
Prepare and Interpret Income Statements; Changes ¡n Both Sales and Production; Lean Production L07—1, L07—2, L07—3
Starfax, Inc., manufactures a small part that is widely used in various electronic products such as home computers. Results for the first threeyears of operations were as follows (absorption costing basis):
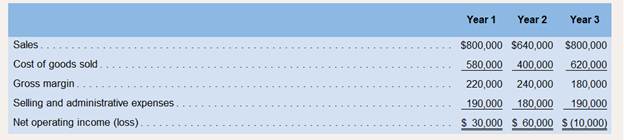 In the latter part of Year 2, a competitor went out of business and in the process dumped a large number of units on the market. As a result,Starfax’s sales dropped by 20% during Year 2 even though production increased during the year. Management had expected sales to remain constant at 50,000 units; the increased production was designed to provide the company with a buffer of protection against unexpected spurts in demand. By the start of Year 3, management could see that it had excess inventory and that spurts in demand were unlikely. To reduce the excessive inventories, Starfax cut back production during Year 3, as shown below:
In the latter part of Year 2, a competitor went out of business and in the process dumped a large number of units on the market. As a result,Starfax’s sales dropped by 20% during Year 2 even though production increased during the year. Management had expected sales to remain constant at 50,000 units; the increased production was designed to provide the company with a buffer of protection against unexpected spurts in demand. By the start of Year 3, management could see that it had excess inventory and that spurts in demand were unlikely. To reduce the excessive inventories, Starfax cut back production during Year 3, as shown below:
 Additional information about the company follows:
Additional information about the company follows:
a. The company’s plant is highly automated. Variable manufacturing expenses (direct materials, direct labor. and variablemanufacturing
b. A new fixed manufacturing overhead rate is computed each year based that year’s actual fixed manufacturing overhead costsdivided by the actual number of units produced.
c. Variable selling and administrative expenses were $1 per unit sold in each year. Fixed selling and administrative expensestotaled $140.000 per year.
d. The company uses a FIFO inventory flow assumption. (FIFO means first-in first-out. In other words, it assumes that theoldest units in inventory are sold first.)
Starfax’s management can’t understand why profits doubled during Year 2 when sales dropped by 20% and why a loss was incurred during Year3 when sales recovered to previous levels.
Required:
1. Prepare a contribution format variable costing income statement for each year.
2. Refer to the absorption costing income statements above.
a. Compute the unit product cost in each year under absorption costing. Show how much of this cost is variable and how much is fixed.
b. Reconcile the variable costing and absorption costing net operating income figures for each year.
3. Refer again to the absorption costing income statements. Explain why net operating income was higher in Year 2 than it was in Year 1under the absorption approach, in light of the fact that fewer units were sold in Year 2 than in Year 1.
4. Refer again to the absorption costing income statements. Explain why the company suffered a loss in Year 3 but reported a profit in Year1 although the same number of units was sold in each year.
5. a. Explain how operations would have differed in Year 2 and Year 3 if the company had been using Lean Production, with the result thatending inventory was zero.
