
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
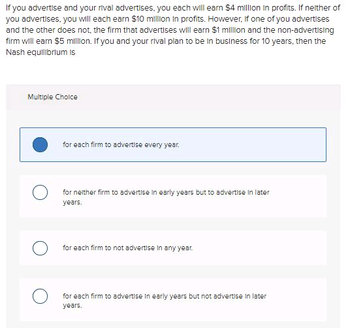
Transcribed Image Text:If you advertise and your rival advertises, you each will earn $4 million in profits. If neither of
you advertises, you will each earn $10 million in profits. However, if one of you advertises
and the other does not, the firm that advertises will earn $1 million and the non-advertising
firm will earn $5 million. If you and your rival plan to be in business for 10 years, then the
Nash equilibrium is
Multiple Choice
for each firm to advertise every year.
for neither firm to advertise in early years but to advertise in later
years.
for each firm to not advertise in any year.
for each firm to advertise in early years but not advertise in later
years.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- q52 If you advertise and your rival advertises, you each will earn 14 million in profits. If neither of you advertises, you will each earn 20 million in profits. However, if one of you advertises and the other does not, the firm that advertises will earn 10 million and the non-advertising firm will earn 16 million. If you and your rival plan to be in business for only one year, the Nash equilibrium is a. for each firm to advertise. b. for the other firm to advertise and your firm not to advertise. c. for your firm to advertise and the other not to advertise. d. for neither firm to advertise.arrow_forwardAirbus and Boeing are the two largest producers of commercial aircraft in the world. They are each trying to determine whether or not they should build an ultra-large passenger plane. They have both decided that building such a plane would be profitable, but only if one of them produces it. The market is simply not large enough for them to both make profits selling this new plane. Consequently, if they both produce the plane, each will lose $10 billion. If only one of them produces, that firm will make $50 billion. Regardless of what the other does, if they choose not to produce the plane, they neither make nor lose money. a. Construct the normal or strategic form of this game and find the pure strategy NE. b. Airbus is a corporation in the European Community while Boeing is an American corporation. The EC has a long history of subsidizing Airbus as well as other man- ufacturers it deems important. Let us remodel this game assuming that the EC tells Airbus that if Airbus produces the…arrow_forwardPLAYER B LEFT RIGHT UP 5 FOR A, 30 FOR B 10 FOR A, 12 FOR B PLAYER A DOWN -2 FOR A, 10 FOR B 8 FOR A, 15 FOR B In the above game, the players are seeking to maximize the number they recieve. They choose at the same time. What is the Nash equillibrium? Player A will choose UP and player B will choose LEFT Player A will UP and player B will choose RIGHT Player A will choose DOWN and player B will choose LEFT Player A will choose DOWN and player B will choose RIGHT Player A will choose LEFT and player B will choose UP Player A will choose LEFT and player B will choose DOWN Player A will choose RIGHT and player B will choose UP Player A will choose RIGHT and player B will choose DOWNarrow_forward
- q13-arrow_forwardTwo hunters are on a stag hunt. They split up in the forest and each have two strategies: hunt for a stag (S), or give up the stag hunt and instead hunt for rabbit (R). If they both hunt for a stag, they will succeed and each earn a payoff of 9. If one hunts for stag and the other gives up and hunts for rabbit, the stag hunter receives 0 and the rabbit hunter 8. If both hunt for rabbit then each receives 7. Compute all Nash equilibria for this game, called 'The Stag Hunt', depicted below. Which of these equilibria do you think is most likely to be played? Why? S R S 9,9 8,0 R 0,8 7,7arrow_forwardThe world has changed a bit. Microsoft and Google could still either cooperate or compete in the market for social media video software currently captured by Tik Tok, but their payoffs have changed. The table below shows their profits in billions of USD in each scenario. Use your mouse to point and click on the Nash equilibrium outcome(s). [There may be more than one so make sure you work out all the best response strategies]. Microsoft Cooperate 3,3 4,0 Cooperate O Don't cooperate O Google Don't cooperate O O 0,4 1,1arrow_forward
- Consider the following game matrix with two players- Player 1 and Player 2 with their respective strategies. Which of the following statements is correct such as x>y>b>a Players Player2 Player 1 A B C D (Y, Y) (b, x) (x, a) (AE) is the one of many Nash equilibria (C) is the unique Nash equilibria (C. D) is the unique Nash equilibria (A. E) and (B. F) are two Nash equilibria E (a, b) (x, y) (y, a) F (a,x) (a, b) (b, b)arrow_forwardBoeing and Airbus are the two primary producers of passenger aircraft. Both firms are preparing to announce their new long-distance jets. Each firm can design their plan to maximize comfort or the number of seats. If both firms choose to maximize the same characteristic they will sell 100 planes each and if they maximize different characteristics they will each sell 150 planes each. Both firms want to maximize sales. Draw a game tree and find the equilibrium strategies and payoffs. Show your work.arrow_forwardAlice and Betsy are playing a game in which each can play either of two strategies, leave or stay. If both play the strategy leave, then each gets a payoff of $400. If both play the strategy stay, then each gets a payoff of $800. If one plays stay and the other plays leave, then the one who plays stay gets a payoff of $C and the one who plays leave gets a payoff of $D. When is the outcome where both play leave a Nash equilibrium? a) never, since 800 > 400 b) when 400 > C and D > 800 but not when 800 > D c) whenever 400 > C d) when D > C and C > 400 e) whenever d < 800arrow_forward
- Let's think about a traditional game theory principal agent game. In this game we have two players, Lauren and Jason Lauren will choose to invest $500 dollars with Jason If she doesn't invest the money, she keeps the $500 and Jason gets nothing If she does invest the money, then Jason has a choice-he can cooperate by investing Lauren's money and then splitting the profit of another $500. This would give Lauren $750 (her original $500 investment plus $250 of profit) and would give Jason $250. Jason's other choice is to appropriate, or to steal Lauren's money and not invest it. If he does this, Lauren ends up with nothing and Jason has the entire $500. The following diagram outlines this game. Principal Agent Game Jason (750.250) Invest appropriate 10. 500) doninve What will happen in this game? Lauren will not invest Lauren will invest and Jason will cooperate Lauren will invest and Jason will appropriate Next pagearrow_forwardTwo firms are competing to establish one of two new wireless communication standards, A or B. A strategy is a choice of standard, and an outcome of this game is a choice of standard by each firm – for example, (A, B) represents the case where Firm 1 decides to develop standard A and Firm 2 develops standard B. Here, the first letter will always correspond to Firm 1’s decision, and the second letter to Firm 2’s decision. Firm 1 has the following preferences over outcomes, in order of highest to lowest preferred: it prefers (A, A) to (B, A) to (A, B) to (B, B). Firm 2 prefers (A, B) to (A, A) to (B, A) to (B, B). Suppose that firms simultaneously decide which standard to develop. What is the pure strategy Nash equilibrium? Is the answer (B,B)? If not please explian what is the answer?arrow_forwardHand written solutions are strictly prohibitedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education