
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Can someone please show your work for tracking the radiolabel: draw structures indicating position of the radiolabeled carbon, giving names (not abbreviations) of metabolites and enzymes,
The cell needs ribose 5-phosphate and NADPH. Note the structure, shown above – this is used as a starting point for the formation of ribose 5-phosphate while also generating NADPH. The red asterisk (*) denotes a radiolabeled carbon - where would the radiolabel end up? List all the names’ enzymes and intermediates involved in this conversion. Show all structures.
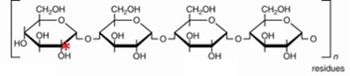
Transcribed Image Text:HO
CH₂OH
OH
OH
CH₂OH
он
OH
CH₂OH
он
OH
CH OH
OH
OH
residues
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please provide Typed solution in details, you can use only handwritten diagramarrow_forwardPlease asnwer the following question: Suppose you specifically want to measure the amount of beta-glucose present in a sample. You have an enzyme that reacts specifically with the beta form of the sugar,and produces a signal that is easy to measure. However, every time you try to measure the amount of beta-glucose, mutarotation occurs and the alpha form of the sugar is converted into beta!! Can you suggest a simple way of overcoming this problem so you could measure only the beta form of the sugar? HINT: Is there a way you can prevent mutarotation?arrow_forwardAll of the following products of biosynthesis are nitrogen-rich tetrapyrrole structures that can be synthesized from Krebs cycle intermediates (in some plants, animals, or bacteria), with the exception of: triglyceride molecules chlorophyll b molecules vitamin B12 molecules chlorophyll a molecules heme molecules Identify the Krebs cycle enzyme that consumes a six-carbon substrate molecule, producing a five-carbon product molecule along with NADH, and one molecule of CO2. succinyl CoA synthetase a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase malate dehydrogenase isocitrate dehydrogenase citrate synthasearrow_forward
- Complete the description of the pentose phosphate pathway by filling the correct term to each blank. The pentose phosphate pathway is a two‑stage pathway that generates ______ , which is a reductant in many biosynthetic reactions and takes part in detoxifying reactive oxygen species, and __________ , which is a nucleotide (DNA and RNA) precursor. The substrate for the pentose phosphate pathway is ___________arrow_forwardI don't understand it. Can u help me? Can u help me to explain this to me, pleasearrow_forwardUsing the data in this table, what is the AG° (in KJ/mol) for the reduction of FAD by water?arrow_forward
- A fasting animal is fed palmitic acid that has a 14C-labeled carboxyl group. After allowing sufficient time for fatty acid breakdown and resynthesis to palmitic acid the 14C label can be found in the molecule (the methyl carbon is carbon 16) at: Multiple answers:Multiple answers are accepted for this question Select one or more answers and submit. For keyboard navigation...SHOW MORE a Carbon-15 b Carbon-13 c Carbon-11 d Carbon-9 e Carbon-7 f Carbon-5 g Carbon-3 h Carbon-16 i CO2 i think its c but not sure c or h please helparrow_forwardCyclic AMP (CAMP) is an important signaling molecule in cells. The synthesis and degradation of CAMP is diagrammed in the following figure: ATP ©2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 12pt Adenylyl cyclase Edit View Insert Format Tools Table Paragraph Pyrophosphate 3'c- P-P₁ 5'C BI Both caffeine (coffee, cola) and theophylline inhibit the enzyme phosphodiesterase that converts CAMP to AMP, allowing cAMP levels to temporarily remain high. Briefly discuss the possible effect of these drugs on the second messenger action of CAMP. What might the effect of caffeine of theophylline be on a signaling pathway? CAMP UA Phosphodiesterase T² H₂O AMP ⠀arrow_forwardOne of the steps in psilocybin biosynthesis is the phosphorylation of 4-hydroxytryptamine By the enzyme Psik as shown below, that involves the hydrolysis of ATP. NH₂ OH HO Psik HO of A& ADP 4-hydroxytryptamine ATP norbaeocystin The standard free energy changes for each reaction is shown in the Table below. J reaction 4-hydroxytryptamine + P₁ → norbaeocystin ATP → ADP+ Pi (b) What is the equilibrium constant at 37 °C? AG 27.7 kJ/mol -32.2 kJ/mol (a) Write the net reaction. What is the standard free energy change for the net reaction? (c) In the cell, the concentration of ATP is 3.1 mM, the concentration of P; Is 5.90 mM, and the Concentration of ADP is 220 μM. What will AG Be if the concentration of norbaeocystin Is always kept at 1/100 of the concentration of 4-hydroxytryptamine?arrow_forward
- Please answer questions 10 and 11 using the first picture for reference.arrow_forwardIntermediates of a pathway are shown in the following scheme. Using curved arrows, show the mechanism of each step labeled with a blue letter. Draw out abbreviated structures of the coenzymes, so that you can effectively show all arrow pushing. You may abbreviate the coenzymes by putting R groups on the molecule, but do draw out the parts of the structure that are involved in the arrow pushing. Some of the transformations will require you to show multiple structures to show all of the arrow pushing (particularly some of the coenzyme-mediated steps). You do not need to show specific amino acid residues that perform the catalysis. You can abbreviate acidic amino acid residues “Enz–B–H” and basic residues “B–Enz”.arrow_forwardHow many grams (net) of the following metabolites (ATP, NADH, Ethanol, and CO2) will be produced during glycolysis-alcoholic fermentation from 360 grams of Fructose? Write the numbers only (NO UNITS) of each metabolite. Molecular Weights: Fructose = 180, ATP = 500, Ethanol = 46, CO2 = 44, NADH = 663 %3D ATP = grams, NADH = grams, Ethanol = grams, CO2 = gramsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON