
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.5.4P
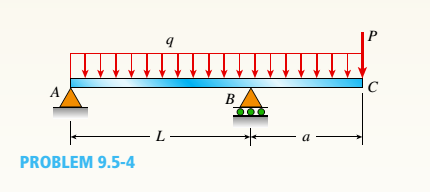
Beam ABC is loaded by a uniform load q and point load P at joint C. Using the method of superposition, calculate the deflection at joint C. Assume that L = 4 m, a =2ra, q = 15 kN/m, P = 7.5 kN, £ = 200 GPa, and / = 70.8 X 106 mm4.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
7. A motor shaft rotating at 1440 r.p.m. has to transmit 15 kW to a low speed shaft rotating at 500 r.p.m.
The teeth are 20° involute with 25 teeth on the pinion. Both the pinion and gear are made of cast iron
with a maximum safe stress of 56 MPa. A safe stress of 35 MPa may be taken for the shaft on which
the gear is mounted. Design and sketch the spur gear drive to suit the above conditions. The starting
torque may be assumed as 1,25 times the running torque.
Ruins 20 LW at 100 nm to another shaft running approxi
6.
A two stage reduction drive is to be designed to transmit 2 kW; the input speed being 960 r.p.m. and
overall reduction ratio being 9. The drive consists of straight tooth spur gears only, the shafts being
spaced 200 mm apart, the input and output shafts being co-axial.
2 A metal block of mass m = 10 kg is sliding along a frictionless surface with an initial speed
Vo, as indicated below. The block then slides above an electromagnetic brake that applies a
force FEB to the block, opposing its motion. The magnitude of the electromagnetic force
varies quadratically with the distance moved along the brake (x):
10
FEB = kx²,
with k
= 5
N
m²
V₁ = 8 m/s
m = 10 kg
FEB
Frictionless surface
Electromagnetic brake
⇒x
Determine how far the block slides along the electromagnetic brake before stopping, in m.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a...Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a simply...Ch. 9 - -3 The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam is loaded with a point...Ch. 9 - A I-meter-long, simply supported copper beam (E =...Ch. 9 - A wide-flange beam (W 12 x 35) supports a uniform...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded, steel wide-flange beam with...
Ch. 9 - What is the span length L of a uniformly loaded,...Ch. 9 - -6 Calculate the maximum deflection of a uniformly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam with a uniform load (see figure)...Ch. 9 - A gold-alloy microbeam attached to a silicon wafer...Ch. 9 - Obtain a formula for the ratio c/maxof the...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam model is often used to represent...Ch. 9 - B cams AB and CDE are connected using rigid link...Ch. 9 - -12 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -13 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -14 A cantilever beam AB supporting a triangularly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has a length L = 12 ft and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam with an overhang is subjected to d...Ch. 9 - -17 A cantilever beam AB is acted upon by a...Ch. 9 - -18 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -19 Derive the equations of the deflect ion curve...Ch. 9 - -20 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -21 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -22 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -23 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -1 Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -2 A simple beam AB is subjected to a distrib uted...Ch. 9 - -3 The simple beam AB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - -4 A beam with a uniform load has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -5 The distributed load acting on a cantilever...Ch. 9 - -6 A cantilever beam .4B is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - -7 A beam on simple supports is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -9 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -10 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 1600 ksi) is loaded...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 12 GPa) carries a...Ch. 9 - Copper beam AB has circular cross section with a...Ch. 9 - Beam ABC is loaded by a uniform load q and point...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam of a length L = 2.5 ft has a...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam carries a trapezoidal...Ch. 9 - -5-7 A cantilever beam AB carries three equalaly...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports five equally spaced...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure has an...Ch. 9 - Beam ACE hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - What must be the equation y =f(x) of the axis of...Ch. 9 - -12 Determine the angle of rotation Band...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACE shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to load P at...Ch. 9 - Use the method of superposition to find the angles...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9,5-15 for the anti-symmetric...