
To analyze:
The process by which unsaturation affects the membrane fluidity.
Given:
Introduction:
The saturated fatty acids have no scope of addition of any molecule due to the presence of double bonds. The unsaturated fatty acids increase the membrane fluidity. In cold temperatures, the amounts of unsaturated fatty acids are high to prevent the membrane from damaging leading to the death of the organism. An experiment to comparatively study the fluidity and composition of cell membranes was conducted by the researchers. They maintained arctic sculpin at 0°C, a group of goldfish at 5°C, other group of goldfish at 25°C, desert pupfish at 34°C, and rats at normal temperature of 21°C and incubated them for several days. Researchers then extracted the membranes of the neuronal cells of all these animals.
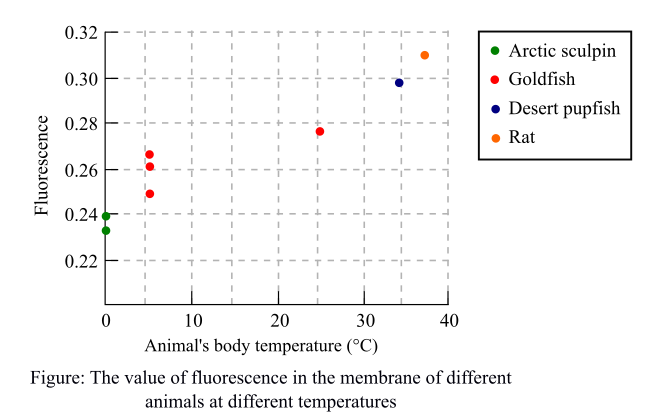
A fluorescent molecule to each of the extracted membranes was added and the membranes were incubated at 20°C. Fluorescence was measured and a graph was plotted by them, which indicates fluorescence against the body temperature of each of the animals.
The following graph depicted the fluorescence of each animal at different temperatures. The more the value of fluorescence, less will be the movement of molecules depicting a less fluid membrane.
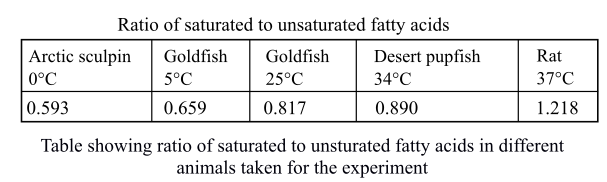
The following table was drawn by the researchers showing the ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids in the phospholipid phosphatidyl choline for different animals taken into consideration.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- In this cartoon, imagine that Romeo is a potassium ion (K+) and Juliet is a sodium ion (Na+). Explain why they're stuck on their own sides of the membrane and what they need to get through it. The Parameclum Parlor Wherefore art thou, Romeo?! Fm stuck behind this semipermeable membrane! Star-crossed solutes Ameba Sistersarrow_forwardIn general, what is the relationship between membrane fluidity and membrane permeability?arrow_forwardWhy the composition of biological membrane varies ? Should it be helpful in membrane physiology ?arrow_forward
- What kind of membrane transport occurs when pre-synaptic neurons release neurotransmitters? A Endocytosis B Exocytosis © Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusionarrow_forward"Tight junctions perform two distinct functions: they seal the space between cells to restrict paracellular flow and they fence off plasma membrane domains to prevent the mixing of apical and basolateral membrane proteins" is true or false.arrow_forwardDifference between Osmosis and Diffusionarrow_forward
- At this point, go over your answers to the activit ies given earlier in this lesson before you fill out the table below. Table 20: Interdependence of Function and Fom in the Cell Membrane Which components of the cell membrane enable it to perform this function? Function of the Cell Membrane How do these components help the cell membrane in performing this function? iully control the passage of substances through its membrane. However, all activit ort, involve energy. This leads us to another characte As stated in the first section of this lesson, maintaining homeostasis requires ise this in poweringarrow_forwardLeft Compartment Right Compartment 7 grams of Z per liter solution 4 grams of XY per liter of solution total volume = 1 liter. total volume = 1 liter Solute Z has a molecular weight of 20 (non-dissociable) Solute XY has a molecular weight of 10 (dissociates into X+ and Y-) 1. If the membrane is impermeable to all solutes, and there are 7 g/l of solute in the left compartment, what concentration of XY (g/l) in right compartment would make the solutions isotonic?arrow_forwardFor most neurons, the extracellular concentration of chloride ions (Cl-) is 108 mM, whilethe intracellular concentration of Cl- is 5 mM.If the plasma membrane becomes more permeable to Cl-, would there be Clinflux or Cl- efflux at an RMP of -70 mV? Why?arrow_forward
- Concerning permeability what type of membrane is the cell membrane?arrow_forwardLeft Compartment Right Compartment 7 grams of Z per liter solution 4 grams of XY per liter of solution total volume = 1 liter total volume = 1 liter Solute Z has a molecular weight of 20 (non-dissociable) Solute XY has a molecular weight of 10 (dissociates into X+ and Y-) If X+ and Y- are ions, which are permeable through the membrane, and Z is not, what will happen and why?arrow_forwardDescribe the two ways that the cell can increase/decrease membrane fluidity.arrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
