
a.
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
a.
Answer to Problem 37E
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Alternate hypothesis:
Explanation of Solution
It is given that among a sample of 500 chips produced by less expensive machine, 70 chips were defective and among a sample of 400 chips produced by more expensive machine, 20 chips were defective. The manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
Hypothesis:
Hypothesis is an assumption about the parameter of the population, and the assumption may or may not be true.
Let
Claim:
Here, the claim is that the manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Null hypothesis is a statement which is tested for statistical significance in the test. The decision criterion indicates whether the null hypothesis will be rejected or not in the favor of alternate hypothesis.
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is less than or equal to 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Alternate hypothesis:
Alternate hypothesis is contradictory statement of the null hypothesis
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
b.
Find the value of test statistic.
b.
Answer to Problem 37E
The value of test statistic is 4.4776.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is less than or equal to 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Point estimates:
The total number of chips produced by less expensive machine is
The point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the less expensive machine is obtained as follows:
Thus, the point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the less expensive machine is 0.14.
The total number of chips produced by more expensive machine is
The point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the more expensive machine is obtained as follows:
Thus, the point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the more expensive machine is 0.05.
Estimate of pooled proportion:
The estimate of pooled proportion is obtained as follows:
Thus, the estimate of pooled proportion is 0.1.
Test statistic:
The test statistic for testing the difference between two proportions is,
Under the null hypothesis,
The test statistic is obtained as follows,
Thus, the test statistic is 4.4776.
c.
Check whether the null hypothesis is rejected at
c.
Answer to Problem 37E
The null hypothesis is rejected at
Explanation of Solution
P-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P-value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot.
- Choose View Probability > OK.
- Under Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter 0 as mean and 1 as standard deviation.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Under Define shaded area by choose X value and Right Tail.
- In X-value enter 4.4776.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
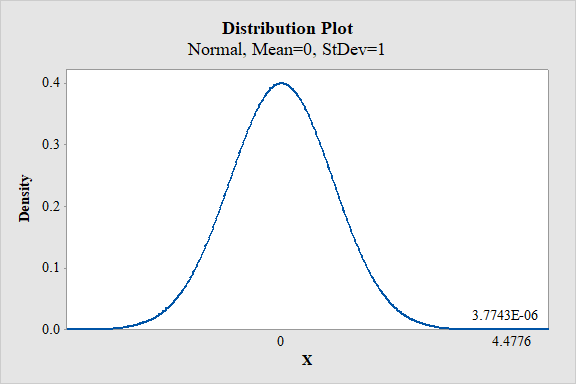
From the MINITAB output, the P-value is
Thus, the P-value is
Decision rule based on P-value:
If
If
Here, the level of significance is
Conclusion based on P-value approach:
The P-value is
Here, P-value is less than the
That is,
By the rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
d.
Find the machine that has to be bought by manufacturer.
d.
Answer to Problem 37E
The manufacturer has to by the more expensive machine.
Explanation of Solution
From part (c), it is known that the null hypothesis is rejected.
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
The claim was that, the manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
Since, the claim of the manufacturer is satisfied. The manufacturer has to buy the more expensive machine.
Thus, the manufacturer has to buy more expensive machine.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential Statistics
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





