
Modified Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134261430
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.12, Problem 37P
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the following reaction in which C is the most stable and B the least stable of the three species and the transition state going from A to B is more stable than the transition state going from B to C:
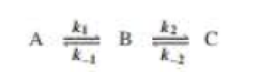
- a. How many intermediates are there?
- b. How many transition states are there?
- c. Which step has the greater rote constant in the forward direction?
- d. Which step has the greater rate constant in the reverse direction?
- e. Of the four steps, which has the greatest rate constant?
- f. Which is the rote-determining step in the forward direction?
- g. Which is the rate-determining step in the reverse direction?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the following reaction in which C is the most stable and B the least stable of the three species and the transition state going from A to B is more stable than the transition state going from B to C:a.How many intermediates are there? b. How many transition states are there? c. Which step has the greater rate constant in the forward direction? d. Which step has the greater rate constant in the reverse direction? e. Of the four steps, which has the greatest rate constant? f. Which is the rate-determining step in the forward direction? g. Which is the rate-determining step in the reverse direction?
None
The reaction for the formation of product X:A + B --> C + D (slow)B + D --> X (fast)The intermediate in the reaction is...a. Xb. Cc. Ad. Be. D
Chapter 5 Solutions
Modified Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 5.1 - What is the molecular formula for each of the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 4PCh. 5.1 - Determine the degree of unsaturation and then draw...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 6PCh. 5.2 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 8PCh. 5.2 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 5.3 - How many carbons are in the planar double-bond...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 17PCh. 5.6 - a. Which of the monosubstituted cyclohexanes in...Ch. 5.6 - a. Calculate the percentage of isopropylcylohexane...Ch. 5.6 - a. for which reaction in each set will S be more...Ch. 5.6 - a. For a reaction with H = 12 kcal/ mol and S =...Ch. 5.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 5.9 - Prob. 24PCh. 5.9 - How many different alkenes can be hydrogenated to...Ch. 5.9 - The same alkane is obtained from the catalytic...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 27PCh. 5.9 - Rank the following compounds from most stable to...Ch. 5.10 - Prob. 29PCh. 5.10 - Prob. 30PCh. 5.11 - The rate constant for a reaction can be increased...Ch. 5.11 - Prob. 33PCh. 5.11 - a. Which reaction has a greater equilibrium...Ch. 5.12 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step...Ch. 5.12 - a. Which step in the reaction coordinate diagram...Ch. 5.12 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the...Ch. 5.13 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5 - Prob. 40PCh. 5 - Draw the structure of a hydrocarbon that has six...Ch. 5 - Draw the condensed structure for each of the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43PCh. 5 - Prob. 44PCh. 5 - Prob. 45PCh. 5 - Name the following:Ch. 5 - Prob. 47PCh. 5 - Prob. 48PCh. 5 - Prob. 49PCh. 5 - In a reaction in which reactant A is in...Ch. 5 - Which bond is stronger? Briefly explain why.Ch. 5 - Prob. 52PCh. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - By following the curved red arrows, draw the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 55PCh. 5 - Prob. 56PCh. 5 - Draw structures for the following: a....Ch. 5 - Prob. 58PCh. 5 - a. Which of the following reactions has the larger...Ch. 5 - Prob. 60PCh. 5 - a. What is the equilibrium constant for a reaction...Ch. 5 - Prob. 62PCh. 5 - Prob. 63PCh. 5 - Given that the free energy of the twist-boat...Ch. 5 - Prob. 65PCh. 5 - Prob. 1PCh. 5 - Prob. 2PCh. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - Prob. 6PCh. 5 - Draw curved arrows to show the movement of the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - Prob. 9PCh. 5 - Prob. 10P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rate of a reaction is found to increase nine-fold when the concentration of one reactant is tripled. The order of the reaction with respect to this reactant is a. first.b. second.c. one-quarter. d. one-half. e. third.arrow_forwardbased on the fallowin reactionarrow_forwardReaction A and reaction B have identical frequency factors, but reaction B has a higher activation energy than reaction A. Which reaction has a faster rate at room temperature? A. Reaction A B. Reaction Barrow_forward
- Figure out the answers to a,b,c using the graph. Use image as referencearrow_forwardConsider the following hypothetical reaction coordinate diagram with stages represented by I, II, and III, and choose the true statement about the steps in the forward and reverse mechanisms. Which is a TRUE statement? a) Step II --> III is faster and less energetically favorable than step II -->I b) Step II --> III is faster and more energetically favorable than step II -->I c) Step II --> III is slower and less energetically favorable than step II -->I --> Ill is slower and more energetically favorable than | || ||| d) Step II step II -->Iarrow_forwardDetermine the number of transition states and intermediates if you consider the energy diagram of the multi-step reaction below? ÇH3 ÇH3 ÇH3 ÇH3 OH H20 step 2 OH* +cr step 3 -CI step 1 + Cr A B D A. 3 transition states and 3 intermediates B. 2 transition states and 2 intermediates C. 3 transition states and 2 intermediates D. 2 transition states and 3 intermediates E. 2 transition states and 1 intermediatearrow_forward
- Pracdne o8 Consider the following reaction co-ordinate diagram H20 H20 Br A D Energy Reaction Co-ordinate a) Identify the various species on the diagram by adding the letter identifying each of the structures. b) Which species does the first transition state of the overall reaction most resemble? What kind of transition state is this? c) Which species does the second transition state of the overall reaction most resemble? What kind of transition state is this?arrow_forwardConsider the given reaction diagram below: Energy How many intermediates are formed all in all? How many elementary reaction steps are there? How many transition steps have energies lower than the starting material (SM)? Choose... Choose... Choose... SM Reaction Coordinate Parrow_forwardE (kJ-mol") s/d/e/1FAlpQLSSGCE8gt218c6JoHMWME1A8Nydt8M4g1yG93D-2LPpoMij_g/formResponse Question 39: Select the reactions in Figure 39 that can be represented by the accompanying energy diagram? * Reaction A Reaction B Reaction C Figure 39 t (s) CH-C-NH-CH D + HN-H + HO-O HO-H HO HCI CH-CH-CH3 oH + 20° LIFE Digitalarrow_forward
- The kinetics of a reaction are observed to be third-order. The least likely mechanism a. involves three molecules reacting together in a single step. b. involves a fast step followed by a slow step. c. involves more than one intermediate. d. involves a single intermediate.arrow_forwardConsidering both the forward and reserve directions, which step has the smallest rate constant in the reaction coordinate diagram shown below? F B E A E going to G O A going to C O E going to C O C going to E C going to A G going to Earrow_forwardNOTE: II only is the incorrect answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License