
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Suppose the five potential entrants are identical in that each faces the same entry cost of $300. Given the total number of companies in the market, the accompanying table reports a company’s net profit (or payoff) if it enters. As before, the payoff from staying out of the market is zero, and each company can choose either enter or do not enter. Find all Nash equilibria.
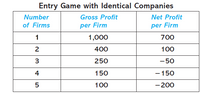
Transcribed Image Text:Entry Game with Identical Companies
Number
Gross Profit
Net Profit
of Firms
per Firm
per Firm
1
1,000
700
2
400
100
250
-50
4
150
-150
100
- 200
LO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The options for the last 3 fill-in-the-blanks are "Up" or "Down." Thank you!arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardThe count is three balls and two strikes, and the bases are empty. The batter wants to maximize the probability of getting a hit or a walk, while the pitcher wants to minimize this probability. The pitcher has to decide whether to throw a fast ball or a curve ball, while the batter has to decide whether to prepare for a fast ball or a curve ball. The strategic form of this game is shown here. Find all Nash equilibria in mixed strategies.arrow_forward
- In 'the dictator' game, one player (the dictator) chooses how to divide a pot of $10 between herself and another player (the recipient). The recipient does not have an opportunity to reject the proposed distribution. As such, if the dictator only cares about how much money she makes, she should keep all $10 for herself and give the recipient nothing. However, when economists conduct experiments with the dictator game, they find that dictators often offer strictly positive amounts to the recipients. Are dictators behaving irrationally in these experiments? Whether you think they are or not, your response should try to provide an explanation for the behavior.arrow_forwardJane is interested in buying a car from a used car dealer. Her maximum willingness to pay for thecar is 12 ($12,000). Bo, the dealer, is willing to sell the car as long as he receives at least 9($9,000). What is the Nash bargaining solution to this game?arrow_forwardFinding Nash Equilibria Consider the following two player, normal form game: Player 1 Player 2 C L (2,1) U M (-2,-2) D R (2, -1) (1,2) (-1, 1) (0,0) (3,1) (0,0) (-1,-1) Find all pure and mixed strategy Nash equilibria. Calculate each player's expected payoffs at each equilibrium.arrow_forward
- In the normal form game below, the payoff matrix depends on the parameter a. 1 1 2 ABC a 0,2 6,4 -2,4 b 0, -24 -2a, 2a 8, 2 C 4,0 0,4 0, 14 Find the values of a, for which at least one pure strategy Nash equilibrium exists. Compute the value of a for which the expected payoff is the same for both players when the mixed strategy profile (01,02) = ((1/3,2/3,0), (0,1/4,3/4)) is played. Find the best response of player 1 (as a function of the parameter a) to player's 2 mixed strategy o2 = (1/2,1/2,0). Assuming a = 0 eliminate iteratively all dominated strategies and find a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in this game.arrow_forward1.a) If the three executives of a fraudulent organization report nothing to the authorities, each gets a payoff of 100. If at least one of them blows the whistle, then those who reported the fraud get 28, while those who didn’t get -100. Suppose they play a symmetric mixed-strategy Nash equilibrium where each is silent (does not report fraud) with probability p. What is p?A, 0.1B, 0.28C, 0.5D, 0.8 b) In a two-player game, with strategies and (some known and some unknown) payoffs as shown below, suppose a mixed-strategy equilibrium exists where 1 plays C with probability 3/4, and Player 2 randomizes over X, Y, and Z with equal probabilities. What are the pure-strategy equilibria of this game? A, (A, Y) and (B, X)B, (A, Z) and (C, Y)C, (B, X) and (C, X)D, (C, X) and (C, Y)arrow_forwardDetermine all of the Nash equilibria (pure-strategy and mixed-strategy equilibria) of the following game:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education