b. If Lean Production had been used during Year 2 and Year 3, what would the company’s net operating income (or loss) have been ineach year under absorption costing? No computations are necessary.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- Norenberg Corporation manufactures a variety of products. The following data pertain to the company's operations over the last two years: Variable costing net operating income, last year $ 88,600 Variable costing net operating income, this year $ 96,100 Increase in Ending inventory, last year 600 units Decrease in Ending inventory, this year 2,300 units Fixed manufacturing overhead cost per unit this year and last year $ 7 per unit What was the absorption costing net operating income this year? Select one: a. $80,000 b. $100,500 c. $108,000 d. $112,200arrow_forwardThe following information was extracted from the first year absorption-based accounting records of COCOMELON Co. (refer to image) If COCOMELON Co. had used variable costing in its first year of operations, how much income (loss) before income taxes would it have reported? a. (P6,000) b. P54,000 c. P26,000 d. P2,000arrow_forwardVariable-Costing and Absorption-Costing Income Borques Company produces and sells wooden pallets that are used for moving and stacking materials. The operating costs for the past year were as follows: During the year, Borques produced 200,000 wooden pallets and sold 204,300 at 9 each. Borques had 8,200 pallets in beginning finished goods inventory; costs have not changed from last year to this year. An actual costing system is used for product costing. Required: 1. What is the per-unit inventory cost that is acceptable for reporting on Borquess balance sheet at the end of the year ? How many units are in ending inventory? What is the total cost of ending inventory? 2. Calculate absorption-costing operating income. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What would the per-unit inventory cost be under variable costing? Does this differ from the unit cost computed in Requirement 1? Why? 4. Calculate variable-costing operating income. 5. Suppose that Borques Company had sold 196,700 pallets during the year. What would absorption-costing operating income have been? Variable-costing operating income?arrow_forward
- Jellison Company had the following operating data for its first two years of operations: Jellison produced 90,000 units in the first year and sold 80,000. In the second year, it produced 80,000 units and sold 90,000 units. The selling price per unit each year was 12. Jellison uses an actual costing system for product costing. Required: 1. Prepare income statements for both years using absorption costing. Has firm performance, as measured by income, improved or declined from Year 1 to Year 2? 2. Prepare income statements for both years using variable costing. Has firm performance, as measured by income, improved or declined from Year 1 to Year 2? 3. Which method do you think most accurately measures firm performance? Why?arrow_forwardCost Classification, Income Statement Gateway Construction Company, run by Jack Gateway, employs 25 to 30 people as subcontractors for laying gas, water, and sewage pipelines. Most of Gateways work comes from contracts with city and state agencies in Nebraska. The companys sales volume averages 3 million, and profits vary between 0 and 10% of sales. Sales and profits have been somewhat below average for the past 3 years due to a recession and intense competition. Because of this competition, Jack constantly reviews the prices that other companies bid for jobs. When a bid is lost, he analyzes the reasons for the differences between his bid and that of his competitors and uses this information to increase the competitiveness of future bids. Jack believes that Gateways current accounting system is deficient. Currently, all expenses are simply deducted from revenues to arrive at operating income. No effort is made to distinguish among the costs of laying pipe, obtaining contracts, and administering the company. Yet all bids are based on the costs of laying pipe. With these thoughts in mind, Jack looked more carefully at the income statement for the previous year (see below). First, he noted that jobs were priced on the basis of equipment hours, with an average price of 165 per equipment hour. However, when it came to classifying and assigning costs, he needed some help. One thing that really puzzled him was how to classify his own 114,000 salary. About half of his time was spent in bidding and securing contracts, and the other half was spent in general administrative matters. Required: 1. Classify the costs in the income statement as (1) costs of laying pipe (production costs), (2) costs of securing contracts (selling costs), or (3) costs of general administration. For production costs, identify direct materials, direct labor, and overhead costs. The company never has significant work in process (most jobs are started and completed within a day). 2. Assume that a significant driver is equipment hours. Identify the expenses that would likely be traced to jobs using this driver. Explain why you feel these costs are traceable using equipment hours. What is the cost per equipment hour for these traceable costs?arrow_forwardSuppose Grainy Day is considering discontinuing its tasty loops product line. Assume that during the past year, the tasty loops' product line income statement showed the following: A B 1 Sales revenue $7,550,000 2 Less: Cost of goods sold 6,400,000 3 Gross profit 1,150,000 4 Less: Operating expenses 1,650,000 5 Operating income (loss) $(500,000) Fixed manufacturing overhead costs account for 40% of the cost of goods, while only 30% of the operating expenses are fixed. Since the tasty loops line is just one of the company's cereal operations, only $780,000 of direct fixed costs (the majority of which is advertising) will be eliminated if the product line is discontinued. The remainder of the fixed costs will still be incurred by the company. If the company decides to discontinue the product line, what will happen to the company's operating income? Should Grainy Day discontinue the tasty loops product line?arrow_forward