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCD consisting of a simple span BD and an...Ch. 9 - A horizontal load P acts at end C of the bracket...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC having flexural rigidity EI = 75 kN irT...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation 0Band deflectionCh. 9 - -22 A simple beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - The overhanging beam A BCD supports two...Ch. 9 - A thin metal strip of total weight W and length L...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 9 - A beam A BCD rests on simple supports at B and C...Ch. 9 - The compound beam ABC shown in the figure has a...Ch. 9 - A compound beam ABC DE (see figure) consists of...Ch. 9 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and held...Ch. 9 - -30. Calculate the deflection at point C of a beam...Ch. 9 - Compound beam ABC is loaded by point load P = 1.5...Ch. 9 - The compound beam shown in the figure consists of...Ch. 9 - -33 Find the horizontal deflection hand verti cal...Ch. 9 - The fr a me A BCD shown in the heure is squeezed...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by counterclockwise...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by force P at 2L/3...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCDE has simple supports at B and D and...Ch. 9 - A frame ABC is loaded at point C by a force P...Ch. 9 - The wing of a large commercial jet is represented...Ch. 9 - The wing of a small plane is represented by a...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find required distance d (in terms of L) so that...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has two triangular loads as...Ch. 9 - -1 A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a uniform...Ch. 9 - The load on a cantilever beam AB has a triangular...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation BBand the...Ch. 9 - -5 Calen1ate the deflections S 3a ndCh. 9 - A cantileverbeam^Cßsupportstwo concentrated loads...Ch. 9 - Obtain formulas for the angle of rotation 0Aat...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to a load in the...Ch. 9 - -10 The simple beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to couples M0and 2A0...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - Beam ACB hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - -4 A simple beam ABCD has moment of inertia I near...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC has a rigid segment from A to B and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC has a moment of inertia 1,5 from...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam A B supports a...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam AB supports a...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 97-10, but now use the tapered...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACE is constructed with square cross...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded simple beam AB (see figure) of...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L supports a...Ch. 9 - A propped cantilever beam AB of length L and with...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is subjected to loads...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC with simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supporting a uniform load q over...Ch. 9 - The frame shown in the figure consists of a beam...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is loaded at the...Ch. 9 - The simple beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC supports a concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam ACB supports two concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam A CB shown in the hgure is...Ch. 9 - The frame A BC support s a concentrated load P at...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC DE supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC is subjected to a couple...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC rests on a simple support...Ch. 9 - A symmetric beam A BCD with overhangs at both ends...Ch. 9 - A heavy object of weight W is dropped onto the...Ch. 9 - An object of weight Wis dropped onto the midpoint...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6 It is...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 20 kN falls through a height h = 1,0...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 4000 lb falls through a height h =...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with a rectangular cross...Ch. 9 - A heavy flywheel rotates at an angular speed m...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height /;...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam JA of length Land height/; (see...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC of height h has a sliding...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height h (see...Ch. 9 - Beam AB has an elastic support kR at A, pin...