
Problem 7-29 Current liabilities
The following selected transactions were taken from the books of Ripley Company for 2018:
- 1. On February 1, 2018, borrowed $70,000 cash from the local bank. The note had a 6 percent interest rate and was due on June 1, 2018.
- 2. Cash sales for the year amounted to $240,000 plus sales tax at the rate of 7 percent.
- 3. Ripley provides a 90-day warranty on the merchandise sold. The warranty expense is estimated to be 1 percent of sales.
- 4. Paid the sales tax to the state sales tax agency on $210,000 of the sales.
- 5. Paid the note due on June 1 and the related interest.
- 6. On November 1, 2018, borrowed $20,000 cash from the local bank. The note had a 6 percent interest rate and a one-year term to maturity.
- 7. Paid $2,100 in warranty repairs.
- 8. A customer has filed a lawsuit against Ripley for $1 million for breach of contract. The company attorney does not believe the suit has merit.
Required
a. Answer the following questions:
(1) What amount of cash did Ripley pay for interest during 2018?
(2) What amount of interest expense is reported on Ripley’s income statement for 2018?
(3) What is the amount of warranty expense for 2018?
b. Prepare the current liabilities section of the
c. Show the effect of these transactions on the financial statements using a horizontal statements model like the one below. Use + for increase, − for decrease, and NA for not affected. In the

a.1
Calculate the amount of cash that company R paid for interest during 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Interest Expense: The cost of debt which is incurred during a particular accounting period is called interest expense. The interest amount is a fixed interest rate payable on the principal amount of debt.
Calculate the amount of cash that company R paid for interest during 2018.
On February 1, Year 1, Company R borrowed $70,000 cash from bank at 6% interest rate and due on June 1, Year 1. Hence, the cash paid for interest during 2018 is calculated as below:
Cash paid for interest = Principal amount× Interest rate×Time= $70,000 × 6% × 4 months12 months= $1,400
Hence, cash paid for interest expense during 2018 is $1,400.
a.2
Calculate the amount of interest expense that is reported on Company R’s income statement for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Interest Expense: The cost of debt which is incurred during a particular accounting period is called interest expense. The interest amount is a fixed interest rate payable on the principal amount of debt.
Calculate the amount of interest expense that is reported on Company R’s income statement for 2018.
On February 1, Year 1, Company R borrowed $70,000 cash from bank at 6% interest rate and due on June 1, Year 1. On November 1, Year 1, Company R borrowed $20,000 cash from bank at 6% interest rate and a one-year term to maturity. Hence, the total interest expense for 2018 is calculated as below:
| Calculation of interest expense for 2018 | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Interest expense on $70,000 borrowings ($70,000 × 6% × [4 ÷ 12]) | $1,400 |
| Interest expense om$20,000 borrowings ($20,000 × 6% × [2 ÷ 12]) | $200 |
| Total interest expense | $1,600 |
Table (1)
Hence, the amount of interest expense that is reported on Company R’s income statement for 2018 is $1,600.
a.3
Calculate the amount of warranty expense for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Warranty: It is an agreement made by the company to provide guarantee against the defects in the products.
Calculate the amount of warranty expense for 2018.
Company R provides a 90-days warranty on the merchandise sold. The estimated warranty expense is to be 1% of sales. Total sales are $240,000. Hence, the amount of warranty expense for 2018 is calculated as below:
Warranty expense = $240,000 × 1%= $2,400
Hence, the amount of warranty expense for 2018 is $2,400.
b.
Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at December 31, 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Current liability: Current liability is an obligation that the companies need to pay from its current assets or creation of other current liabilities within a fiscal year or the operating cycle whichever is higher.
Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at December 31, Year 1.
| Company R | |
| Balance sheet (partial) | |
| As on December 31, Year 1 | |
| Current Liabilities: | |
| Interest Payable | $ 200 |
| Sales Tax Payable | 2,100 |
| Warranty Payable | 300 |
| Notes Payable | 20,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $22,600 |
Table (2)
Hence, total current liabilities as on December 31, 2018 are $22,600.
Working notes:
Prepare the T-accounts to calculate the current liabilities as on December 31, 2018.
| Interest payable | |||
| 6. refer table (1) | $200 | ||
| Ending Balance | $200 | ||
| Sales tax payable | |||
| 4. ($210,000 × 7%) | $14,700 | 2. ($240,000 × 7%) | $16,800 |
| Ending Balance | 2,100 | ||
| Warranty payable | |||
| 7. | $2,100 | 3. ($240,000 × 1%) | $2,400 |
| Ending Balance | 300 | ||
| Notes payable | |||
| 1. | 70,000 | ||
| 5. | 70,000 | 6. | 20,000 |
| Ending Balance | 20,000 | ||
Note: A customer filed a lawsuit against Company R for $1million for breach of contract. Company R’s attorney does not believe the suit has merit. Hence, it is deemed to be remote obligation (contingent liability). Remote obligations are not reported in the financial statements or disclosed in the notes to the statements.
c.
Show the effect of these transactions on the financial statements using a horizontal statements model. Use + for increase, − for decrease, and NA for not affected. In the Cash Flow column, indicate whether the item is an operating activity (OA), investing activity (IA), or financing activity (FA).
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation: Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below.
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity
Show the effect of these transactions on the financial statements using a horizontal statements model.
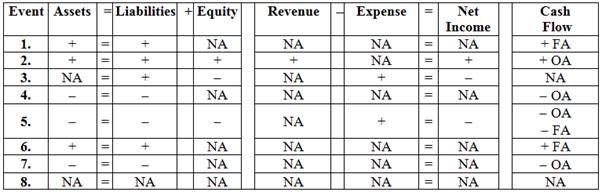
Figure (3)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Journalize entries and prepare a bank reconciliation 1. Cash balance per bank, July 31, $8,004. 2. July bank service charge not recorded by the depositor $46. 3. Cash balance per books, July 31, $8,096. 4. Deposits in transit, July 31, $3,266. 5. $1,840 collected from a customer for Sheridan Company in July by the bank through electronic funds transfer. The collection has not been recorded by Sheridan Company. 6. Outstanding checks, July 31, $1,380.arrow_forwardSales reported on the income statement for Lansing Corp. were $315,420. The accounts receivable balance declined by $29,750 over the year. Determine the amount of cash received from customers.arrow_forwardCompute the company's gross profit percentage of this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- OPD, who is claimed as a dependent by his parents, is 17. He received income of $3,400 from a trust fund and $700 from wages. He had $1,200 in itemized deductions. What is his taxable income? I need help with this financial accounting problem using accurate calculation methods.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardPlease give me answer with accounting questionarrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





