
Concept explainers
Using Figures 8.7 and 8.9 as a guide, draw a dinucleotide composed of C and A. Next to this, draw the complementary dinucleotide in an antiparallel fashion. Connect the dinucleotides with the appropriate hydrogen bonds.
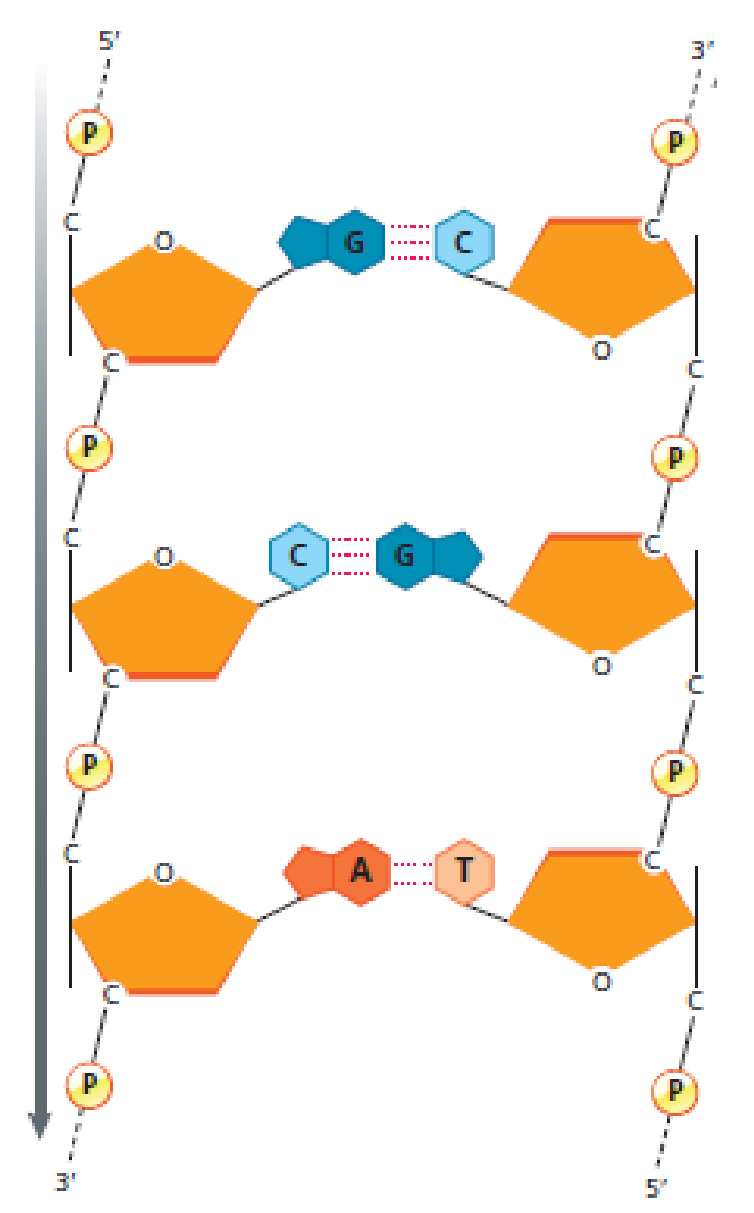
FIGURE 8.9 The two polynucleotide chains in DNA run in opposite directions. The left strand runs 5′ to 3′, and the right strand runs 3′ to 5′. The base sequences in each strand are complementary. An A in one strand pairs with a T in the other strand, and a C in one strand is paired with a G in the opposite strand.
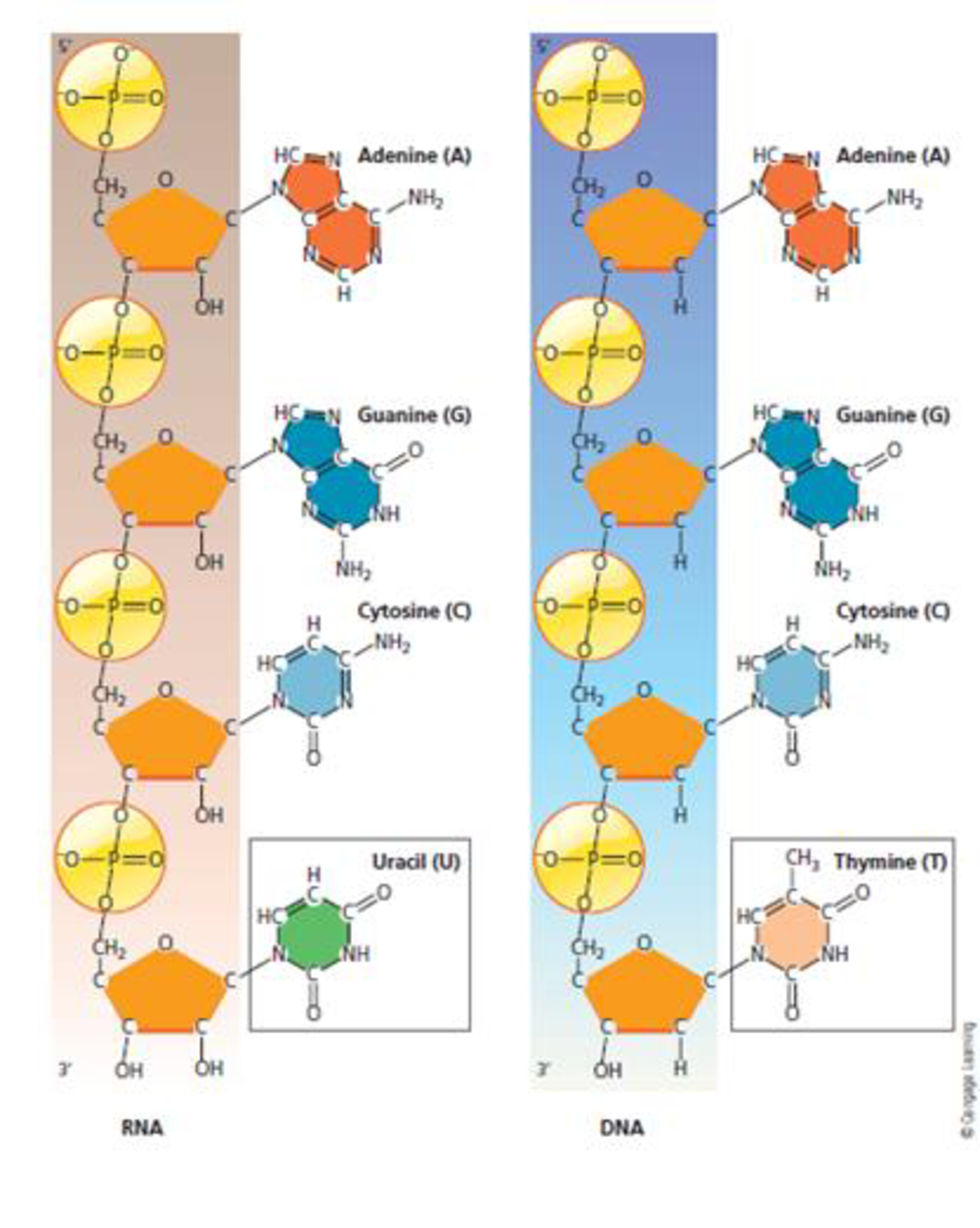
FIGURE 8.7
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
- How many kilobases of the DNA strand below will code for the protein product?arrow_forwardDraw the chemical structure of a dinucleotide composed of A and G. Opposite this structure, draw the dinucleotide composed of T and C in an antiparallel (or upside-down) fashion. Form the possible hydrogen bonds.arrow_forwardFor the following DNA sequence: 3’–CGATACGGCTATGCCGGCATT–5’ Write: a) the sequence of the complementary DNA strandarrow_forward
- The following is diagram of a generalized tetranucleotide. Carbons exist at corners on the shapes and phosphate groups are filled circles. A. Is this a DNA or an RNA Molecule? B. Where is the 3’ end of this tetranucleotide? C. Given that the DNA strand which served as a template for the synthesis of this tetranucleotide was composed of the bases 5’-ACAG-3’, where are the expected bases?arrow_forwardDraw a stylized diagram of double-stranded DNA. Use a pentagon for sugar, a circle for phosphate and a square for bases. Label each base A, T, C or G. Show two pairs of nucleotides connected via hydrogen bonds (use all 4 letters). Show the polarity of each strand and clearly indicate the number of hydrogen bonds in each pair of nucleotides. Draw a solid-line circle around a nucleotide. Draw a dashed-line circle around a nucleoside. Indicate a phosphodiester bond using an arrow.arrow_forwardIn the DNA double-helix structure, the larger of the two grooves formed by the helical twist where certain base pairs are exposed is called the:arrow_forward