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1: Determine the length, angle of contact, and width of a 9.75 mm thick leather belt required to transmit 15 kW from a motor running at 900 r.p.m. The diameter of the driving pulley of the motor is 300 mm. The driven pulley runs at 300 r.p.m. and the distance between the centers of two pulleys is 3 meters. The density of the leather is 1000 kg/m³. The maximum allowable stress in the leather is 2.5 MPa. The coefficient of friction between the leather and pulley is 0.3. Assume open belt drive.arrow_forward5. A 15 kW and 1200 r.p.m. motor drives a compressor at 300 r.p.m. through a pair of spur gears having 20° stub teeth. The centre to centre distance between the shafts is 400 mm. The motor pinion is made of forged steel having an allowable static stress as 210 MPa, while the gear is made of cast steel having allowable static stress as 140 MPa. Assuming that the drive operates 8 to 10 hours per day under light shock conditions, find from the standpoint of strength, 1. Module; 2. Face width and 3. Number of teeth and pitch circle diameter of each gear. Check the gears thus designed from the consideration of wear. The surface endurance limit may be taken as 700 MPa. [Ans. m = 6 mm; b= 60 mm; Tp=24; T=96; Dp = 144mm; DG = 576 mm]arrow_forward4. G A micarta pinion rotating at 1200 r.p.m. is to transmit 1 kW to a cast iron gear at a speed of 192 r.p.m. Assuming a starting overload of 20% and using 20° full depth involute teeth, determine the module, number of teeth on the pinion and gear and face width. Take allowable static strength for micarta as 40 MPa and for cast iron as 53 MPa. Check the pair in wear.arrow_forward
- I want to solve these choicesarrow_forward2. A spur gear made of bronze drives a mid steel pinion with angular velocity ratio of 32: 1. The pressure angle is 14½. It transmits 5 kW at 1800 r.p.m. of pinion. Considering only strength, design the smallest diameter gears and find also necessary face width. The number of teeth should not be less than 15 teeth on either gear. The elastic strength of bronze may be taken as 84 MPa and of steel as 105 MPa. Lewis factor for 14½½ pressure angle may be taken 0.684 0.124 y = No. of teeth as [Ans. m 3 mm; b= 35 mm; Dp = 48 mm; D= 168 mm]arrow_forwardQ2. Determine the safety factors for the bracket rod shown in Figure 2 based on both the distortion-energy theory and the maximum shear theory and compare them. Given: The material is 2024-T4 aluminum with a yield strength of 47 000 psi. The rod length /= 6 in. and arm a = 8 in. The rod outside diameter od 1.5 in., id = 1 in, h=2 in., t=0.5 in., Load F= 1000 lb. Assumptions: The load is static and the assembly is at room temperature. Consider shear due to transverse loading as well as other stresses. (Note: solve in SI units) wall tube Figure 2 armarrow_forward
- The question has been set up with all the cuts needed to accurately derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). Using the cuts free body diagrams set up below, derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). If you use the method of cuts then validate your answers using calculus or vice versa.arrow_forwardIt is required to treat 130 kmol/hr of chloroform-air feed gas mixture that contains 12% chloroform. It is required to remove 93% of chloroform using 150 kmol/hr of solvent that contains 99.6% water and 0.4% chloroform. The cross sectional area of the column is 0.8 m². Calculate the column height using the following data; kx'.a = 1.35 (kmol/m³.s (Ax)), and ky'.a = 0.06 (kmol/m³.s (Ay)), kx/ky = 1.35, and the equilibrium data are: X 0 0.0133 0.033 y 0 0.01 0.0266 0.049 0.064 0.0747 0.0933 0.1053 0.0433 0.06 0.0733 0.111 0.1 0.12 0.14arrow_forward४ B: Find the numerical solution for the 2D equation below and calculate the temperature values for each grid point shown in Fig. 2 (show all steps). (Do only one trail using following initial values and show the final matrix) [T1] T₂ T3 [T] 1 = [0] 0 0 d dx dx) (ka)+4(ka) = dy -20xy, k = 1 + 0.3 T ge L=3cm, 4x= Ay B.Cs.: at x=0=LT=0°C at y=0-L T=10°C Fig. (2)arrow_forward
- : +0 العنوان use only Two rods fins) having same dimensions, one made orass (k = 85 Wm K) and the mer of copper (k = 375 W/m K), having of their ends inserted into a furna. At a section 10.5 cm a way from furnace, the temperature of brass rod 120 Find the distance at which the ame temperature would be reached in the per rod ? both ends are ex osed to the same environment. ns 2.05 ۲/۱ ostrararrow_forwardFor the beam show below, draw A.F.D, S.F.D, B.M.D 6 kN/m 1 M B. 3 M Marrow_forward1. Two long rods of the same diameter-one made of brass (k=85w/m.k) and the other made of copper (k=375 w/m.k) have one of their ends inserted into a furnace (as shown in the following figure). Both rods are exposed to the same environment. At a distance of 105 mm from the furnace, the temperature of the brass rod is 120°C. At what distance from the furnace will the same temperature be reached in the copper rod? Furnace 105 mm T₁ Brass rod ⑪ h Too- x2- Ti Copper rodarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY