
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305971493
Author: N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
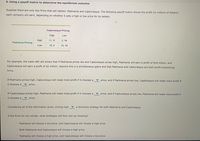
Transcribed Image Text:6. Using a payoff matrix to determine the equilibrium outcome
Suppose there are only two firms that sell tablets: Padmania and Capturesque. The following payoff matrix shows the profit (in millions of dollars)
each company will earn, depending on whether it sets a high or low price for its tablets.
Capturesque Pricing
High
Low
High
11, 11
2, 18
Padmania Pricing
Low
18, 2
10, 10
For example, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $18 million, and
Capturesque will earn a profit of $2 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing
firms.
If Padmania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a
▼ price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more profit if
it chooses a
price.
If Capturesque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a
price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more profit if
it chooses a
price.
Considering all of the information given, pricing high
a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque.
If the firms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing?
O Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price.
O Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price.
O Padmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price.

Transcribed Image Text:For example, the lower-left cell shows that if Padmania prices low and Capturesque prices high, Padmania will earn a profit of $18 million, and
Capturesque will earn a profit of $2 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Padmania and Capturesque are both profit-maximizing
firms.
If Padmania prices high, Capturesque will make more profit if it chooses a
price, and if Padmania prices low, Capturesque will make more profit if
it chooses a ▼ price.
If Capturesque prices high, Padmania will make more profit if it chooses a
price, and if Capturesque prices low, Padmania will make more profit if
it chooses a
v price.
Considering all of the information given, pricing high
v a dominant strategy for both Padmania and Capturesque.
If the firms do not collude, what strategies will they end up choosing?
O Padmania will choose a low price, and Capturesque will choose a high price.
O Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a high price.
O Padmania will choose a high price, and Capturesque will choose a low price.
Both Padmania and Capturesque will choose a low price.
True or False: The game between Padmania and Capturesque is not an example of the prisoners' dilemma.
True
O False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is predatory pricing?arrow_forwardSometimes oligopolies in the same industry are very different in size. Suppose we have a duopoly where one firm (Film A) is large and the other film (Film B) is small, as the prisoners dilemma box in Table 10.4 shows. Assuming that both films know the payoffs, what is the likely outcome in this case?arrow_forwardIf the firms in a monopolistically competitive market are earning economic profits or losses in the short run, would you expect them to continue doing so in the long run? Why?arrow_forward
- Aside from advertising, how can monopolistically competitive films increase demand for their products?arrow_forwardDoes each individual in a prisoners dilemma benefit more from cooperation or from pursuing self-interest? Explain briefly.arrow_forwardWhat is predatory pricing? How might it reduce competition, and why might it be difficult to tell when it should be illegal?arrow_forward
- What is the relationship between product differentiation and monopolistic competition?arrow_forwardSuppose that, due to a successful advertising campaign, a monopolistic competitor experiences an increase in demand for its product. How will that affect the price it charges and the quantity it supplies?arrow_forwardWhen OPEC raised the price of oil dramatically in the mid-1970s, experts said it was unlikely that the cartel could stay together over the long term-that the incentives for individual members. to cheat would become too strong. More than fort),r years later, OPEC still exists. Why do you think OPEC has been able to beat the odds and continue to collude? Hint: You may wish to consider non-economic reasons.arrow_forward
- Suppose the market for Hula Hoops is monopolized by a single firm. a. Draw the initial equilibrium for such a market. b. Now suppose the demand for Hula Hoops shifts outward slightly. Show that, in general (contrary to the competitive case), it will not be possible to predict the effect of this shift in demand on the market price of Hula Hoops. c. Consider three possible ways in which the price elasticity of demand might change as the demand curve shifts: It might increase, it might decrease, or it might stay the same. Consider also that marginal costs for the monopolist might be increasing, decreasing, or constant in the range where MR=MC Consequently, there are nine different combinations of types of demand shifts and marginal cost slope configurations. Analyze each of these to determine for which it is possible to make a definite prediction about the effect of the shift in demand on the price of Hula Hoops.arrow_forwardIf you were developing a product (like a web browser) for a market with significant barriers to entry, how would you try to get your product into the market successfully?arrow_forwardFor many years, the Justice Department has tried to break up large firms like IBM, Microsoft, and most recently Google, on the grounds that their large market share made them essentially monopolies. In a global market, where U.S. films compete with firms from other countries, would this policy make the same sense as it might in a purely domestic context?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305971493
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:Cengage Learning