
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The total energy required to break the bonds in the reactant molecules needs to be calculated.
Concept Introduction : The total bond energy can be defined as the summation of individual bond energies of the bonds in the molecule.
The total energy required to break the bonds in the reactant molecules is 1358 kJ.
The bond energy of 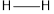 is 432 kJ/mol,
is 432 kJ/mol, 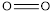 is 142 kJ/mol
is 142 kJ/mol
In the reaction,
The total bond energy can be calculated as the sum of bond energies of 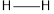 and
and 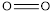 bonds.
bonds.
Total energy (E)= 2 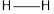 bond) +
bond) + 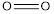 bond)
bond)
(b)
Interpretation: The total energy released by the formation of bonds in the product molecule needs to be calculated.
Concept Introduction : The total bond energy can be defined as the summation of individual bond energies of the bonds in the molecule.
The total energy released by the formation of bonds in the product molecule is 1836 kJ.
In the reaction,
The total bond energy of the product molecule can be calculated as the bond energy of  molecule.
molecule.
The bond energy of  is 459 kJ/mol.
is 459 kJ/mol.
So,
(c)
Interpretation: The reaction is endothermic or exothermic needs to be determined using the value of (a) and (b).
Concept Introduction : The total bond energy can be defined as the summation of individual bond energies of the bonds in the molecule.
If the energy value is positive, then the reaction is an endothermic reaction and if the energy value is negative, the reaction is an exothermic reaction.
The reaction,
From (a) and (b), we can determine that the reaction is endothermic or exothermic by calculating the heat of the reaction.
So,
Therefore, the reaction is an endothermic reaction.
The reaction is an endothermic reaction because, the heat of reaction is
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward(a) The following synthesis of the molecule shown in the circle has a major problem. What is this problem? (2 pts) 1) HBr (no peroxides) 2) H- NaNH2 Br 3) NaNH, 4) CH3Br 5) H2, Pd (b) Starting with the molecule shown below and any other materials with two carbons or less, write out an alternate synthesis of the circled molecule. More than one step is needed. Indicate the reagent(s) and the major product in all the steps in your synthesis. (5 pts) 2024 Fall Term (1) Organic Chemistry 1 (Lec) CHEM 22204 02[6386] (Hunter College) (c) Using the same starting material as in part (b) and any other materials win two carpons or less, write out syntheses of the circled molecules shown below. More than one step is needed in each case. Indicate the reagent(s) and the major product in all the steps in your synthesis. You may use reactions and products from your synthesis in part (b). (5 pts)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