- SOLVE THE GIVEN MCQS: 1) Kaaua Corporation has provided the following data for its two most recent years of operation: Selling price per unit $ 83 Manufacturing costs: Variable manufacturing cost per unit produced: Direct materials $ 13 Direct labor $ 7 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 4 Fixed manufacturing overhead per year $ 396,000 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable selling and administrative expense per unit sold $ 4 Fixed selling and administrative expense per year $ 72,000 Year 1 Year 2 Units in beginning inventory 0 2,000 Units produced during the year 12,000 11,000 Units sold during the year 10,000 9,000 Units in ending inventory 2,000 4,000 Which of the following statements is true for Year 2? A The amount of fixed manufacturing overhead deferred in inventories is $534,000 B The amount of fixed manufacturing overhead deferred in inventories is $78,000 C The amount of fixed…arrow_forwardA company produces products A and B, each of which can be sold at an intermediate phase of production or can be processed further to make a more refined product. Information about the company's products follows: Product A B Costs incurred to get product to intermediate stage $65,000 $35,000 O Decrease in profitability of $75,000 Increase in profitability of $5,000 None of the above Increase in profitability of $80,000 O Increase in profitability of $85,000 Additional Sales value at intermediate stage processing costs $150,000 $59,000 What would be the impact on profitability of processing Product A further, rather than selling product A at the intermediate stage? $75,000 $15,000 Sales value at completion $230,000 $69,000arrow_forwardBell enterprises currently produces several products. Model L78 is showing a net operating loss as indicated by the following condensed income statement prepared for the year ended Dec 31. Sales (1500 units at $320). $480,000 Variable costs(1500 units at $240) $360,000 Contribution margin $120,000 Fixed cost. $125,000 Operating loss. $(5,000) You have been hired by Bell Ent to help analyse the decision as to whether to eliminate Model L78. Upon investigation you discover that if Model L78 is eliminated, $20,000 of the fixed costs shown on the above condensed income statement can be eliminated. The rest of the fixed costs allocated to Model L78 are common fixed costs that will be allocated to the remaining two products. Assess whether Bell Ent should discontinue Model L78.arrow_forward
- ! Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] O'Brien Company manufactures and sells one product. The following information pertains to each of the company's first three years of operations: Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative Fixed costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expenses a. Compute the unit product cost for Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3. b. Prepare an income statement for Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3. During its first year of operations, O'Brien produced 98,000 units and sold 74,000 units. During its second year of operations, it produced 80,000 units and sold 99,000 units. In its third year, O'Brien produced 90,000 units and sold 85,000 units. The selling price of the company's product is $78 per unit. Req 4A 4. Assume the company uses absorption costing and a LIFO inventory flow assumption (LIFO…arrow_forwardSierra Company incurs the following costs to produce and sell its only product. Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expenses 10 9. %24 24 $87,750 $ 315,000 During this year, 29,250 units were produced and 25,250 units were sold. The Finished Goods inventory account at the end of this year shows a balance of $84,000 for the 4,000 unsold units. Required: 1-a. Calculate this year's ending balance in Finished Goods inventory two ways-using variable costing and using absorption costing. 1-b. Does it appear that the company is using variable costing or absorption costing to assign costs to the 4,000 units in its Finished Goods inventory? 2. Assume that the company wishes to prepare this year's financial statements for its stockholders. a. Is Finished Goods inventory of $84,000 the correct amount to include on the…arrow_forwardRequired Information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Ramort Company reports the following for its single product. Ramort produced and sold 20,000 units this year. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses Sales price Compute gross profit under absorption costing. RAMORT COMPANY Gross Profit (Absorption Costing) Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit 1,200,000 $10 per unit $ 12 per unit $3 per unit $ 40,000 per year $ 2 per unit $ 65,200 per year $ 60 per unitarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning


