
Concept explainers
Practice Problem F.1
Show how you might use a sulfur ylide to prepare

Interpretation:
The sulfur ylide required for the preparation of the given compounds is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Sulphur ylide acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes and ketones.
The intermediate formed in the reaction of sulphur ylide and carbonyl carbon is generally an epoxide rather than an alkene.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
The reactant used are:
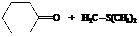
The reactant used are:
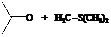
Explanation of Solution
a)
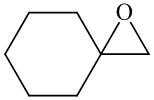
In the formation of the given product, the ketone used is cyclo hexanone. In the first step, sulfur ylide acts as a nucleophile (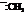 group of sulfur ylide) and attacks the carbonyl carbon of cyclo hexanone. After this,
group of sulfur ylide) and attacks the carbonyl carbon of cyclo hexanone. After this, 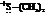 group is removed from the sulfur ylide, which results in the formation of the epoxy ring. The whole reaction can be shown as follows:
group is removed from the sulfur ylide, which results in the formation of the epoxy ring. The whole reaction can be shown as follows:
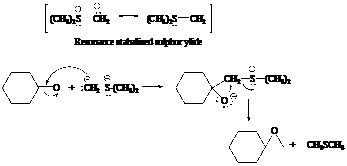
Hence, cyclohexane is used in combination with sulfur ylide to form the given compound.
b)
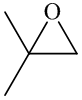
In the formation of the given product, the ketone used is acetone. In the first step, sulfur ylide acts as a nucleophile (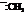 group of sulfur ylide) and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetone. After this,
group of sulfur ylide) and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetone. After this, 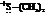 group is removed from the sulfur ylide which results in the formation of the epoxy ring.
group is removed from the sulfur ylide which results in the formation of the epoxy ring.
The whole reaction can be shown as follows:
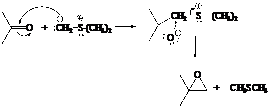
Hence, acetone is used in combination with sulfur ylide to form the given compound.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Microbiology: An Introduction
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIndicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- 1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


