
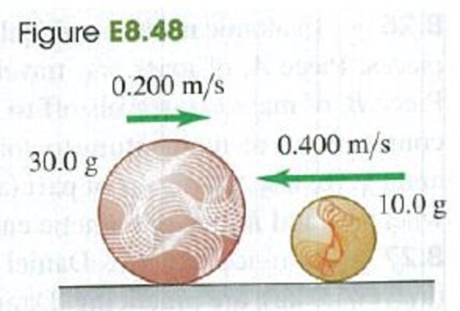
A 10.0-g marble slides to the left at a speed of 0.400 m/s on the frictionless, horizontal surface of an icy New York sidewalk and has a head-on, elastic collision with a larger 30.0-g marble sliding to the right at a speed of 0.200 m/s (Fig. E8.48). (a) Find the velocity of each marble (magnitude and direction) after the collision. (Since the collision is head-on, all motion is along a line.) (b) Calculate the change in momentum (the momentum after the collision minus the momentum before the collision) for each marble. Compare your values for each marble, (c) Calculate the change in kinetic energy (the kinetic energy after the collision minus the kinetic energy before the collision) for each marble. Compare your values for each marble.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
University Physics (14th Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
- Two skateboarders, with masses m1 = 75.0 kg and m2 = 65.0 kg, simultaneously leave the opposite sides of a frictionless half-pipe at height h = 4.00 m as shown in Figure P11.49. Assume the skateboarders undergo a completely elastic head-on collision on the horizontal segment of the half-pipe. Treating the skateboarders as particles and assuming they dont fall off their skateboards, what is the height reached by each skateboarder after the collision? FIGURE P11.49arrow_forwardAssume the pucks in Figure P11.66 stick together after theircollision at the origin. Puck 2 has four times the mass of puck 1 (m2 = 4m1). Initially, puck 1s speed is three times puck 2s speed (v1i = 3v2i), puck 1s position is r1i=x1ii, and puck 2s position is r2i=y2ij. a. Find an expression for their velocity after the collision in terms of puck 1s initial velocity. b. What is the fraction Kf/Ki that remains in the system?arrow_forwardInitially, ball 1 rests on an incline of height h, and ball 2 rests on an incline of height h/2 as shown in Figure P11.40. They are released from rest simultaneously and collide in the trough of the track. If m2 = 4 m1 and the collision is elastic, find an expression for the velocity of each ball immediately after the collision. FIGURE P11.40 Problems 40 and 41.arrow_forward
- A cannon is rigidly attached to a carriage, which can move along horizontal rails but is connected to a post by a large spring, initially unstretchcd and with force constant k = 2.00 104 N/m, as shown in Figure P8.60. The cannon fires a 200-kg projectile at a velocity of 125 m/s directed 45.0 above the horizontal. (a) Assuming that the mass of the cannon and its carriage is 5 000 kg, find the recoil speed of the cannon. (b) Determine the maximum extension of the spring. (c) Find the maximum force the spring exerts on the carriage. (d) Consider the system consisting of the cannon, carriage, and projectile. Is the momentum of this system conserved during the firing? Why or why not?arrow_forwardA water molecule consists of an oxygen atom with two hydrogen atoms bound to it (Fig. P8.36). The angle between the two bonds is 106. If the bonds are 0.100 nm long, where is the center of mass of the molecule? Figure P8.36arrow_forwardSand from a stationary hopper falls onto a moving conveyor belt at the rate of 5.00 kg/s as shown in Figure P8.64. The conveyor belt is supported by frictionless rollers and moves at a constant speed of v = 0.750 m/s under the action of a constant horizontal external force Fext supplied by the motor that drives the belt. Find (a) the sands rate of change of momentum in the horizontal direction, (b) the force of friction exerted by the belt on the sand, (c) the external force Fext, (d) the work done by Fext in 1 s, and (e) the kinetic energy acquired by the falling sand each second due to the change in its horizontal motion. (f) Why are the answers to parts (d) and (e) different? Figure P8.64arrow_forward
- A 100-g firecracker is launched vertically into the air and explodes into two pieces at the peak of its trajectory. If a 72-g piece is projected horizontally to the left at 20 m/s, what is the speed and direction of the other piece?arrow_forwardWhat exhaust speed is required to accelerate a rocket in deep space from 800 m/s to 1000 m/s in 5.0 s if the total rocket mass is 1200 kg and the rocket only has 50 kg of fuel left?arrow_forwardFrom what might be a possible scene in the comic book The X-Men, the Juggernaut (mJ) is charging into Colossus (mC) and the two collide. The initial speed of the Juggernaut is vJi and the initial speed of Colossus is vCi. After the collision, the final speed of the Juggernaut is vJf and the final speed of Colossus is vCf as they each bounce off of the other, heading in opposite directions. a. What is the impulse experienced by the Juggernaut? b. What is the impulse experienced by Colossus? c. In your own words, explain how these impulses must compare with each other and how they are related to the average force each superhero experiences during the collision.arrow_forward
- Two bumper cars at the county fair are sliding toward one another (Fig. P11.54). Initially, bumper car 1 is traveling to the east at 5.62 m/s, and bumper car 2 is traveling 60.0 south of west at 10.00 m/s. They collide and stick together, as the driver of one car reaches out and grabs hold of the other driver. The two bumper cars move off together after the collision, and friction is negligible between the cars and the ground. a. If the masses of bumper cars 1 and 2 are 596 kg and 625 kg respectively, what is the velocity of the bumper cars immediately after the collision? b. What is the kinetic energy lost in the collision? c. Compare your answers to part (b) from this and Problem 54. Is one answer larger than the other? Discuss and explain any differences you find.arrow_forwardA mother pushes her son in a stroller at a constant speed of 1.52 m/s. The boy tosses a 56.7-g tennis ball straight up at 1.75 m/s and catches it. The boys father sits on a bench and watches. a. According to the mother, what are the balls initial and final momenta? b. According to the father, what are the balls initial and final momenta? c. According to the mother, is the balls momentum ever zero? If so, when? If not, why not? d. According to the father, is the balls momentum ever zero? If so, when? If not, why not?arrow_forwardA 5-kg cart moving to the right with a speed of 6 m/s collides with a concrete wall and rebounds with a speed of 2 m/s. What is the change in momentum of the cart? (a) 0 (b) 40 kg m/s (c) 40 kg m/s (d) 30 kg m/s (e) 10 kg m/sarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