- 1) You will start off by laying out your individual nucleotides for the first strand using the following sequence: A, C, G, T. 2. Using a pem or pemcil, indicate the phosphodiester bond that forms between each of the nucleotides. Look at figure 7 Label the 5' and 3' ends of the strand you just built. Identify and label one purine and one pyrimidine nitrogen base. 2. You are now ready to build your second strand. The second strand will be antiparallel. You will need to flip the nucleotides upside down to form hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases. Remember, A bonds to T through 2 hydrogen bonds and C to G with 3 hydrogen bonds. Draw in the hydrogen bonds with a chalk marker. Look at figure 8. Label the 5' and 3' ends of the second strand. Take a photo of your completed molecule and insert it into your lab notebook. 3. Explain dehydration synthesis, including what atoms are removed, and what molecule becomes a byproduct of these reactions.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the DNA dinucleotide C-T. Identify the 5′ and 3′ ends of this dinucleotide.arrow_forwarddraw a picture of a SINGLE strand of DNA (a polynucleotide) composed of 9 (nine) nucleotides of your choice. Do use ALL 4 nucleotides. Use 3 simple symbols to represent the phosphate, the sugar, and the base in each nucleotide. For example, use a circle with the letter “P” for the phosphate in the backbone, a square with the letter “S” for the sugar in the backbone, and a triangle with the letter “A, T, C or G” for the bases.As you draw the diagram be sure to put solid lines for the covalent bonds you are creating to join new nucleotides to the elongating DNA chain.arrow_forward
- What is the nucleotide sequence of the complementary strand of the DNA molecule: 5’-AATGCGATCTTCAT-3’? Indicate the 5’ and 3’ ends. Follow the same format as the given sequence.arrow_forwardA) Draw the structure and give the name of a nucleotide made of G + ribose. B) Write the complementary base sequence for the matching strand in the DNA section shown below.5’ – C T G T A T A C G T T A – 3’ Please answer both partsarrow_forwardWrite the sequence of the complementary DNA strand that pairs with each of the following DNA base sequences:(a) TTAGCC(b) AGACATarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
