic molecule. Knowing this, what would you need to
add to this diagram to accurately reflect how these signalling events are possible and why?
The csRu MRNA and protein are represented in the diagram below.
MRNA 5'
AUG
3'
ribosome
protein
DNA
ligand
binding
domain
signal
kinase
transmembrane
domain
domain
binding
sequence
domain
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
extracellular fluid
Transcribed Image Text:Info:
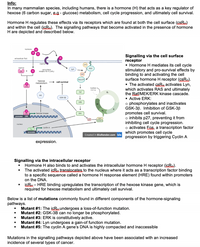
In many mammalian species, including humans, there is a hormone (H) that acts as a key regulator of
hexose (6 carbon sugar, eg - glucose) metabolism, cell cycle progression, and ultimately cell survival.
Hormone H regulates these effects via its receptors which are found at both the cell surface (csRu)
and within the cell (icRu). The signalling pathways that become activated in the presence of hormone
H are depicted and described below.
hormone
Signalling via the cell surface
receptor
· Hormone H mediates its cell cycle
stimulatory and pro-survival effects by
binding to and activating the cell
surface hormone H receptor ( .
· The activated csRH activates Lyn,
which activates RAS and ultimately
the Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade.
· Active ERK:
o phosphorylates and inactivates
GSK-3B. Inhibition of GSK-3B
promotes cell survival.
o inhibits p27, preventing it from
inhibiting cell cycle progression.
o activates Egs, a transcription factor
which promotes cell cycle
progression by triggering Cyclin A
extracellular fluid
inactive
(GTP
inactive
RAS
Lyn
cel-surtace
receptor for H (csR.)
RAS-GTP
hехose
metabolism
cell survival
Gphase
(esting)
Raf
G,
HK
GSK-38
MEK
hexose kinase
ERK
promoter HRE
COKI
Cyclin A
cyclin A
Fos
A promoter
Created in BioRender.com bìo
expression.
Signalling via the intracellular receptor
Hormone H also binds to and activates the intracellular hormone H receptor (icRu).
The activated icRu translocates to the nucleus where it acts as a transcription factor binding
to a specific sequence called a hormone H response element (HRE) found within promoters
on the DNA.
icRu - HRE binding upregulates the transcription of the hexose kinase gene, which is
required for hexose metabolism and ultimately cell survival.
Below is a list of mutations commonly found in different components of the hormone-signaling
pathways.
Mutant #1: The icRuundergoes a loss-of-function mutation.
Mutant #2: GSK-3B can no longer be phosphorylated.
Mutant #3: ERK is constitutively active.
Mutant #4: Lyn undergoes a gain-of function mutation.
Mutant #5: The cyclin A gene's DNA is highly compacted and inaccessible
Mutations in the signalling pathways depicted above have been associated with an increased
incidence of several types of cancer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the normal cycle of Ras activity, when Ras is bound to y activity that removes a phosphate to convert GTP back to GDP and this it is inactive. Activation of Ras involves exchanging GDP for The Ras protein has intrinsic Ras. inactivates activates ATP GTP «< Questic A Moving to another question will save this response. ADP GDP GTPase Clo nucleasearrow_forwardbacterial cell needs to synthesize arginine if it is absent in the environment. If arginine is present in its diet, however, the cell will activate a repressor protein which blocks transcription of the genes that code for the enzymes that synthesize arginine. This is an example of which type of regulation? Group of answer choices Repressible Inducible Attenuation Post-translationalarrow_forwardFor the protein Calmodulin-1: 1) this protein have any secondary, tertiary and/or quaternary structures present? 2) Are there any molecular additions to this protein that are not amino acids?For both questions, can you explain if so, where specifically? The protein Calmodulin-1 is stated to have the molecular function of signaling receptor binding which is interrelated with the biological function of calcium-mediated signaling. Can you explain this relationship?arrow_forward
- Histamine acts by binding to specialized membrane proteins called histamine H 1 receptors. These receptors, found in specific cells, are integral membrane proteins that possess seven transmembrane a-helical regions. The amino terminus of the protein is extracellular, while the C-terminus is cytoplasmic. The binding of histamine to the extracellular portion of the H 1 receptor prompts a conformational change in the intracellular C-terminus region of the protein. This conformational change triggers numerous intracellular signaling events that stimulate the immune response in cells containing the receptor. There are numerous anti-histamine drugs available commercially. Some of the most popular are shown here side by side with histamine: HCHS NH- Allegra H2N histamine Claritin Propose a reasonable mode of action by which these antihistamines exert their activity. Include relevant details about the system of your own choosing.arrow_forwardplease identify amino acids in the N terminus in the picture below.arrow_forwardLook at the figure and predict what would happen if the SRPRNA was unable to stimulate the GTPase activities of the GTPbindingproteins within SRP and the SRP receptor.arrow_forward
- While studying the secretory pathway, you make the following observation about proteins destined for the ER: Proteins translated in vitro in the absence of microsomes migrate more slowly on an SDS PAGE gel than those translated in the presence of microsomes. What might account for the observed protein size difference? A. SRP, present only in microsomes, and binds to and removes the signal sequence from the protein, resulting in a protein is smaller and migrates more quickly on a gel. B. Signal peptidase, present only in the microsomes, cleaves the signal sequence from the protein, making the protein smaller and therefore migrate more quickly. C. In vitro translated proteins tend to be larger due to a more stable poly A tail D. Signal peptidase, present only in the microsomes, adds a signal sequence to the protein, making the protein larger and therefore migrate more slowly.arrow_forwardThe seed of the castor bean (Ricinus communis) contains large amounts of ricin, a deadly poison for animals, including humans. One of the two subunits of this toxin is a lectin that binds terminal N-acetylgalactosamine residues on glycoproteins on the surface of eukaryotic cells, allowing the other subunit to enter the cell and kill it by preventing proteins from being made. Select the possible antidotes that could prevent or reverse ricin-mediated entry of the toxin. a high concentration of N-acetylgalactosamine an oligosaccharide with the same structure as that recognized by ricin a compound that prevents synthesis of extracellular glycoproteins a compound that activates enzymes that break down glycogen into glucose an enzyme that degrades lipopolysaccharidesarrow_forwardWhen you think about the primary structure of the mannose-6-P receptor, assuming that it is an integral membrane protein with one membrane-spanning domain and assuming that it has a ERSS, what are all of the different protein domains that must be present in this protein's primary structure to get it to where it needs to go and to carry out all of the functions/activities? (Draw a schematic of the protein structure/sequence and explain each region). What do you think would happen to a soluble protein that normally contains a KDEL tag (ER retrieval) if the tag was cleaved off (where would the protein end up)?arrow_forward
- Please answer both, thank youarrow_forwardThe enzymes GICNAC phosphotrasnferase is a key enzyme involved in the transporting of proteins from the trans-Golgi to the lysozyme. In addition to the catalytic function of the enzyme that involves certain sugars, what is the second critical function of this enzyme? O It recognizes internal signal sequences found on lysozyme-targeted proteins. O It drives the binding of a phosphorylated GlcNac group onto a mannose residue. O It facilitates the reversible binding of specific proteins to the M6P receptor O In is essential for the recruitment of clathrin triskelions to the budding vesicle.arrow_forwardThe G-protein Ras is involved in proliferative signaling, and is mutated is a large fraction of human cancers. Almost all mutations in Ras mutate the glycine at codon 12. These mutations lock Ras in an active conformation. How will the GTPase activity of a Ras protein with a G12 mutation compare to a normal Ras protein without the mutation? (10 words maximum)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education